
Research Article
Austin J Radiol. 2024; 11(5): 1245.
Assessment of Compliance of Radiology Reports with RCR-QSI Guidelines
Bhansali PS*; Gautam AA; Kumar S; Zende UM; Zope AM; Suryavanshi K
Department of Radiology, Symbiosis Medical College for Women and Symbiosis University Hospital and Research Centre, Symbiosis International (Deemed University), Lavale, Pune, India
*Corresponding author: Bhansali PS, Department of Radiology, Symbiosis Medical College for Women and Symbiosis University Hospital and Research Centre, Symbiosis International (Deemed University), Gram- Lavale, Taluka- Mulshi, District- Pune- 412115, Maharashtra, India. Tel: +91- 9657059366 Email: pratikshasbhansali@gmail.com
Received: September 20, 2024 Accepted: October 10, 2024 Published: October 17, 2024
Abstract
Radiology reports in standardized format help in conveying meaningful accurate information to the clinicians, patients and thereby improve patient care. A good report helps in ensuring consistency and accuracy in the information provided by the radiologists. It is an important conduit which helps in improving communication between radiologists and referring physicians and hence beholds a huge value in better patient care. The aim of our project was to assess the compliance of the radiology imaging report formats for various imaging modalities with Royal College of Radiologists- Quality Standard for Imaging (RCR-QSI) Guidelines. The study was conducted in Department of Radiology- Symbiosis University Hospital and Research Centre in two cycles. After the 1st cycle, areas for improvement were assessed and necessary suggestions were informed to the radiologists. Five parameters of every imaging modality (USG, X-ray, CT scan, MRI) were assessed- Technique, clinical profile, observations, diagnosis and differential with differential diagnosis and further management. Data was analysed and McNemar’s test was used as the test for statistical significance. A highly statistically significant improvement was observed in the ‘technique’ parameter of USG, which was from 4% in the first cycle to 92% in the second cycle. X-ray, CT scan and MRI reports showed complete 100% compliance, that is, optimum results in all parameters in the second cycle. The notable improvements in second cycle suggested that the strategic interventions for improvement were effective and proved their crucial role in compliance of reports in future.
Keywords: Radiology reports; Format; Technique; Compliance
Abbreviations: RCR-QSI: Royal College of Radiologists; Quality Standard for Imaging; CT- Computed Tomography; MRI- Magnetic Resonance Imaging; USG- Ultrasonography
Background
Radiology reports are a key-component in guiding patient management right from diagnosis, supporting clinical decision making, and overall patient care [1]. A radiology report adhered to standard format includes various components like technique used to carry out a certain imaging modality, mentioning of clinical profile, observations, diagnosis with differential diagnosis and further management [2]. Detailed description of each parameter ensures clear and systematic delivery of data and enhances accurate interpretation by the clinicians too [3]. Clinical profile helps in knowing the context of the findings and helps in its corelation with the report. Technique helps in understanding the quality of image, based on which the report was made. Observations are the heart of the report [4]. Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and further management help in the planning and continuity of the treatment [5]. Thus, the quality of the report has huge effect on the treatment, care and management of the patient [6]. The aim of this project was to assess the compliance of the radiology imaging report formats for various imaging modalities with Royal College of Radiologists- Quality Standard for Imaging (RCR-QSI) Guidelines. The study was conducted in two cycles and the compliance was assessed after making necessary improvements in the first cycle. The objectives were to- improve the radiology imaging report formats to match the RCR- QSI guidelines and meet the standards of good imaging services.
