
Case Report
Austin J Reprod Med Infertil. 2015; 2(5): 1024.
Congenital Choroid Plexus Papilloma of Right Ventricle Following Treatment with Phlebotonic during Pregnancy
Haller-Kikkatalo K1,2,3* and Õiglane-Šlik E4
¹Competence Centre on Reproductive Medicine and Biology, Estonia
²Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Tartu, Estonia
³Women´s Clinic, Tartu University Hospital, Estonia
4Department of Neurology, Children´s Clinic, Tartu University Hospital, Estonia
*Corresponding author: Haller-Kikkatalo K, Department of Immunology, Institute of Biomedicine and Translational Medicine, University of Tartu, Ravila 19, Tartu 50411, Estonia
Received: June 02, 2015; Accepted: August 08, 2015; Published: August 10, 2015
Abstract
An extremely rare congenital choroid plexus papilloma of right ventricle of the brain was diagnosed in a newborn at three weeks of age. Due to the increasing production of the liquor the tumor was removed surgically 2 days later. The baby was exposed to flavonoids, Diosmin and Hesperidin (DH) during fetal development due to maternal treatment regimens of posttrombotic venal insufficiency. Flavonoids, as “plant origin” have often been considered to be safe and due to the venotonic and tissue protective properties are mainly used to cure chronic venous insufficiency in human. However, DH has not been used during pregnancy and even though being useful to mother, the benefits of DH may be reversed to unfavorable effect for developing fetus. Especially since flavonoids play a dual role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis depending of certain member of flavonoid or animal tissue used in experiment. Evidence of putative tumorigenic side-effect of DH mediated by cellular DNA damage directly, via oxidative stress, by interacting with cellular aryl hydrocarbon receptor or affecting vascularization processes via expression of growth factors, has been available since 1998 and is in constant growth. Here we draw attention to the safety of DH, which has not been proved yet, at least during pregnancy. Therefore, special precaution should be taken when DH is desired to use from the beginning of pregnancy and for a long period during pregnancy. The data available today, either directly or indirectly indicate the risk for congenital vascular tumors in human fetus if exposed to DH.
Keywords: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; Diosmin; Fetal development; Hesperidin; Neovascularization; Oxidative stress
Case Presentation
Congenital choroid plexus papilloma of the brain belongs to the group of congenital choroid plexus tumors [1]. Among these, congenital vascular choroid plexus papilloma of newborns, in particular, accounts for about 1/3 of all congenital brain tumors [2] which constitutes the calculated annual incidence rate of 0.05-0.09 cases per 100 000 children ≤36 months [1,2]. A 10-year retrospective study in Canada identified only 2 cases with congenital/fetal/neonatal brain choroid plexus papilloma and only one of them is still alive [2]. There are few other clinical reports of rare cases of papilloma of the given structure occurring at early childhood [3-6] and are therefore not classified as congenital.
Micronized Diosmin 450mg and Hesperidin 50mg (DH) in addition to warfarin treatment was prescribed twice a day to the 30 year old female after an incident of venous thrombosis of deep femoral vein while using oral contraceptives. The treatment with warfarin was replaced with subcutaneous injections of sodium enoxaparin 20mg/d and oral acetylsalicylic acid 100mg/d 1.5 years later because of pregnancy planning [7,8]. The treatment regime of DH, sodium enoxaparin and acetylsalicylic acid continued during pregnancy up to 6 weeks after delivery. Anormosomic baby boy was born at 39th gestational week via Caesarian section due to fetopelvis disproportion (Head Circumference (HC) was 37.5cm) and fetal tachycardia. The course of pregnancy and procedure for delivery was uncomplicated but the newborn suffered from a mild asphyxia.
At three weeks old he was diagnosed with congenital choroid plexus papilloma of right ventricle of the brain (Figure 1). The HC=41.8cm, large fontanel 4x7cm, sagittal suture was opened 3mm, bilateral Graefe sign turned positive, child was extremely restless, Babinski symptom bilaterally positive. Due to the increasing production of the liquor tumor hold evident and tremendous risk for brain damage, hydrocephaly or death, the tumor was removed by urgent surgery through opened large fontanel at the age of 25 days. Cranial trepanation was performed nearby largely opened large fontanel and tumor was extirpated from right ventricle and the remaining part of it through foramen Monroe. The course of surgery was uncomplicated and since the circulation of liquor was not interrupted no catheter was replaced. The tumor was histologically benign papilloma of choroid plexus. Postoperative HC=40cm, large fontanel was hollowed, Babinski symptom minimally expressed. Electron-Encephalography (EEG) performed on 5th postoperative day revealed underlying damage at the projection of right hemisphere. The general development of child was satisfactory during the following 3 postoperative years. At the age of 3, the right occipitaltemporal partial epilepsy with secondary generalized seizures and loss of consciousness was manifesting.
