
Research Article
Austin J Radiol. 2021; 8(1): 1121.
Determination of Gestational Age by Fetal Kidney Length Measurement after the 20th Week in Healthy Women with Uncomplicated Pregnancy in Tertiary Care Centre
Joshi BR*, Chaurasia AK and Khanal UP
Department of Radiodiagnosis, TU Teaching Hospital, Nepal
*Corresponding author: Birendra Raj Joshi, Department of Radiodiagnosis, TU Teaching Hospital, Nepal
Received: January 25, 2021; Accepted: February 12, 2021; Published: February 19, 2021
Abstract
Introduction: Various organs are measured to estimate the gestational age of fetus. Sonographically derived parameters used to date pregnancy include Crown rump length, Biparietal diameter, Head circumference, Femoral length and Abdominal circumference. Fetal kidney length, transcerebellar diameter and placental thickness are emerging as new parameters and are claiming to be more accurate in certain situations. In Nepalese context fetal kidney length has not been studied yet so this study was done to fill this need.
Methodology: Obstetric sonography was performed in 108 pregnant women with uncomplicated pregnancy to evaluate the efficacy of FKL as a measure to calculate the predicted gestational age. Gestational age ranged from 20 weeks to term. Only patient with known LMP, previous history of normal menstrual cycle and without any exclusion criteria were included in the study.
Results: The study showed mean fetal kidney length at 20-24, 25-29, 30- 34 and 35-37 weeks gestation as 22.5±0.5, 26.9±0.7, 32.32±0.7 and 36.3±0.6 respectively. Overall in combined second and third trimester , fetal kidney length showed strong linear correlation with gestation age with highest significant Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.989 as compared to other parameters (BPD=0.986, HC=0.976, AC=0.971, FL=0.984).
Conclusion: Fetal kidney showed strongest linear correlation with clinical gestational age and it also demonstrated positive correlation with biparietal diameter, head circumference, abdominal circumference and femur length. Therefore fetal kidney length can be used as a reliable parameter for determination of gestational age.
Keywords: Fetal kidney length; Ultrasonography; Gestational age
Introduction
Accurate gestation age assessment is pivotal to quality maternity care. Failure can result in iatrogenic prematurity or post maturity, both being associated with increased perinatal morbidity and mortality. Obstetric sonography plays an important role in the accurate determination of intrauterine gestational age [1].
The last two decades have seen a tremendous progress in application of ultrasound as a diagnostic modality revolutionizing the management towards better care. This is particularly due to its noninvasive and non-ionizing nature besides its cost effectiveness leading to wider acceptability. The exemplary safety record of diagnostic ultrasound is probably an important reason that it has become so widely used [2]. Crown rump length measurement has been described to predict gestational age accurately to within ±4.7 days. In the second trimester, most commonly used biometric indices for dating pregnancies are the fetal biparietal diameter and femur length. However, as gestational age progress, they become increasingly unreliable because of the biological variability of size in relation to age. Accurate dating of pregnancies remains a problem, especially in women who consult late for maternity care and are uncertain of the date of their LMP.
Using all the above parameters this variability can be reduced by 25% to 30% [3]. There are conditions like oligohydromnios, multiple gestation, breech presentation and Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR) that can alter the shape of the fetal skull which in turn can affect the BPD and increase the variability [4]. The present study was undertaken to validate the fetal kidney length measurement as an additional morphological measurement of fetal growth with less variability in Nepalese population. The objectives of the study were to derive nomogram for estimating the gestational age of the fetus from ultrasonographically measured fetal kidney length in Nepalese population and to determine a correlation between the fetal kidney length and the gestational age between 20th week of gestation and term as determined by the LMP and other sonographic parameters
Materials and Methods
Prospective cross-sectional study was done in healthy women with uncomplicated pregnancy between the 20th week of gestation and term referred from the Obstetrics and Gynaecology Department of a tertiary center and 108 subjects were included in this study. The study period was twelve months; from 5th November 2019 to 5th November 2020. Measurements were obtained in the sagittal plane, when full length of kidney with renal pelvis was visualized. Maximum length of right or left (since in previous studies showed no significant difference in size of either kidney)8 fetal kidney was measured from upper pole to lower pole at least thrice and mean of the measurements was taken. An informed consent was taken from patients after explaining about the study. No extra cost was charged from the patients for the study. Study was done after ethical clearance from the Institutional Review Board.