Methodology
The study was conducted in Department of Radiology- Symbiosis University Hospital and Research Centre in two cycles. After the 1st cycle, areas for improvement were assessed and necessary suggestions were informed to the radiologists. Instructions to avoid non-compliance were also given. Data from 100 reports was collected in each cycle (USG, X-rays, MRI, CT scans- 25 each). Systematic random sampling technique was applied, wherein every 5th imaging from every modality on Monday and Thursday was selected. The data was collected from 1st January 2024 to 31st March 2024, and was compared with the data collected in the first cycle (from 1st October 2023 to 30th December 2023). Five parameters of every modality were assessed- Technique, clinical profile, observations, diagnosis and differential with differential diagnosis and further management. One point was assigned to every parameter reported. Zero points were given for inappropriate filling of data. The data was compiled, tabulated, and analysed using MS-Excel. McNemar’s test was used as the test for statistical significance, to assess if there was significant improvement during the second cycle of assessment. p-value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant. p-value <0.001 was considered as very highly statistically significant.
Observations
In cycle I, CT Scan reports showed highest compliance in all parameters (in 40% reports-as shown in Figure 9), followed by MRI (12% reports- Figure 13), X-rays (4% reports- Figure 5) and USG reports. No complete compliance (5/5 parameters) was seen in in any reports. The USG reports were compliant with only (3-4/5) parameters, with the frequency of 4/5 parameters being 20% (Figure 1).
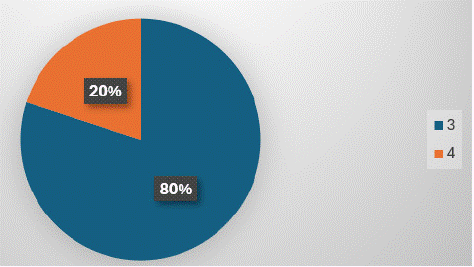
Figure 1: Maximum number of parameters (4/5 points) were covered in 20% of USG reports.
Technique, observations, and differential diagnosis were mentioned in reports of all modalities (Figure 2,6,10 & 14) except, least reporting of technique (4%) in USG scan reports (Figure 4).
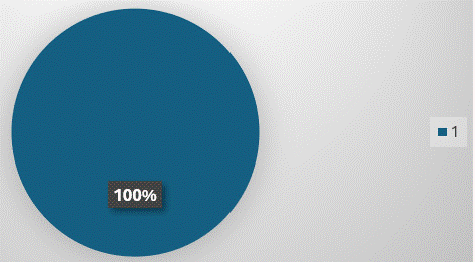
Figure 2: “Further management”, “Observations” and “Differential Diagnosis” are reported in all USG reports.
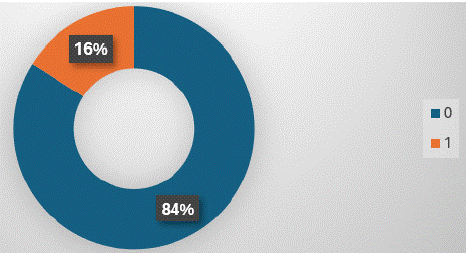
Figure 3: Clinical profile is reported less frequently (16% times) in USG reports.
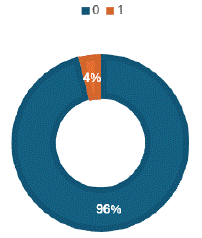
Figure 4: ‘Technique is reported least frequently (4% times) in USG reports.
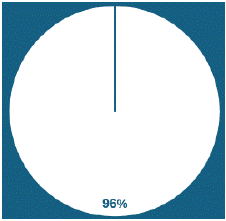
Figure 5: Only 4% X-ray reports completely fulfilled the criteria of QSI reporting.
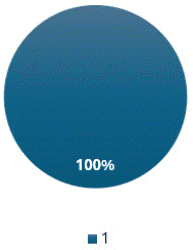
Figure 6: “Technique”, “Observations” and “Differential Diagnosis” are reported in all X-ray reports.
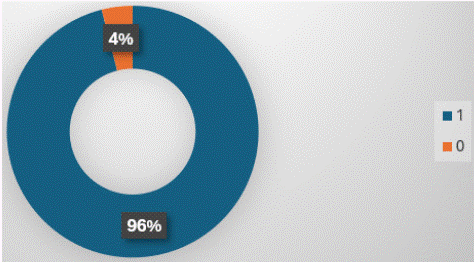
Figure 7: “Further management” is mentioned in 96% of X-ray reports.