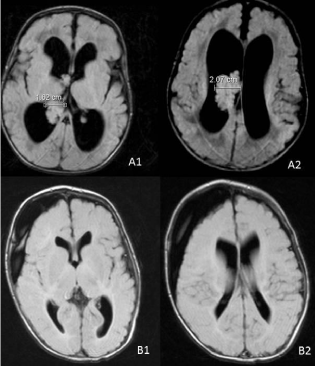
Figure 1: Magnet resonance tomographic image with fluid attenuation
inversion recovery regime of choroid plexus papilloma in the right ventricle
of the brain (A) and of postsurgical status 72 days after operation (B). A1 –
papilloma in the right lateral ventricle reaching partly to into the third ventricle,
A2 – papilloma in the widened right ventricle, B1, B2 – subdural hygroma at
the right side of the brain with maximal depth 1.9cm and equal seized lateral
ventricles, no sign of the papilloma.
During expecting the second child, the mother was prescribed again to use sodium enoxaparin 20mg/d and acetylsalicylic acid 100mg/d, but not DH. The second child was born healthy 2 years later.
Discussion and Conclusion
A flavonesdiosmin (3’,5,7-trihydroxy-4’-methoxyflavone- 7-rutinoside) and a flavanonehesperidin (3′,5,7-trihydroxy-4′- methoxyflavanon) belong to the family of plant polyphenolic compounds named flavonoids. Flavonoidsplay a dual role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis acting either as anticarcinogens or inhibit the growth of tumor cells [9-14], or others act as cocarcinogens, are mutagenic or able to induce DNA damage [9,15]. DH are a potent venotonic protecting veins from damaging factors and are therefore mainly used to cure chronic venous insufficiency [16-18]. For these indications, the DH has been reported to be effective, harmless and has been in use for long time by now [16-22]. The treatment of venous insufficiency with DH benefits from various effects providing cellular protection to already increased inflammatory state and oxidative stress in vitro or in non-pregnant patients [23-26] or following chemically induced carcinogenesis [14,27-31]. Even though DH has many health benefits for chronic diseases, these benefits need reevaluations when it comes to pregnancy where developing fetus is involved. In general, DH treatment during pregnancy has not been contradicted since no teratogenic effect has been detected in animal experiments [32]. The safety of hesperidin was stated based on the detection of viable mice fetuses with no external, visceral, and skeletal adverse effects observed. However, the hemorrhagic area in the brain was detected in one fetus treated with hesperidin, but was considered statistically insignificant due to low prevalence [32]. It is worth noticing, that similar occasion is reflected also in current case, where the newborn boy had vascular abnormality in the plexus choroideus but was otherwise healthy. Literature provides few cases where diosmin has been used in human pregnancy, but all have been near full term of pregnancy and for very short period of time [33,34]. In current case, DH was used during entire pregnancy, covering also the most sensitive periods of fetal development. The safety statement of diosminin human pregnancy [35] relies on minimal transplacental passage in rodents detected in a study in 1994 [17]. No later studies or studies on human are available to contradict the passage of diosmin through the placenta. On the contrary, because of their lipophilicity [36,37] and low molecular mass [38,39] of diosmin about 608kDa and hesperidin ca610 kDa, theses bioflavonoids among others [36] pass through the feto-placental barrier from mother to fetus.