Exclusion criteria were unknown or inaccurate date of last menstrual period, oligohydramnios, diabetic mother, pre eclampsia, multiple gestations, fetal anomalies and intrauterine growth restriction. All relevant clinical history was obtained and the correct LMP was confirmed. An ultrasonography was performed with patient in supine position. Good acoustic coupling was obtained using synthetic ultrasound gel. Obstetric ultrasound scans were performed using Samsung Accuvix A30 ultrasound scanner using a 3.5 MHz convex probe. Images were recorded in the films using the mobile phone camera.
In all the patients following parameters were obtained. They are BPD, HC, AC, FL, FKL, fetal heart rate, estimated fetal weight, AFI and placental position. Plane used for measuring BPD and HC were section through the third ventricle and thalamus. Cavum septi pellucidi should be visible in the anterior portion of the brain and the tentorial hiatus in the posterior portion of the brain. The cursors were positioned in outer edge of near calvarial wall to inner edge of far calvarial wall for BPD. For HC the cursors were positioned in outer edge of the near calvarial wall and the outer edge of the far calvarial wall. AC was taken outer margin to outer margin in the plane showing the umbilical vein perpendicular to the fetal spine and the stomach bubble. The FL was obtained by aligning the transducer to the long axis of the diaphysis. Measurement cursors were placed at the junction of the cartilaginous epiphysis and bone.
Fetal kidney length was obtained in the sagittal plane, when full length of kidney with renal pelvis was visualized. Maximum length of any single (since in previous studies showed no significant difference in size of either kidney) [5] fetal kidney was measured from upper pole to lower pole at least thrice and mean of the measurements was taken.
Data were collected in predesigned proforma and entered in Statistical Package of Social Services (SPSS) IBM version 23. The discrete data were represented in frequency (%) and categorical data were represented in Mean±SD and analytical statistics was performed using independent sample “t” test. Pearson chi square test was used to test the association between the qualitative datas. The p-value of <0.05 shows the statistical significance difference. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to see the correlation between two continuous variables. For predicting GA from fetal kidney length regression equation GA=a+βFKL was used.
Results
The study was done in age group between 22 year to 36 year with mean age group of 27.5 and SD 3.5. Among the subjects 42.6 % were multiparous and 57 % were primi. In this study the highest number of cases was of 33 week i.e. 10 cases (9.3 %) while lowest was in 36 predicting gestational age 20 to 37 week (Table 4). The association between the fetal measurements and CGA. The correlation for CGA vs. BPD, HC and FL was almost similar (r: 0.986, 0.976, and 0.984 respectively). The correlation was best for CGA vs. FKL (r: 0.989) and least for CGA vs. AC (r: 0.971). All the correlations were statistically significant (Figure 1 & Table 5). Reveals the association between the fetal measurements and FKL. The correlation was best for FKL vs. CGA, FL (r: 0.989 and 0.981) and least for FKL vs. AC (r: 0.966). All the correlations were statistically significant (Table 6).
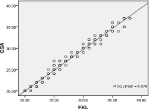
Figure 1: Scatter diagram showing correlation between CGA and FKL.
FKL
95% CI
CGA
Mean
SD
lower
upper
20
20.4
0.5
19.96
20.84
21
21.6
0.5
21.23
21.97
22
22.5
0.5
22.1
22.9
23
23.4
0.5
22.96
23.84
24
24.6
0.5
24.16
25.04
25
25.1
0.7
24.58
25.62
26
25.9
0.7
25.38
26.42
27
26.4
0.8
25.81
26.99
28
28.1
0.6
27.68
28.52
29
29
0.7
28.39
29.61
30
30.4
0.5
29.96
30.84
31
31.4
1
30.66
32.14
32
31.8
0.8
31.16
32.44
33
33.3
0.7
32.87
33.73
34
34.7
0.8
34.06
35.34
35
36
1.2
34.82
37.18
36
35.3
0.6
34.62
35.98
37
37.4
0.5
36.96
37.84
Table 1: Mean fetal kidney length at various gestational ages.
Intercept coefficient (a)
SE
Slope coefficient (β)
SE
p
R2
FKL
0.312
0.423
0.998
0.015
<0.001
0.978
The regression equation is y=a+βX
GA = 0.312+0.998 FKL
Table 2: Regression coefficients of GA while predicting FKL.
FKL (mm)
CGA (weeks)
20
20.3
21
21.2
22
22.2
23
23.2
24
24.2
25
25.2
26
26.2
27
27.2
28
28.2
29
29.2
30
30.2
31
31.2
32
32.2
33
33.2
34
34.2
35
35.2
36
36.2
37
37.2
Table 3: Nomogram of FKL.