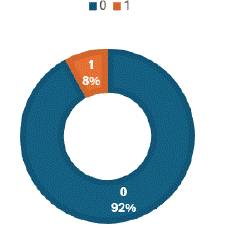
Figure 8: “Clinical profile” is mentioned in only 8% of X-ray reports.
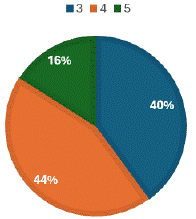
Figure 9: 40% of CT Scan reports completely fulfilled the criteria of QSI reporting.
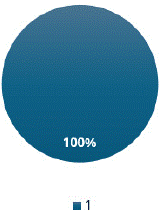
Figure 10: “Technique”, “Observations” and “Differential Diagnosis” are reported in all CT-Scan reports.
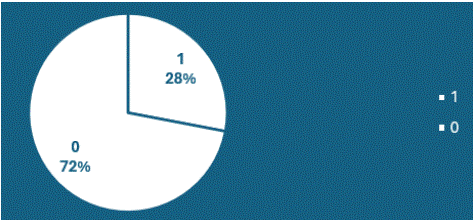
Figure 11: ‘Clinical profile is the least frequently mentioned parameter (28% times) in CT-Scan reports.
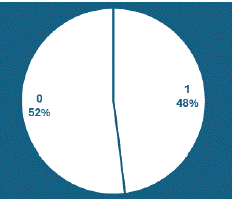
Figure 12: “Further management” is mentioned in 48% of CT Scan reports.
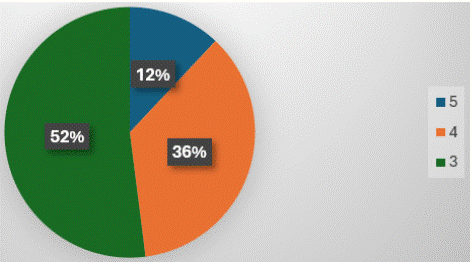
Figure 13: 12% of MRI reports completely fulfilled the criteria of QSI reporting.
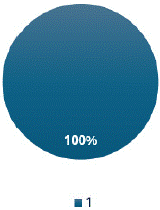
Figure 14: “Technique”, “Observations” and “Differential Diagnosis” are reported in all MRI reports.
Further management was mentioned most frequently in USG reports (100%- Figure 6), followed by X-ray (96%- Figure 7), CT scans (48%-Figure 12) and MRI (40%- Figure 16).
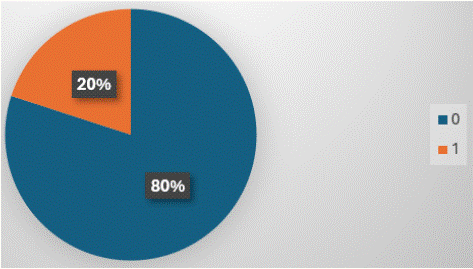
Figure 15: ‘Clinical profile is the least frequently mentioned parameter (20% times) in MRI reports.
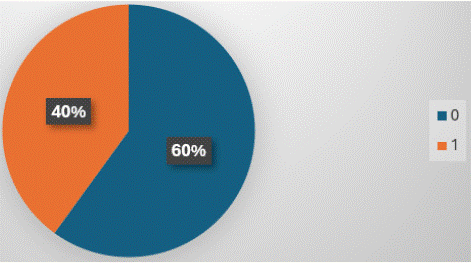
Figure 16: “Further management” is mentioned in 40% of MRI reports.
Clinical profile was mentioned least frequently among all imaging reports in all modalities. Highest frequency of mentioning clinical profile was in CT scans (28% reports-Figure 11), followed by MRI (20% reports-Figure 15), USG scans (16% reports- Figure 7) and X-ray (8% reports-Figure 8).