There are a number of mechanisms by which DH could affect developing fetus. Apart from common ability of flavonoids to interact directly with DNA [15], diosmin affects gene expression and modifies cell function [40-42] by interacting with cellular Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) in a cell type specific manner [43,44]. The AhR-agonistic effect of diosmin is rather substantial reaching up to 25% of the maximal response induced by most toxic 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-P-Dioxin (TCDD) [43]. TCDD is one of the dioxinsused as a reference standard for hazard and risk assessment of these environmental and dietarycontaminants [45,46]. Also, dioxins, or TCDD, have been used to identify several harmful effect of AhR activation during fetal development. The yet developing fetus is most sensitive to AhR mediated effect starting already from the developmental stage of morulae (day 3-4 after fertilization) [47]. Later, the effect of AhR activation on cell cycle progression versus arrest is tissue-sensitive [36] impairing preferentially the formation of rapidly developing organ systems [48,49]. AhR activation during fetal development may interfere with brain development by affecting the function of neurotransmitters [50] and by altering intracellular enzymatic signaling [51]. Same time, AhR activation is unlikely involved in major disturbances of the human brain tissue [36] substantial to abort the pregnancy, but rather milder to cause health problems after birth. However, there is no certainty whether the epilepsy in current case is a direct consequence of AhR mediated effect of diosmin, or the brain tissue was suffering from increased intracranial pressure during development due to increased liquor production of papilloma.
As shown already a long time ago, diosmin induces the expression of CYP1A1 [44] via AhR [52]. The activity of CYP1A1 generates genotoxic metabolites harming DNA structure [53] and mediating carcinogenetic properties in a cell [44].There is a question of current case, whether the tumor was initiated by cellular cancerogenesis mechanisms or alternatively, was it the consequence of disturbed vascular development. Importantly, AhR activation may cause disturbances in vascularization of certain tissues, causing cardiovascular embryotoxicity of dioxins [54], altering the shape and causing neovascularization of certain blood vessels in the brain of developing Zebrafish [55]. The vascularization process seems to be disturbed in certain blood vessels rather than affecting entire vascular system in the body [55-57]. Brain vasculature is unique because cranial vessel pattering is intertwined with neural development [55,58]. In the line with these data, no clinically relevant blood vessel malformations was detected in the little boy anywhere else in the body but in the plexus choroideus.
Apart from AhR mediated effect of dioxins, these compounds induce abnormal vascularization via promoting the expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in mouse model and in human cell line [59]. Since VEGF regulates the development of blood vessels in normal tissues but also in tumors [60] dioxins may initiate neovascularization in normal tissue and promote the vascular growth in already tumorigenic tissues.
The congenital choroid plexus papilloma of right ventricle of the brain is extremely rare disease [1,2]. Definitely, in such a rare disease the etiologic factors are not the ones to occur very commonly in the population, but are expected to be rare and specific. Also, as venous insufficiency treated with flavonoids is more prevalent in elderly women [61] and the coexistence of pregnancy with long term flavonoid treatment is also rare, meaning no epidemiological studies cannot be performed thus far to assure the association. Also, it is well appreciated, that there are distinct risk factors, the way these factors affect and the speed of the affect for fetal carcinogenesis and that for tumors acquired slowly during the lifetime exposing many different risk factors. Available data indicate that the safety of phlebotonic DH is not sufficiently studied yet and the use of DH may be hazardous to developing fetus. Special precaution should be taken when DH is desired to use from the beginning of pregnancy and for a long period during pregnancy.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the Estonian Research Council (institutional research funding and IUT34-16).
Conflict of Interest
Authors consult the patient in his development and in coupling the epilepsy.
References
- Lafay-Cousin L, Keene D, Carret AS, Fryer C, Brossard J, Crooks B, et al. Choroid plexus tumors in children less than 36 months: the Canadian Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium (CPBTC) experience. Childs Nerv Syst. 2011; 27: 259-264.
- Manoranjan B, Provias JP. Congenital brain tumors: diagnostic pitfalls and therapeutic interventions. J Child Neurol. 2011; 26: 599-614.
- Anselem O, Mezzetta L, Grangé G, Zerah M, Benard C, Marcou V, et al. Fetal tumors of the choroid plexus: is differential diagnosis between papilloma and carcinoma possible? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 38: 229-232.
- Haliasos N, Brew S, Robertson F, Hayward R, Thompson D, Chakraborty A. Pre-operative embolisation of choroid plexus tumours in children. Part II. Observations on the effects on CSF production. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013; 29: 71-76.
- Phi JH, Goobie SM, Hong KH, Dholakia A, Smith ER. Use of tranexamic acid in infants undergoing choroid plexus papilloma surgery: a report of two cases. Paediatr Anaesth. 2014; 24: 791-793.
- Shuto T, Sekido K, Ohtsubo Y, Tanaka Y, Hara M, Yamaguchi K, et al. Choroid plexus papilloma of the III ventricle in an infant. Childs Nerv Syst. 1995; 11: 664-666.
