
Clinical Image
Austin J Radiol. 2021; 8(5): 1141.
Tabetic Arthropathy
Hajar A¹*, Laila J¹ and Laamrani FZ²
¹Department of Emergency, Ibn Sina University Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Mohammed V University, Rabat, Morocco
²Department of Radiology, Ibn Sina University Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Mohammed V University, Rabat, Morocco
*Corresponding author: Adil Hajar, Department of Emergency, Ibn Sina University Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Mohammed V University, Rabat, Morocco
Received: May 15, 2021; Accepted: June 10, 2021; Published: June 17, 2021
Keywords
Syphilis; Tabetic arthropathy; Knee joint
Clinical Image
Tabetic Arthropathy (TA) defines bone- and joint-destructive processes associated with neurosensory deficits due to syphilis infection. It occurs at the late stages of the disease, and affects 10% of patients with Tabes Dorsalis. The mean age at diagnosis is 60 years with a predilection for male patients. TA became less common thanks to the early diagnosis of syphilis infection, but its management remains complicated given the severity of injuries and the lack of specific treatment. TA can affect every joint, mainly the knees. Patients usually present with a single painless and swollen joint. Deformities are seen in advanced stages.
Plain radiographs and CT findings include subchondral sclerosis, osteophytosis, subluxation, and soft tissue swelling. MRI shows articular destruction with irregularities of articular surfaces, deformation, and intraarticular effusion. It also helps differentiate neuropathic osteoarthropathy from other articular diseases as infection, osteonecrosis, and psoriatic arthritis (Figure 1 and 2).
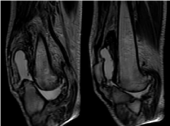
Figure 1: Sagittal T2-W MRI images of the knee joint showing intra articular
effusion with the destruction of the articular surfaces and the joint ligaments
causing dislocation.

Figure 2: Axial T2-W and T1-W post contrast FAT SAT MRI images of the
knee joint showing effusion with synovium thickening that enhances on post
contrast images (synovitis) (white arrows).