After the 1st cycle, necessary areas of improvement were assessed and strategies for improvement were formulated after discussion with the radiologists. They were as follows:
Improvement Needed
Technique to be mentioned in USG reports. Clinical profile and further management to be mentioned in all reports.
Strategies to Improve
Default inscription of technique, highlighted in bold letters in USG report formats helped in improvement in mentioning this parameter in the USG reports.
Rapidly informing the radiologists about the errors in reports, by the physicians or colleagues can also help in better optimum compliance during the second cycle. Regular audits should continue to ensure that improvements are maintained and to identify any new areas of decline. Continued education and training might be necessary to sustain the high levels of reporting quality, especially in areas that had significant gaps initially. Additional data collection on the reasons for inappropriate reporting in some areas could provide insights into specific training or resources needed. For example- Ensuring that clinicians mention relevant clinical data- including history, clinical suspicion, and appropriateness of investigation in the radiology request forms. The 2nd cycle was conducted after informing all the radiologists about the necessary areas of improvement and the suggested strategies to tackle the areas of lacunae.
In the 2nd cycle, (as shown in Figure 17) maximum number of parameters (5/5) were covered in 92% of USG reports. In the previous cycle, only 20% of USG reports covered maximum parameters (4/5).
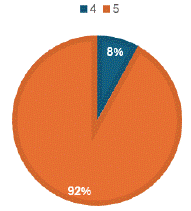
Figure 17: Maximum number of parameters (5/5 points) were covered in 92% of USG reports. (Cycle2).
Also, technique was reported in 92% USG reports (shown in Figure 18), which was seen only in 4% of USG reports in the previous cycle.
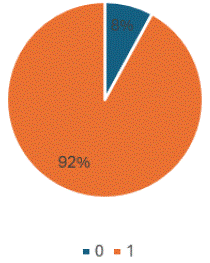
Figure 18: ‘Technique is not reported in only 8% USG reports.
It was also noted that all X-ray, CT scan and MRI reports mentioned all 5/5 parameters (Figure 19).
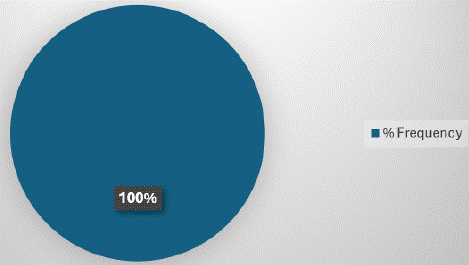
Figure 19: Maximum number of parameters 5/5 were presented in all X-ray, CT scan and MRI reports.
Table I represents all the imaging modalities according to the percentage of fulfilling all the parameters necessary for a standard reporting format as assessed in both the first and second cycles and the improvement along with its significance. The significance was calculated using McNemar’s test. P-value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant. P-value <0.001 was considered as very highly statistically significant.
Parameters
CYCLE I
CYCLE II
Improvement
p-value
Significance
USG
Technique
4%
92%
88%
0.0000027
Very highly statistically significant.
Clinical profile
16%
100%
84%. Optimum results in 2nd cycle.
0.0000045
Very highly statistically significant.
Observations
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
Diagnosis+ D/D
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
Further management
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
X-ray
Technique
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
Clinical profile
8%
100%
92%. Optimum results in 2nd cycle.
0.0000016
Very highly statistically significant.
Observations
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
Diagnosis+ D/D
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
Further management
96%
100%
4%. Optimum results in 2nd cycle.
0.317
Not statistically significant.
CT-Scan
Technique
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
Clinical profile
28%
100%
72%. Optimum results in 2nd cycle.
0.000022
Very highly statistically significant.
Observations
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
Diagnosis+ D/D
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
Further management
48%
100%
52%. Optimum results in 2nd cycle.
0.0003
Very highly statistically significant.
MRI
Technique
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
Clinical profile
20%
100%
80%. Optimum results in 2nd cycle.
0.0000077
Very highly statistically significant.
Observations
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
Diagnosis+ D/D
100%
100%
Optimum results in both cycles
_
Stable optimum result.
