
Clinical Image
Austin J Radiol. 2021; 8(5): 1142.
X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy on a Child
Hajar A*, Nazik A, Latifa C and Siham EH
Department of Radiology, Children Hospital, IBN SINA University Hospital, Medical University of RABAT, Morocco
*Corresponding author: Adil Hajar, Department of Radiology, Children Hospital, IBN SINA University Hospital, Medical University of RABAT, Morocco
Received: May 15, 2021; Accepted: June 10, 2021; Published: June 17, 2021
Keywords
X-linked; Adrenoleukodystrophy; MRI
Clinical Image
X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is an inherited neurodegenerative disease due to the accumulation of Very Long- Chain Fatty Acids (VLCFA) in the cerebral White Matter (WM) resulting in severe inflammatory demyelination.
Clinical presentation depends on the phenotype that varies according to the patient’s age.
MRI is the key imaging modality to evaluate ALD as it shows early abnormalities that precede clinical findings. It demonstrates symmetric white matter hyperintensity on T2-weighted and FLAIR images (Figure 1 and 2) and hypo- or isointensity on T1-weighted images. Post-contrast enhancement at the edges of affected white matter is predictive of disease progression. MRI presentation varies based on the involved regions and patterns of progression.
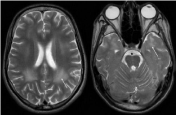
Figure 1: Axial T2-W cerebral MRI images demonstrating symmetric white
matter hyperintensity in parietal ant temporal lobes (arrows).

Figure 2: Coronal T2-W FLAIR cerebral MRI image demonstrating corpus
callosum hyperintensity (arrow).
Hematopoietic cell transplantation is indicated in the early stages of the disease. Corticosteroid replacement therapy is used in patients with adrenocortical insufficiency.
The images bellow were obtained in a 12 years old child, who presented with progressive motor and cognitive impairment.