
Research Article
Phys Med Rehabil Int. 2024; 11(5): 1245.
Quercetin Phospholipids Supplementation as a Natural Relief in Osteomuscular Health
Irene Miniati1; Pier Luigi Davolio5; Simona Busi5; Giovanna Petrangolini6*; Felice Galluccio2-4
1Azienda Unità Sanitaria Locale (USL) Toscana Centro, 50122 Florence, Italy
2Fisiotech Lab Studio, Rheumatology and Pain Management, 50136 Florence, Italy
3MoMaRC Morphological Madrid Research Center, Ultradissection Spain EchoTraining School, Madrid, Spain
4Center for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine (CRAPM), Wan Fang Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan
5Farmad Laboratori Firenze Srl, Florence, Italy
6Medical Department, Indena SpA, 20139 Milan, Italy
*Corresponding author: Giovanna Petrangolini, Medical Department, Indena SpA, 20139 Milan, Italy. Email: giovanna.petrangolini@indena.com
Received: December 03, 2024; Accepted: December 20, 2024; Published: December 27, 2024
Abstract
Quercetin, a polyphenol substance, was found in several foods, including apples, grapes, onions, berries, broccoli, citrus fruits, green tea, coffee and red wine. The properties of quercetin are well known, including antioxidant/antiinflammatory, vasodilator, anti-allergic, anti-fatigue and senolytic. In the present case reports in joint health, one month quercetin phospholipid supplementation significantly reduced both NRS and FIHOA scores in erosive hand osteoarthritis subjects. No side effects related to the supplementation was detected, thus quercetin phospholipid supplementation would represent a valid safe support in joint health and pain management as add-on natural support.
Keywords: Hand osteoarthritis; Quercetin phospholipid; Inflammation; Sophora japonica; Joint health
Introduction
Erosive Hand Osteoarthritis (EHOA) is a severe disease causing hand joint inflammation and pain [1]. Affecting especially females, as in general reported as arthritis, EHOA is a persistent and progressive condition that could be not reversed [2,3], so the quality of life can be heavily affected.
The goal of the treatment is to reduce the severity of symptoms and to maintain joint function.
Recent reviews highlighted the important role of diet in arthritis and in general in chronic inflammatory diseases [4,5]; subjects under chronic treatments may be also supported by nutraceutical supplementation [6].
Therefore, polyphenols can be important for their antiinflammatory activity. Quercetin’s benefits in rheumatoid arthritis animal models are recently summarized [7], and are due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and osteoprotective properties. Inhibition of the free radicals such as Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS), was produced by quercetin; Nitric Oxide Synthase iNOS as well as lipid peroxidation, involved in inflammation processes, were reduced by quercetin, strongly supporting its anti-inflammatory properties [8]. In human clinical studies, quercetin phospholipids supplementation improved also training and performance in healthy amateur triathlon athletes [9], and it was useful for chronic fatigue in a double-bind placebocontrolled trial [10]. Senolytic properties were also shown by quercetin in combination with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib in human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [11] and in supporting the management of COVID-19 lung disease [12-16].
The present prospective clinical study was performed to evaluate the potential benefits of a supplement containing quercetin phospholipids, the optimized formulation of quercetin [17] in sunflower lecithin, in modulating long chronic inflammation in erosive hand osteoarthritis subjects.
Methods
Population
Fifty subjects with erosive hand osteoarthritis (between 40 and 85 years), including 8 males and 42 females, with at least 4 of Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) for pain assessment [18] were selected in this retrospective case series. The NRS is a modified version of the VAS that consists of a segmented numerical scale with 11 points ranging from 0 to 10. Subjects were asked to select a corresponding number to indicate the pain intensity they are experiencing. This scale can be administered verbally or graphically [18]. Diagnosis was made by X-ray radiographic evaluation of hand. Subjects willing to collaborate signed informed consent.