BPD GA
HC GA
AC GA
FL GA
FKL
Pearson Correlation
0.986
0.976
0.971
0.984
0.989
p
<0.001
<0.001
<0.001
<0.001
<0.001
Table 4: Correlation co-efficient of clinical gestational age with BPD, HC, AC, FL, FKL.
Intercept coefficient (a)
SE
Slope coefficient (β)
SE
p
R2
Sep (days)
BPD
-1.866
0.49
1.05
0.017
<0.001
0.973
6.1
HC
-2.88
0.668
1.073
0.023
<0.001
0.952
8.3
AC
-2.684
0.729
1.065
0.025
<0.001
0.943
9.1
FL
-3.558
0.549
1.082
0.019
<0.001
0.968
6.9
FKL
0.312
0.423
0.997
0.015
<0.001
0.978
5.3
Table 5: Regression coefficients of GA while predicting various parameters.
CGA
BPD GA
HC GA
AC GA
FL GA
Pearson Correlation coefficient (r)
0.989
0.978
0.972
0.966
0.981
p
<0.001
<0.001
<0.001
<0.001
<0.001
Table 6: Correlation co-efficient of FKL with CGA, BPD, HC, AC, FL GA.
Discussion
A linear relationship was found during the late second (20wks to 28wks) and third (29 wks to term) trimester between the fetal kidney growth measured in mm and the gestational age in weeks. The relationship was statistically significant. In present study, FKL correlates well with gestational age with correlation coefficient of 0.989 in the late second and third trimester. Overall in combined second and third trimester, FKL correlates with gestation age with highest correlation coefficient of 0.989 as compared to other parameters (BPD=0.986, HC=0.976, AC=0.971, FL=0.984). Cohen et al., [5] studied the ultrasound measurement of fetal kidney length in 397 fetuses from 18 to 41 wks of pregnancy. The study included only normal fetuses, and the gestational age was estimated using LMP and fetal biometry. The mean fetal kidney lengths were found to be greater when compared to our study. According to this study, strong correlation existed as in present study between fetal kidney length measurement and gestational age estimated by fetal biometry (biparietal diameter=0.81, femoral length=0.82, abdominal circumference=0.80, and an average of the three=0.82). The study concluded that there was no correlation between height and weight of the patients and fetal kidney length. The study also stated that there no significant difference between the right and left kidney lengths (r=0.91). Yusuf et al., included 102 pregnant women after 30 weeks of gestation. All the patients had dating scan done at early weeks of pregnancy. The fetal kidney length measurement showed a linear correlation with gestational age with highly significant correlation (r=0.990). The result of this study was similar to present study and concluded that measurement of fetal kidney length can be used as an additional parameter for the estimation of gestational age [6]. Our values for kidney length at different gestational ages were lower than those reported by Konje JC et al., [7] and higher than Ansari et al., [8]. The regression coefficient of present study was 0.977 while other studies regression coefficient were Nahid Yusuf et al., 0.99, Konje JC et al., 0.97, J J Kansaria et al., 0.90 and Bardhan j et al., 0.99. All results were significant however some differences were there in values due to the number of operators (multiple vs. two skilled operators), type of study (cross-sectional vs. longitudinal), estimation of gestational age (rounded vs. exact) and quality of ultrasound machine (older vs. newer) [6,7,9].
In present study the most accurate was fetal kidney length with standard error of 5.3 days, while most inaccurate was abdominal circumference with standard error of 9.1 days. Konje JC et al., studied gestational age determination by measuring fetal kidney length after 24th week of gestation in 73 pregnant women with uncomplicated pregnancies. Serial measurement of fetal biometry and kidney length were done from 24 to 38 weeks of gestation with interval of 2 weeks. Using this gestational age was calculated and compared with crown-rump length (taken between 8-10 weeks of gestation) dating. The results showed that FL and fetal kidney length are the best parameters for determination of gestational age (+10.29 and 10.96 days respectively). Their conclusion was similar to present study [7].
J J Kansaria et al., did a study in 70 antenatal women between 22- 38 weeks of gestation with interval of 2 weeks. The most accurate was fetal kidney length with standard error of 9.17 days, while the most inaccurate was abdominal circumference with standard error of 11.14 days. They concluded that fetal kidney length predicted gestational age with better precision than other biometric indices [9].