- Kher A, Bauersachs R, Nielsen JD. The management of thrombosis in pregnancy: role of low-molecular-weight heparin. Thromb Haemost. 2007; 97: 505-513.
- de Vries JI, van Pampus MG, Hague WM, Bezemer PD, Joosten JH. FRUIT Investigators. Low-molecular-weight heparin added to aspirin in the prevention of recurrent early-onset pre-eclampsia in women with inheritable thrombophilia: the FRUIT-RCT. J Thromb Haemost. 2012; 10: 64-72.
- Plaumann B, Fritsche M, Rimpler H, Brandner G, Hess RD. Flavonoids activate wild-type p53. Oncogene. 1996; 13: 1605-1614.
- Hiramoto K, Ojima N, Sako K, Kikugawa K. Effect of plant phenolics on the formation of the spin-adduct of hydroxyl radical and the DNA strand breaking by hydroxyl radical. Biol Pharm Bull. 1996; 19: 558-563.
- Agullo G, Gamet-Payrastre L, Manenti S, Viala C, Remesy C, Chap H, et al. Relationship between flavonoid structure and inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: a comparison with tyrosine kinase and protein kinase C inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997; 53: 1649-1657.
- Constantinou A, Mehta R, Runyan C, Rao K, Vaughan A, Moon R. Flavonoids as DNA topoisomerase antagonists and poisons: structure-activity relationships. J Nat Prod. 1995; 58: 217-225.
- Larsen AK, Escargueil AE, Skladanowski A. Catalytic topoisomerase II inhibitors in cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2003; 99: 167-181.
- Dung TD, Day CH, Binh TV, Lin CH, Hsu HH, Su CC, et al. PP2A mediates diosmin p53 activation to block HA22T cell proliferation and tumor growth in xenografted nude mice through PI3K-Akt-MDM2 signaling suppression. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012; 50: 1802-1810.
- Hodek P, Hanustiak P, Krízková J, Mikelova R, Krízková S, Stiborová M, et al. Toxicological aspects of flavonoid interaction with biomacromolecules. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2006; 27 Suppl 2: 14-17.
- Cospite M. Double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation of clinical activity and safety of Daflon 500 mg in the treatment of acute hemorrhoids. Angiology. 1994; 45: 566-573.
- Meyer OC. Safety and security of Daflon 500 mg in venous insufficiency and in hemorrhoidal disease. Angiology. 1994; 45: 579-584.
- Ho YH, Tan M, Seow-Choen F. Micronized purified flavonidic fraction compared favorably with rubber band ligation and fiber alone in the management of bleeding hemorrhoids: randomized controlled trial. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000; 43: 66-69.
- Friesenecker B, Tsai AG, Intaglietta M. Cellular basis of inflammation, edema and the activity of Daflon 500 mg. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1995; 15 Suppl 1: 17-21.
- Gohel MS, Davies AH. Pharmacological agents in the treatment of venous disease: an update of the available evidence. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2009; 7: 303-308.
- Labrid C. Pharmacologic properties of Daflon 500 mg. Angiology. 1994; 45: 524-530.
- Cohen JM, Akl EA, Kahn SR. Pharmacologic and compression therapies for postthrombotic syndrome: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Chest. 2012; 141: 308-320.
- Abdel-Salam OM, Youness ER, Mohammed NA, Abd-Elmoniem M, Omara E, Sleem AA. Neuroprotective and hepatoprotective effects of micronized purified flavonoid fraction (Daflon(R)) in lipopolysaccharide-treated rats. Drug Discov Ther. 2012; 6: 306-314.
- Beyer G, Melzig MF. Effects of selected flavonoids and caffeic acid derivatives on hypoxanthine-xanthine oxidase-induced toxicity in cultivated human cells. Planta Med. 2003; 69: 1125-1129.
- Krzyściak W, Cierniak A, Kὀzka M, Kozieƚ‚ J. Oxidative DNA Damage in Blood of CVD Patients Taking Detralex. Open Cardiovasc Med J. 2011; 5: 179-187.
- Yamamoto M, Jokura H, Suzuki A, Hase T, Shimotoyodome A. Effects of continuous ingestion of hesperidin and glucosyl hesperidin on vascular gene expression in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2013; 59: 470-473.
- So FV, Guthrie N, Chambers AF, Moussa M, Carroll KK. Inhibition of human breast cancer cell proliferation and delay of mammary tumorigenesis by flavonoids and citrus juices. Nutr Cancer. 1996; 26: 167-181.