Exclusion criteria were: treatment with anti-inflammatory agents (topical or systemic) at least 3 weeks before study; other ongoing therapies like Disease-Modifying Osteoarthritis Drug (DMOAD), Symptomatic Slow-Acting Drug for Osteoarthritis (SYSADOA), laser/tecar therapies or infiltration with steroids within the previous 3 months, intolerance to active ingredients, or diseases such as diabetes mellitus, hearth or kidney failure that could affect the study outcome.
NRS score, where 0 = “no pain at all” and 10 = “worst possible pain” measured before supplementation (Time 0) and after 30 days supplementation (Time 30) was the primary outcome.
Secondary outcome was represented by the Functional Index for Hand OsteoArthritis (FIHOA) [19], measuring hand-related functional impairment scoring from 0 (no functional impairment) to 30 points (maximal impairment), measured at time 0 and 30.
Subjects who are unable to sign the consent form were excluded.
Supplement and Administration Schedule
Subjects were supplemented with one tablet/day for one month of QUE-FITTM (Farmad Laboratori Firenze Srl), corresponding to 500 mg of quercetin formulated in phospholipids standardized to contain 40% of quercetin (Quercefit™, Indena SpA).
Statistical Evaluation
Data are expressed as means ± S.D. Analysis of Wilcoxon two tailed test at 0 and 30 days was performed, with significance set at p<0.05.
Results
Fifty participants receiving supplementation were collected as case reports; only one subject withdraw for personal reasons not related to supplementation, therefore 49 subjects completed the supplementation period.
Results are shown in Figure 1 (NRS score) and Figure 2 (FIHOA score).
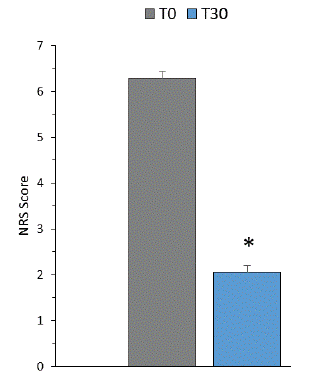
Figure 1: NRS score at 0 and 30 days of supplementation in joint health.
Data are expressed as means ± S.D., n=49, *p<0.0001 vs basal (T0) by
Wilcoxon t test.
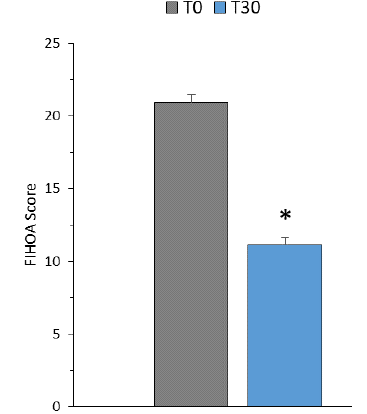
Figure 2: FIHOA score at 0 and 30 days of supplementation in joint health.
Data are expressed as means ± S.D., n=49, *p<0.0001 vs basal (T0) by
Wilcoxon t test.
A highly significant decrease in NRS score (about 67.2%, p<0.0001) was observed after 30 days of supplementation with quercetin phospholipids in respect to the basal score.
The classical FIHOA index utilized in the present study is a measure, originally developed by Dreiser [20], to evaluate hand function [19]. After 30 days, the FIHOA index significantly decreased of 46.8 % in respect of the basal index (p<0.0001).
The supplementation with quercetin phospholipids, 500 mg once daily, was safe and no adverse effects were detected during the study.
Discussion
These case series evaluated the potential benefits of quercetin phospholipid supplementation as natural support to joint health and pain management in hand chronic erosive arthritis subjects after 30-days. Quercetin displayed anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative stress, and osteo-protective properties. It is already known that pain and inflammation caused by osteoarthritis was reduced by quercetin, as already reported regarding the reduction of COX-2 and cytokines (TNF-a, IL-1β, IL-17) production, as well as Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) levels, decrease of proteoglycan degradation [21] and NF-kB activation inhibition of lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress. All those effects were recently reviewed and confirmed by Liu and colleagues [7].
