
Review Article
Austin J Radiol. 2021; 8(3): 1130.
Reporting Radiographers: Hope or Hype
Alahmari A*
Department of Radiology, Al-Namas General Hospital, Saudi Arabia
*Corresponding author: Abdulwahab Alahmari,Department of Radiology, Radiology Specialist, Al-Namas General Hospital, Ministry of Health, Al-Namas City, Saudi Arabia
Received: February 22, 2021; Accepted: March 24, 2021; Published: March 31, 2021
Abstract
For more than 20 years and Reporting Radiographers practice exists in the UK. Today no other country joined the UK to legislate Radiographers’ reporting practice. The aim of this paper is to put a focus on the issue, look is there a necessity to allow Radiographers in the reporting business, and find is there any benefit that can change the decision of health authorities worldwide to allow Radiographers to make clinical reports.
Keywords: Reporting Radiographers; Radiology; Advanced Practice; Radiologists
Introduction
The story of Radiographers report findings in radiographs when Radiographers started using the “Red Dot” system which helps Radiologists with an initial interpretation of any abnormality. In World War II, there was a shortage of Radiologists to read the x-rays, so Weber State University in collaboration with the US Army, trained large numbers of Radiographers a.k.a “Radiologic Technologist in the American system”. Those Radiographers were trained to make radiology diagnoses for the patients (soldiers). Today Radiographers in America, in order to be allowed to interpret radiographs, they need the United States’ Congress to pass a legislation that legalizes Radiographers to interpret radiographs, sonograms, or CT scans.
The Reporting Radiographers started in the UK due to the shortage of Radiologists in the UK and especially in Scotland. There was a time in Scotland, where the radiological service required awaiting of more than 6 weeks (test to report time) which is catastrophic [1]. In London, the waiting time for a radiology report was 1 month in 2017 [2]. The total number of radiologists in the UK is 3622 radiologists in 2018 [3].
There are two types of reporting among radiographers in the UK:
Initial commenting: This is not a report, but a “Red Dot” placed in the corner of the radiographs to give warning or alert to the radiograph interpreter that something wrong within these radiographs. Any radiographer can use the “Red Dot” system. The issue with the Red Dot system is ambiguous and it gives no comment to describe what the Radiographer is seeing as wrong within the radiograph. The training course for Radiographers to use the Red Dot system is one day which is another negative point for this system (Figure 1).
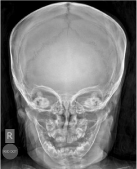
Figure 1: Red Dot used on a skull x-ray by a Radiographer to notify the
Doctor about the abnormality in the picture. It’s an ambiguous way to mention
the left parietal fracture (linear inverted y-shape).
Clinical reporting: This is writing a full report that will be sent directly to the Physician in charge of this case. The treatment plan will be based on the Radiographer’s interpretation. These reports must be made by a qualified Radiographer who finished (a postgraduate certificate, postgraduate diploma, or a master’s degree in interpretation of radiographs that is approved by the Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC) in the UK, three years of training after graduation from post-graduate degree under the supervision of a Radiologist, two years of experience as a radiographer post-bachelor degree, and a bachelor’s degree approved by HCPC in the UK).
Radiographers can be specialized in chest x-ray reporting, abdomen x-ray reporting, and skeletal x-ray reporting for the emergency. As well, reporting for ultrasound can be made by a qualified Sonographer. Some curriculum of M.Sc. in Diagnostic Imaging programs, (like the master’s degree in The University of Hertfordshire 2019 catalogue of post-graduate programs) which contain a CT brain interpretation module. This program has an accreditation from the Society of Radiographers in the UK [4].
Advanced Practice for Radiographers by the Country
North America
There is no role of reporting Radiographers in the United States and Canada, but they have what is called “Radiologist Assistant” where they allowed to do chest, abdomen, and pelvis examinations with administration of contrast media (i.e. IV, oral, and rectal). As well, lumber puncture, joint injection under fluoroscopy guidance, etc. The R.R.A which is an abbreviation for Registered Radiologist Assistant is focused mainly on radiographic and angiographic procedures, but they cannot report a radiographs or sonograms. The total number of R.R.As in the United States and Canada is 657 according to the (Society of Radiology Physician Extenders website, 2020).
The United Kingdom
After a huge conflict between the Royal Society of Radiologists and Society of Radiographers, the Radiographers in the UK, won the right to interpret radiographs with different scops (chest, abdomen. skeletal (appendicular or axial)). The Radiologists in the UK, were worry about losing their jobs to Radiographers who will undertake similar job duties. The total number of reporting Radiographers in the UK today is 259 registered Radiographers [5]. The shortage of radiologists and delay of reporting lead the government to take action which legalization Radiographers’ reporting practice.
