
Case Report
Austin J Radiol. 2022; 9(1): 1183.
Decompensated Neuro-Behçet’s Disease Following Covid-19 Infection
Akkari M1,2, Douma B1,3*, Mansour M1,2, Derbali H1,2, Messelmani M1,2, Zaouali J1,2 and Mrissa R1,2
¹Department of Neurology, Military Hospital of Tunis, Tunisia
²Faculty of Medicine of Tunis, University Tunis el Manar, Tunisia
³Faculty of Medicine of Sousse, University of Sousse, Tunisia
*Corresponding author: Bissene Douma, Department of Neurology, Military Hospital of Tunis, Tunisia
Received: December 14, 2021; Accepted: January 13, 2022; Published: January 20, 2022
Abstract
Introduction: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV- 2) emerged in December 2019. Beside respiratory insufficiency, neurological complications have been observed with COVID-19. Here, we report a case of meningo-encephalitis following Covid-19 infection who decompensated a Neuro-Behçet’s disease.
Case Presentation: A 45-year-old-man which is followed for Neuro-Behçet disease, hospitalized in the intensive care unit for altered state of consciousness. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a hyperintense area adjacent to right occipital horn. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis revealed a meningitis with polymorphonuclear (PMN) cell predominance. The nasopharyngeal RTPCR was positive for SARS-CoV-2. The patient was treated with therapeutic anticoagulation, aciclovir and methylprednisolone sodium succinate and made a complete recovery.
Conclusion: Our study identified a considerable burden of COVID-19 in patients with chronic neurological disorders.
Keywords: Neuro-Behçet disease; Covid-19 infection; Meningoencephalitis; Pandemia
Introduction
Coronavirus disease was first reported in China in December 2019 and contagion has rapidly spread worldwide, becoming a global health problem. COVID-19 pandemic had many impacts on clinical neurology practice.In one hand, preliminary reports warned that coronavirus could have neuroinvasive potential [1]. In the other hand, it could lead to decompensation of chronic neurological disorders.
This brief report describes the first case of patient with decompensated neuro-behçet disease following Covid-19 infection.
We describe the case of a case of Neuro-Behçet’s disease decompensed by Covid-19 infection.
Case Presentation
A 45-year-old-man had been followed up for Neuro-Behet disease since 2015. He had a cerebellar syndrome and Brain MRI revealed radiological signs with the involvement of the brainstem, the thalamus and the internal capsule. He was treated with cyclophosphamide and oral steroids with a good outcome.
In september 2020, he felt generalized fatigue, headache and fever. Two days later, he presented a status epilepticus. He was immediately transferred to our hospital by ambulance. Upon arrival, he had a Glasgow coma scale (GCS) of 7 (E2 V2 M3) and required an endotracheal intubation with a mechanical ventilation. Physical examination revealed an obvious neck stiffness. Brain CT showed no evidence of brain edema. Brain MRI, with a T2-weighted fluid attenuated inversion recovery image, showed a hyperintense area adjacent to right occipital horn without evidence of contrast enhancement (Figure 1). A viral encephalitis was initially evoked in the presence of the MRI findings, but given the history and the clinical presentation, we oriented the diagnosis toward neuroBehçet. Blood investigation showed an increased white cell count (10700), neutrophil dominant, relatively decreased lymphocytes (5000) and increased C-reactive protein (77mg/L). A lumbar puncture was done and the CSF cell count was 200 cells/mL (60% polymorphonuclear (PNN) cells with 20 red blood cells/mL). CSF protein was 1200mg/L associated with normal glucose and chlorides tests. CSF culture was negative. A SARSCoV-2 was suspected and the RT-PCR test was performed using a nasopharyngeal swab. The specific SARSCoV-2 RNA was detected. The chest CT revealed a proximal pulmonary embolism and peripheral ground-glass opacities in the lung.
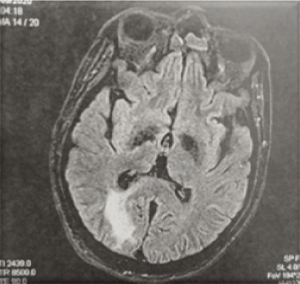
Figure 1: Brain MRI revealed a Flair hyperintense area adjacent to right
occipital horn.
He was admitted in the Intensive care unit with the clinical diagnosis of meningo-encephalitis. He had received therapeutic anticoagulation, aciclovir and methylprednisolone sodium succinate. For seizures, he underwent intravenous administration of Sodium Valproate. Ten days after admission, he had a lumbar puncture, CSF protein was 0.43mg/L associated with 4 cells/mL, the glucose and chlorides were normal. Increased IL-6 levels were detected (25.7pg/ mL, normal range <7pg/mL). Twenty days after, a control brain MRI had revealed a regression of previous lesions (Figure 2).