Further management
40%
100%
60%. Optimum results in 2nd cycle.
0.0001
Very highly statistically significant.
Table 1:
Discussion
After the second cycle of audit, our analysis showed 100% compliance in all parameters, except USG technique. Similar significant improvement was found in the study of David B. Larson, [7] wherein, at the end of their implementation period, 99% adherence to standardized radiology report format was found. Utkarsh Sharma8 carried out a study in Aldershoot, UK which was based only on CT Scan reports. Even their 97% CT Scan reports met the criteria of the audit. Our significant improvements were the result of a session where necessary suggestions were informed to the radiologists. Similar improvement was observed in the reporting formats of Maddux PT, [9] after conducting instructional activities. We undertook an idea after the first cycle of audit to aid in improvement of existing errors, which was wisely implemented in the study of Matthew J. Min, [10] after which they were successful in reducing the errors in their reports. It was about rapidly notifying the radiologists about observed errors in the reports. Thus, we implemented this idea as a strategy for improvement.
Conclusion
A highly statistically significant improvement was observed in the ‘technique’ parameter of USG, which was from 4% in the first cycle to 92% in the second cycle.
X-ray, CT scan and MRI reports showed complete 100% compliance, that is, optimum results in all parameters in the second cycle.
Similar observation of very highly statistically significant improvement was observed in terms of mentioning clinical profile in USG, x-ray, CT scan and MRI forms. In fact, the results were even optimum, that is, 100% in second cycle of clinical profile in USG, X-ray, CT scan and MRI reports.
These substantial increases suggest that the feedback and interventions after cycle 1 were effective. While improvements are notable, ensuring these areas maintain high compliance in future cycles will be crucial.
It is notable that parameters like observations, diagnosis and differential diagnosis, further management in USG, X-ray, CT scan and ‘technique’ parameter in X-ray, CT scan and MRI were already at 100% optimum results in cycle 1 and maintained their status in cycle 2 also. This consistency is ideal and indicates areas where practices were already strong.
References
- Pool F, Goergen S. Quality of the written radiology report: a review of the literature. Journal of the American College of Radiology. 2010; 7: 634-43.
- Goergen SK, Pool FJ, Turner TJ, Grimm JE, Appleyard MN, et al. Evidence-based guideline for the written radiology report: Methods, recommendations and implementation challenges. Journal of medical imaging and radiation oncology. 2013; 57: 1-7.
- Wilcox JR. The written radiology report. Applied Radiology. 2006; 35.
- Ganeshan D, Duong PA, Probyn L, Lenchik L, McArthur TA, Retrouvey M, et al. Structured reporting in radiology. Academic radiology. 2018; 25: 66-73.
- Grieve FM, Plumb AA, Khan SH. Radiology reporting: a general practitioner’s perspective. The British journal of radiology. 2010; 83: 17-22.
- Plumb AA, Grieve FM, Khan SH. Survey of hospital clinicians’ preferences regarding the format of radiology reports. Clinical radiology. 2009; 64: 386-94.
- Larson DB, Towbin AJ, Pryor RM, Donnelly LF. Improving consistency in radiology reporting through the use of department-wide standardized structured reporting. Radiology. 2013; 267: 240-50.
- Sharma U, Gomindes AR, Sharma K, Choudhry J, Searle HK. Compliance With the Royal College of Radiologists Guideline for Actionable Reporting and Its Impact on Patient Care: A Retrospective Analysis of Reporting Practices From a Major Trauma Center. Cureus. 2023; 15: e35921.
- Maddux PT, Farrell MB, Ewing JA, Tilkemeier PL. Improved compliance with reporting standards: A retrospective analysis of Intersocietal Accreditation Commission Nuclear Cardiology Laboratories. Journal of Nuclear Cardiology. 2018; 25: 986-94.
- Minn MJ, Zandieh AR, Filice RW. Improving radiology report quality by rapidly notifying radiologist of report errors. Journal of digital imaging. 2015; 28: 492-8.