Saudi Arabia
There are 34 (Sudanese) Radiographers, work in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia as Reporting Radiographers (in private medical centers) [6]. Radiographers are not allowed in K.S.A to report any scan based on the Saudi Commission for Health Specialties description of Radiographers’ roles. There is no statistical analysis in most of the Middle East countries which allow us to make a judgment wither Reporting Radiographers are a necessity or not? In rural areas of Saudi Arabia, there is a shortage of Radiologists which can be filled by Reporting Radiographers. In Saudi Arabia, there is a 4 years fellowship program for Radiographers which will allow them to study extensive pathophysiology, but they do not teach them radiographic interpretation which is a huge disadvantage of this program [7]. This fellowship program has three tracks; axial imaging, ultrasound, and nuclear medicine. This program named Saudi Specialist Certificate Program for Radiology Technology & Medical Imaging which will give extensive training on all aspect of the chosen field to become a mentor or have executive duties in clinical settings. This program adds nothing to Radiographers except more practice and testing in the same field. This is a professional program that has no similar program worldwide.
Australia and New Zealand
The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists published a 20 pages statement opposing the idea of allowing Radiographers to make any clinical reports, but they accept the red dot system or initial commenting [8].
Radiographers vs. Radiologists
In the UK, Radiographers’ ability to interpret radiological exams was non-inferior to Radiologists based on many published papers [9- 13]. The comparisons between Radiologists and Radiographers were tested on interpreting x-rays, barium enema studies, CT colonoscopy, and upper abdominal ultrasounds. Here is a list of published papers on comparing between Radiologists and Radiographers (Table 1).
Author
Year
Methodology
Interpreted exam
Accuracy Radiologists vs. Radiographers
Note
Brealey, S, et al. [9]
2005
Meta-analysis for 12 studies which contain 30,000 x-rays.
x-ray
93% sensitivity 98% specificity for Radiographers.
The percent increased with more practice.
Murphy M, et al. [10]
2002
Comparative study
Barium enema
95$% accuracy among Radiographers.
Radiographers are very close to Radiologist in reporting barium enema in 788 patients and with training they can report at high standards.
Meertens R, et al. [11]
2013
Systematic review
CT colonoscopy
Sensitivity 76% and specificity 74% among Radiographers.
Radiographers improved overtime.
Hofmann B, et al. [12]
2013
Prospective controlled study
Upper abdominal ultrasound
97% sensitivity and 93% specificity among Songographers.
95% similarity to competing Radiologists.
Leslie A, et al. [13]
2000
Comparative double blind study
Upper abdominal ultrasound
93% accuracy among Sonographers.
There was difference between them on 7 cases the Sonographers were right in 3 cases and Radiologists were right in 4 cases.
Table 1: Comparing between Radiologists and Radiographers.
The advantages of legislating Reporting Radiographers’ practice:
• Decrease the workload on Radiologists.
• Radiographers can take easy cases like; CXR, AXR, skeletal radiographs, etc.
• Allow Radiologists to focus on the complicated cases.
• Radiographers can be sent to rural areas where there is a shortage of Radiologists.
• Low salary for Reporting Radiographers compared to Radiologists’ salary.
• Immediate interpretation and reporting of radiographs for the ER patients (i.e. bones fractures, Joints dislocations, etc.) which will allow fast service.
• Allow Radiographers to take advanced practice which means progress in their field (professional development).
• Solve the low doctor/patient ratio.
• Decrease the numbers of burnout among Radiologists and Radiographers (i.e. Radiologists will not be seeing any simple cases all day long and Radiographers will have a new role).
• Reporting Radiographers can earn a higher salary due to their new role (i.e. not as much as a Radiologist, but higher than average Radiographers).
• Improve radiological services generally.
Radiologists’ concerns
The Royal Society of Radiologists opposed the Society of Radiographers-both in the UK-publically when they were campaigning to allow Radiographers to study and trained on interpreting the radiographs, but eventually the Society of Radiographers won when the UK’s government allowed the Radiographers to be trained on interpreting CXR, AXR, skeletal x-rays. The government instructed the HCPC to recognize the Reporting Radiographers and their training programs due to the pressure that was made by the Society of Radiographers and the bad conditions of the patients in Scotland where they use to need to wait for more than 6 weeks before their scan can be read and reported. In many cases, cancer patients in Scotland suffered spread of the disease (metastasis), and due to the delayed of the radiological service their conditions worsen. As well, in London they use to wait for one month for a radiology report to come out. Due to the Brexit and when the qualified European work force started leaving the UK, it may have complicated the issue in the UK. In the UK, they have measured the need based on “test to report time” which in many undeveloped countries do not have any statistic to see if there is any need for Reporting Radiographers. Radiologists should be afraid of Artificial Intelligence (AI) being implemented in radiology more than being afraid from Reporting Radiographers.