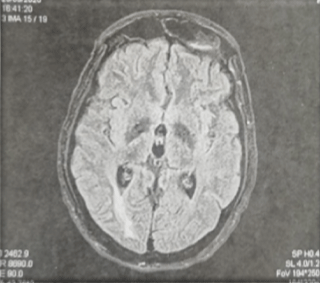
Figure 2: Control brain MRI revealed a regression of the previous lesion.
At day twenty-five, the patient was extubated. He had developed a flaccid tetraparesis with progressing muscle atrophy. He had no bowel or bladder dysfunction. Lactate levels, Serum CK, electrolytes, and CSF analyses were within the normal range. Spinal MRI was normal. A critical illness neuropathy was suspected and the paresis gradually improved by motor rehabilitation.
After one month in the ICU and one week in our departement of neurology, the patient was discharged with GCS score of 15 and modified Rankin Scale (mRS) 3.
Discussion
Our case described the first case of decompensated neuro-behçet disease following Covid-19 infection. It is yet not known whether patients with neurological disorders receiving immunosuppressive therapy are more susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 or not. In fact, recent studies reported that patients with systemic autoimmune diseases had the same prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection as the general population [2].
The most common symptoms of COVID-19 are cough and fever, which can progress to acute respiratory distress syndrome or multiorgan failure [2]. Additionally, several studies reported a wide range of thromboembolic complications including venous as well arterial thrombosis [3].
SARS-CoV-2 can have neuroinvasive potential because some patients showed neurologic symptoms such as headache, anosmia, ageusia [1].
Recently, two cases of meningoencephalitis had been reported as a complication of COVID-19 disease [1]. However no study to date had reported the incrimination of SARS-CoV-2 in the decompensation of neurological disorders such as Neuro-Behçet disease. So far, only one recent paper had studied the characteristics and the outcomes of 10 case-series of Behcet disease with Covid-19 [4]. Only one patient was diagnosed with Neuro-Behcet disease and had been hospitalized, because of acute gastrointestinal hemorrhage whose etiology was not clarified despite various investigations. He was tested positive for COVID-19 [4]. The bleeding resolved spontaneously after one week. On the 9th day, he presented a deep venous thrombosis. In fact, vascular complications are frequent in Behcet-disease. In our case, pulmonar emboly could be a possible complication of neuro-behcet disease or most probably induced by COVID-19. We think that it is a warning to pay attention to thrombotic complications in Behçet patients who may encounter COVID-19 disease. Thromboembolic events are assumed to be caused by endothelitis and hypercoagulable state as a consequence of SARS-CoV-2 related endothelial injury and dysregulated infammatory response [3].
In our case, increased Serum IL-6 levels were found. Studies had reported that IL-6 levels were correlated with BD disease activity [5], but are not specific. In fact, recent studies showed that high IL-6 levels were correlated with the severity of Coronavirus symptoms [5].
We claim that this case is important because through our observation we call for close monitoring of NBD patients as well as other immune compromised patients during SARS-Cov-2 pandemic.
Conclusion
Our study identified a considerable burden of COVID-19 in patients with chronic neurological disorders, and highlights the need for prevention in this group of patients. Further studies are needed to elucidate the direct effects of SARSCoV-2 infection on nervous system. We also have concerns that the incidence of vascular disorder may increase in Behçet’s patients after Pandemia.
Declaration
Author contributions: All authors contributed to the study conception and design
Consent: The patient agreed the doctors could use and publish his disease related article with personal information deleted.
References
- Takeshi Moriguchia, Norikazu Hariib, Junko Gotoa, Daiki Haradaa, Hisanori Sugawaraa, Junichi Takaminoa, et al. A first case of meningitis/encephalitis associated with SARS-Coronavirus-2. International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2020; 94: 55-58.
- Emmi G, Bettiol A, Mattioli I, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with systemic autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2020; 19: 102575.
- Klok FA, Kruip MJHA, van der Meer NJM. Confirmation of the high cumulative incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19: an updated analysis. Thromb Res. 2020.
- Berna Yurttas, Mert Oztas, Ali Tunc, Ilker Inanç Balkan, Omer Fehmi Tabak, Vedat Hamuryudan. Emire Seyahi Characteristics and outcomes of Behçet’s syndrome patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: a case series of 10 patients. Intern Emerg Med. 2020; 1-5.
- Dennis McGonagle, Kassem Sharif, Anthony O’Regan, Charlie Bridgewood. The Role of Cytokines including Interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced Pneumonia and Macrophage Activation Syndrome-Like Disease. 2020; 19: 102537.