According to those anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, quercetin phospholipids was studied as a possible complementary supplement for chronic fatigue syndrome [10] and in supporting food nutrition [9] in sport. Respectively, a relief of symptoms due to chronic fatigue was described after 500 mg/day quercetin phospholipids supplemented for 2 months; as well as the administration of 2 x 250 mg/day of quercetin phospholipids in triathlon athletes resulted more effective than control (without supplementation) in ameliorating endurance time, reducing recovery time, physical discomforts (e.g. pain and cramps), oxidative stress and plasmatic biomarkers related to stress and haemolysis. In allergic reactions quercetin formulated in phospholipids supplementation promoted the early resolution of the acute symptoms and modulated the host's hyper-inflammatory response [22-24]. Recent evidences in preclinical models on senescence processes [12], underlined also the beneficial effect of quercetin phospholipids, associated to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib, in alleviating age and senescence-related disorders, including osteoporosis, hepatic steatosis, neurodegeneration age- and high fat diet-induced vascular calcification, considering quercetin phospholipids as a promising senolytic agent [11].
Results obtained on these case reports on hand osteoarthritis are in line with evidence just described above. Quercetin formulated in phospholipids and supplemented at 500 mg/day for 30 days significantly reduced both NRS score and FIHOA index in osteoarthritis hand erosive subjects. The results are encouraging and possibly related by the anti-inflammatory activity demonstrated by this formulation in previous studies, modulating NF-kB leveling and control COX and LOX activation and cytokine production [9,10,22,23]. Of note, quercetin phospholipids demonstrated its beneficial cascade effect on healthy aging, immunity and relief from fatigue, by balancing the body’s inflammatory response. It may be of interest to plan further studies with a larger number of subjects to support and extend the beneficial properties of quercetin phospholipids revealed in the present results in the joint health and pain management. Thus, quercetin phospholipids resulted with a strong soothing and antioxidant activity to give natural relief to the osteoarticular and muscular human districts.
Author Statements
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to Dr. Paola Misiano and Dr. Martino Meneghin for their valuable editorial support and Dr. Mauro A.M Carai for statistical analysis.
Conflict of Interest
PLD and SB are employees of Farmad Laboratori Firenze, GP is Indena’s employee.
References
- Favero M, Belluzzi E, Ortolan A, Lorenzin M, Oliviero F, Doria A, et al. Erosive hand osteoarthritis: latest findings and outlook. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022; 18: 171-83.
- Haugen IK, Slatkowsky-Christensen B, Bøyesen P, Sesseng S, van der Heijde D, Kvien TK. MRI findings predict radiographic progression and development of erosions in hand osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016; 75: 117-23.
- van Vollenhoven RF. Sex differences in rheumatoid arthritis: more than meets the eye. BMC Med. 2009; 7: 12.
- Long Z, Xiang W, He Q, Xiao W, Wei H, Li H, et al. Efficacy and safety of dietary polyphenols in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 47 randomized controlled trials. Front Immunol. 2023; 14: 1024120.
- Chen LC, Chen YC, Su CY, Hong CS, Ho HO, Sheu MT. Development and characterization of self-assembling lecithin-based mixed polymeric micelles containing quercetin in cancer treatment and an in vivo pharmacokinetic study. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016; 11: 1557-66.
- Puri V, Nagpal M, Singh I, Singh M, Dhingra GA, Huanbutta K, et al. A Comprehensive Review on Nutraceuticals: Therapy Support and Formulation Challenges. Nutrients. 2022; 14: 4637.
- Liu X, Tao T, Yao H, Zheng H, Wang F, Gao Y. Mechanism of action of quercetin in rheumatoid arthritis models: meta-analysis and systematic review of animal studies. Inflammopharmacology. 2023; 31: 1629-45.
- Xu D, Hu MJ, Wang YQ, Cui YL. Antioxidant Activities of Quercetin and Its Complexes for Medicinal Application. Molecules. 2019; 24: 1123.