Crucial point about radiographic reporting
In the UK, when they allowed Radiographers to make the diagnoses and join Diagnostic Imaging programs, at the beginning Radiographers made some reporting mistakes, but the government did not shut the programs down or prohibits Radiographers reporting. The British government let Radiographers to learn more, acquire more experience, and with time Radiographers started to adapt to the new work roles in the clinical practice and started to learn how to make the right diagnoses. If any country will began a Radiographers’ reporting program, they need to give the Radiographers some time and supervision until they succeed.
Names of the interpretation programs
Some British universities still use the old name like radiography or medical imaging for radiologic reporting programs like Cardiff University which is a big mistake [14]. If the program includes only radiographs reporting, it should be named radiographic reporting. If the program has ultrasongrams reporting, it should be named diagnostic ultrasongraphy. If the program has different imaging modalities and interpretations, it should be named diagnostic imaging, diagnostic radiology, or just radiology similar to the names of Cambridge University’s radiology programs [15].
Proposed programs & advanced practice
While many countries suffer from Radiologists’ shortage, it’s essential to have more advanced practice and programs for Radiographers. Since Radiographers graduated from high school, they have been seeing different radiologic scans in their under & postgraduate degrees and during their clinical practice. Therefore, they are more prepared than any Physician who just finished any MBBS or MD degree. There is a proposed master’s program in neuroradiology that can help-in a short period of time-any Radiographer to learn how to interpret neuroradiology scans [16]. As well, Physicians can join this program instead of doing a residency then a fellowship program which will take too much time that many patients and health care systems can’t afford it.
References
- The Royal College of Radiologists. The radiology crisis in Scotland: sustainable solutions are needed now. The Royal College of Radiologists. 2017.
- Mayor S. Waiting times for x-ray results in England are increasing, figures show. BMJ. 2015; 350.
- The Royal College of Radiologists. The NHS does not have enough radiologists to keep patients safe, say three-in-four hospital imaging bosses. The Royal College of Radiologists. 2019.
- University of Hertfordshire & School of Health and Social Work. MSc Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences Diagnostic Imaging. University of Hertfordshire Data Assets-Diagnostic Imaging. 2018.
- Milner RC, Culpan G, Snaith B. Radiographer reporting in the UK: is the current scope of practice limiting plain-film reporting capacity. The British journal of radiology. 2016; 89: 20160228.
- Elkhadir AM, Saeed IO. Sudanese Radiologic Technology Specialist Embrace A challenge: Focus on Image interpretation-A survey Study. International Journal of Radiology. 2018; 5: 144-148.
- Saudi Commission for Health Specialties. Saudi Specialist Certificate Program for Radiology Technology & Medical Imaging. 2011.
- The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists. Image Interpretation by Radiographers - Not the Right Solution Position Statement. Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council. 2018.
- Brealey S, Scally A, Hahn S, Thomas N, Godfrey C, Coomarasamy A. Accuracy of radiographer plain radiograph reporting in clinical practice: a meta-analysis. Clinical radiology. 2005; 60: 232-241.
- Murphy M, Loughran CF, Birchenough H, Savage J, Sutcliffe C. A comparison of radiographer and radiologist reports on radiographer conducted barium enemas. Radiography. 2002; 8: 215-221.
- Meertens R, Brealey S, Nightingale J, McCoubrie P. Diagnostic accuracy of radiographer reporting of computed tomography colonography examinations: a systematic review. Clinical radiology. 2013; 68: e177-e190.
- Hofmann B, Vikestad KG. Accuracy of upper abdominal ultrasound examinations by sonographers in Norway. Radiography. 2013; 19: 186-189.
- Leslie A, Lockyer H, Virjee JP. Who should be performing routine abdominal ultrasound? A prospective double-blind study comparing the accuracy of radiologist and radiographer. Clinical radiology. 2000; 55: 606-609.
- Cardiff University. Radiography. 2019.
- University of Cambridge. In Radiology. Postgraduate Admissions. The Department of Radiology. 2020.
- Alahmari A. Master of Science in neuroradiology: A Proposal of a Master’s Degree. International Journal of Radiology. 2020; 7: 253-256.