The kidney lengths of the present study were compared with studies of Ansari et al and S. Afros et al and it showed a close correlation with these two studies. Compared to above two study in the fetal FKL SD was high in S. Afroz et al., while was lower in Ansari et al study. Our study showed SD variation between ±0.5 to±1.2 in 31 in 31 to 37 week gestational age [8,10]. As like other organs fetal kidney size is also affected by growth variations. But these affect only the antero posterior and transverse diameter of the kidney. The length of the fetal kidney is not affected by growth variations [11,12].
In our study we found that the mean fetal kidney length increased linearly as the gestational age increases. The present study hence validates the recommendation that fetal kidney length can be used as an important sonographic parameter for accurate prediction of fetal gestation age .The results of present study and previously published studies on FKL showed that additional small improvements in accurate estimation of gestational age can be achieved by incorporating the results of FKL with some combination of other fetal biometric parameters. However it should always be remembered that a single USG examination for determining gestational age is unreliable after 30 weeks. So fetal kidney length measurement can be taken as an additional parameter for accurate estimation of gestational age in late trimester in combination with BPD, HC, FL, and AC.
Our charts of fetal kidney were derived from cross sectional data. They were appropriate for comparing renal size at a known gestational age with reference data. They were not suitable for judging the appropriateness of the growth of kidneys across time. A number of observer errors and technical errors can occur in obtaining the fetal kidney length measurements; the major source of errors may be due to uncertainty of end points and skewed, off-axis images of the kidneys. The fetal adrenal gland is relatively large, and, except in near-term infants, it is difficult to separate it from the kidney, due to the lack of perirenal fat and a similar echo pattern. This may result apparent increase in the length of the kidney because of the addition of fetal kidney and adrenal measurement. These possible errors were not evaluated in this study. Notwithstanding the above possible technical and observer errors, the measurements taken in the present study were reasonably accurate.
Conclusion
Fetal kidney length showed a strong positive correlation with fetal gestational age, with a steady growth rate throughout pregnancy. With respect to clinical gestational age the fetal kidney length was more accurate with Pearson Correlation coefficient (r) 0.989 as compared to BPD (r) 0.986, HC (r) 0.976, FL (r) 0.984 and AC (r) 0.971. FKL positively correlated with BPD, HC, AC and FL. FKL can be used as a reliable parameter for determination of gestational age.
References
- Callen PW. Ultrasonography in Obstetrics and Gynecology, 5th ed. California USA: Elsevier Health Sciences. 2011.
- Nyborg W. Safety of medical diagnostic ultrasound. Seminars in Ultrasound. CT and MRI. 2002; 23: 377-386.
- Hadlock FP, Deter RL, Harrist RB, Park SK. Computer assisted analysis of fetal age in the third trimester using multiple fetal growth parameters. Journal of clinical ultrasound. 1983; 11: 313-316.
- Mcleary RD, Kuhns LR, Barr M. Ultrasonography of the fetal cerebellum. Radiology. 1984; 151: 439-442.
- Cohen H, Cooper J, Eisenberg P, Mandel FS, Gross BR, Goldman M, et al. Normal length of fetal kidneys: sonographic study in 397 obstetric patients. AJR American journal of roentgenology. 1991; 157: 545-548.
- Yusuf N, Moslem F, Haque JA. Fetal kidney length: can be a new parameter for determination of gestational age in 3rd trimester. TAJ: Journal of Teachers Association. 2007; 20: 147-150.
- Konje J, Abrams K, Bell S, Taylor D. Determination of gestational age after the 24th week of gestation from fetal kidney length measurements. Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology: The Official Journal of the International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2002; 19: 592-597.
- Ansari SM, Saha M, Paul AK, Mia SR, Sohel A, Karim R. Ultrasonographic study of 793 foetuses: measurement of normal foetal kidney lengths in Bangladesh. Australasian radiology. 1997; 41: 3-5.
- Jeanty P, Rodesch F, Delbeke D, Dumont JE. Estimation of gestational age from measurements of fetal long bones. Journal of ultrasound in medicine. 1984; 3: 75-79.
- Afroz S, Hussain R. Length of the foetal kidneys: A correlation with gestational age. Bangladesh Journal of Ultrasonography. 1996; 3.
- Bertagnoli L, Lalatta F, Gallicchio R, Fantuzzi M, Rusca M, Zorzoli A, et al. Quantitative characterization of the growth of the fetal kidney. Journal of clinical ultrasound. 1983; 11: 349-356.
- Kansaria JJ, Parulekar SV. Nomogram for foetal kidney length. Bombay Hospital Journal. 2009; 51: 155-162.