- Riva A, Vitale JA, Belcaro G, Hu S, Feragalli B, Vinciguerra G, et al. Quercetin phytosome® in triathlon athletes: a pilot registry study. Minerva Med. 2018; 109: 285-9.
- Rondanelli M, Riva A, Petrangolini G, Gasparri C, Perna S. Two-month period of 500 mg lecithin-based delivery form of quercetin daily dietary supplementation counterbalances chronic fatigue symptoms: A double-blind placebo controlled clinical trial. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023; 167: 115453.
- Justice JN, Nambiar AM, Tchkonia T, LeBrasseur NK, Pascual R, Hashmi SK, et al. Senolytics in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results from a first-inhuman, open-label, pilot study. EBioMedicine. 2019; 40: 554-63.
- Lee S, Yu Y, Trimpert J, Benthani F, Mairhofer M, Richter-Pechanska P, et al. Virus-induced senescence is a driver and therapeutic target in COVID-19. Nature. 2021; 599: 283-9.
- Di Pierro F, Derosa G, Maffioli P, Bertuccioli A, Togni S, Riva A, et al. Possible Therapeutic Effects of Adjuvant Quercetin Supplementation Against Early- Stage COVID-19 Infection: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, and Open-Label Study. Int J Gen Med. 2021; 14: 2359-66.
- Di Pierro F, Iqtadar S, Khan A, Ullah Mumtaz S, Masud Chaudhry M, Bertuccioli A, et al. Potential Clinical Benefits of Quercetin in the Early Stage of COVID-19: Results of a Second, Pilot, Randomized, Controlled and Open- Label Clinical Trial. Int J Gen Med. 2021; 14: 2807-16.
- Di Pierro F, Khan A, Iqtadar S, Mumtaz SU, Chaudhry MNA, Bertuccioli A, et al. Quercetin as a possible complementary agent for early-stage COVID-19: Concluding results of a randomized clinical trial. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13: 1096853.
- Rondanelli M, Perna S, Gasparri C, Petrangolini G, Allegrini P, Cavioni A, et al. Promising Effects of 3-Month Period of Quercetin Phytosome. Life (Basel). 2022; 12: 66.
- Riva A, Ronchi M, Petrangolini G, Bosisio S, Allegrini P. Improved Oral Absorption of Quercetin from Quercetin Phytosome®, a New Delivery System Based on Food Grade Lecithin. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2019; 44: 169-77.
- Breivik H, Borchgrevink PC, Allen SM, Rosseland LA, Romundstad L, Hals EK, et al. Assessment of pain. Br J Anaesth. 2008; 101: 17-24.
- Kim SK, Jung UH, Choe JY. Functional index for hand osteoarthritis (FIHOA) is associated with pain, muscle strength, and EQ-5D in hand osteoarthritis. Adv Rheumatol. 2021; 61: 19.
- Dreiser RL, Maheu E, Guillou GB, Caspard H, Grouin JM. Validation of an algofunctional index for osteoarthritis of the hand. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1995; 62: 43S-53S.
- Permatasari DA, Karliana D, Iskandarsyah I, Arsianti A, Bahtiar A. Quercetin prevent proteoglycan destruction by inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9, matrix metalloproteinase-13, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-5 expressions on osteoarthritis model rats. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2019; 10: 2-8.
- Yamada S, Shirai M, Inaba Y, Takara T. Effects of repeated oral intake of a quercetin-containing supplement on allergic reaction: a randomized, placebocontrolled, double-blind parallel-group study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022; 26: 4331-45.
- Cesarone MR, Belcaro G, Hu S, Dugall M, Hosoi M, Ledda A, et al. Supplementary prevention and management of asthma with quercetin phytosome: a pilot registry. Minerva Med. 2019; 110: 524-9.
- Belcaro G, Cesarone MR, Scipione C, Scipione V, Dugall M, Hu S, et al. Quercetin Phytosome reduces the wheal response to histamine injection. ESPERIENZE DERMATOLOGICHE - DERMATOLOGICAL EXPERIENCESMINERVA MEDICA. 2020; 22: 5-9.