- Martinez RM, Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Steffen VS, Caviglione CV, Vignoli JA, Baracat MM, et al. Hesperidin methyl chalcone inhibits oxidative stress and inflammation in a mouse model of ultraviolet B irradiation-induced skin damage. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2015; 148: 145-153.
- Tahir M, Rehman MU, Lateef A, Khan AQ, Khan R, Qamar W, et al. Diosmin abrogates chemically induced hepatocarcinogenesis via alleviation of oxidative stress, hyperproliferative and inflammatory markers in murine model. Toxicol Lett. 2013; 220: 205-218.
- Srinivasan S, Pari L. Ameliorative effect of diosmin, a citrus flavonoid against streptozotocin-nicotinamide generated oxidative stress induced diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2012; 195: 43-51.
- Tanaka T, Tanaka T, Tanaka M, Kuno T. Cancer chemoprevention by citrus pulp and juices containing high amounts of β-cryptoxanthin and hesperidin. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012; 2012: 516981.
- Waalkens-Berendsen DH, Kuilman-Wahls ME, Bär A. Embryotoxicity and teratogenicity study with neohesperidin dihydrochalcone in rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2004; 40: 74-79.
- Buckshee K, Takkar D, Aggarwal N. Micronized flavonoid therapy in internal hemorrhoids of pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1997; 57: 145-151.
- Milchev N, Batashki I, Markova D, Dimitrova E. [Using phlebodia in pregnant women during preterm delivery]. Akush Ginekol (Sofiia). 2008; 47: 7-9.
- [No authors listed]. Monograph. Diosmin. Altern Med Rev. 2004; 9: 308-311.
- Gassmann K, Abel J, Bothe H, Haarmann-Stemmann T, Merk HF, Quasthoff KN, et al. Species-specific differential AhR expression protects human neural progenitor cells against developmental neurotoxicity of PAHs. Environ Health Perspect. 2010; 118: 1571-1577.
- Majumdar S, Srirangam R. Solubility, stability, physicochemical characteristics and in vitro ocular tissue permeability of hesperidin: a natural bioflavonoid. Pharm Res. 2009; 26: 1217-1225.
- https://www.quartzy.com/reagent-detail/2345639/1/Diosmin-biorbyt-orb134524
- Pacifici GM. Placental transfer of antibiotics administered to the mother: a review. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 44: 57-63.
- Singh NP, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti PS. Role of dioxin response element and nuclear factor-kappaB motifs in 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-mediated regulation of Fas and Fas ligand expression. Mol Pharmacol. 2007; 71: 145-157.
- Rowlands JC, Gustafsson JA. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated signal transduction. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1997; 27: 109-134.
- Nebert DW, Dalton TP, Okey AB, Gonzalez FJ. Role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated induction of the CYP1 enzymes in environmental toxicity and cancer. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279: 23847-23850.
- Zhang S, Qin C, Safe SH. Flavonoids as aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists/antagonists: effects of structure and cell context. Environ Health Perspect. 2003; 111: 1877-1882.
- Ciolino HP, Wang TT, Yeh GC. Diosmin and diosmetin are agonists of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor that differentially affect cytochrome P450 1A1 activity. Cancer Res. 1998; 58: 2754-2760.
- Ahlborg UG, Hanberg A. Toxic equivalency factors for dioxin-like PCBs. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 1994; 1: 67-68.
- Van den Berg M, Birnbaum L, Bosveld AT, Brunström B, Cook P, Feeley M, et al. Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. Environ Health Perspect. 1998; 106: 775-792.
- Petroff BK, Valdez KE, Brown SB, Piasecka J, Albertini DF. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist 2,3,7,8-tetrachloro-dibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) alters early embryonic development in a rat IVF exposure model. Reprod Toxicol. 2011; 32: 286-292.
- Barthold JS, Kryger JV, Derusha AM, Duel BP, Jednak R, Skafar DF. Effects of an environmental endocrine disruptor on fetal development, estrogen receptor(alpha) and epidermal growth factor receptor expression in the porcine male genital tract. J Urol. 1999; 162: 864-871.
- Philips BH, Susman TC, Powell WH. Developmental differences in elimination of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) during Xenopus laevis development. Mar Environ Res. 2006; 62 Suppl: S34-37.
- Breier JM, Gassmann K, