
Clinical Image
Austin J Radiol. 2022; 9(2): 1190.
Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema in 20-Year-Old Male
Chaimae A*, Oumaima M, Wilson B, Mustapha O, Meriem F, Ech-Cherif EKN, Mohamed J and Firdaous T
Department of Radiology, Hospital of Specialities, CHU Ibn Sina, Mohamed V University, Rabat, Morocco
*Corresponding author: Abourak Chaimae, Department of Radiology, Hospital of Specialities, CHU Ibn Sina, Mohamed V University, Rabat, Morocco
Received: April 11, 2022; Accepted: April 27, 2022; Published: May 04, 2022
Clinical Image
A young man of 20 years, diagnosed and operated in 2010 for a tumor of the Posterior cerebral Fossa (pilocytic astrocytoma), presented intracranial hypertension syndrome in which a Cerebral MRI found a cystic tumor process with hemorrhage, situated in the right hemisphere and vermis, complicated with an active triventricular hydrocephaly, which he got operated for. During his post-operatory stay in reanimation, he presented acute dyspnea for which a chest CT was performed.
Description
Pulmonary Interstitial emphysema (PIE) is an unusual condition wherein air dissects through alveolar walls into the adjacent interstitial tissues [1], abnormal pathology that occurs more commonly in neonates but can be seen in adults as well [2]. Neonatal etiologies include respiratory distress syndrome, prematurity, Meconium aspiration syndrome, positive pressure ventilation or mechanical ventilation with high peak pressures, pulmonary infection (pneumonia, sepsis, chorioamnionitis), amniotic fluid aspiration, incorrect endotracheal tube placement and Magnesium sulfate antenatal exposures [2]. Other causes in adults include barotrauma, blunt thoracic trauma, lung obstructive diseases, infectious diseases, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and Smoking [2,3].
The pathogenesis of PIE is usually attributed to the access of air to the lung interstitium, via either rupture of airspaces at the lobular periphery or rupture of overdis tended small bronchioles, mainly during mechanical ventilation (also known as Macklin effect) [1,3].
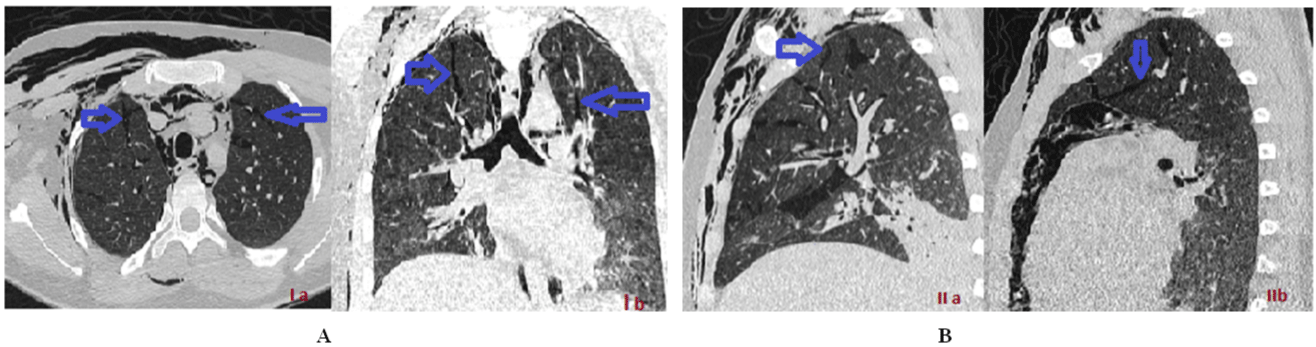
Figure 1A and 1B: Thoracic CT scan, axial, coronal and sagittal sections show interstitial emphysema associated with subcutaneous emphysema and
pneumomediastinum in a 20-year-old male with context of a post-extubation dyspnea, during his hospitalization in resuscitation for surgical following of pilocytic
astrocytoma.
PIE is a diagnosis made mainly from imaging, PIE shows the lung parenchyma filled with a mix of spherical cystic, linear, and oval air containing lucencies. Early changes appear to be linear but slowly progresses to the more cystic formation in the interstitium. Linear radiolucencies are about 3-8 mm long and less than 2mm in width. Cystic-like radiolucencies measure 1-4 mm in diameter. During inspiration, the lung volumes may increase, but premature lungs have decreased lung compliance resulting in hyper distended lungs on imaging [2].
Air leaks can also be seen on imaging. With air leaks, the air in the interstitium is full of large volumes of air, which reduces the gas exchange between the vascular bed and airspaces due to the increased distance. Pneumothorax can form if subpleural cysts end up rupturing. The air leak compresses on the heart from the increased intrathoracic pressures and results in decreased venous return to the heart. Other findings seen on imaging are linear gas collections in the periphery [1].
PIE can sometimes be seen on the anteroposterior supine chest X-ray, but it requires sequential studies to see the disease progression, then a CT scan would be the next step for diagnostic imaging [1,2].
PIE is usually treated with early administration of surfactant and with the optimal mechanical ventilator setting: high-frequency oscillation ventilation and positive end-expiratory pressure, low inspiratory pressure. The goal is to allow proper expiration as the lungs are over distended [1,3].
References
- Thais Mauad, Felipe BP do Nascimento, Marisa Dolhnikoff, Milena CM Picka, Paulo HN Saldiva on behalf of BIAS. Pulmonary interstitial emphysema in fatal asthma: case report and histopathological review BMC Pulmonary Medicine. 2018: 1-3.
- Ruchi Jalota, Fatima Anjum. Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2021.
- Akihiro Nakamata, Nanae Tsuchiya, Tetsuhiro Miyara, Murasaki Shiotani, Shinji Gibo, Sadayuki Murayama. Computed tomography findings, temporal course, and clinical relevance of subpleural pulmonary interstitial emphysema in patients with pneumomediastinum. Acta Radiologica Open. 2021: 10.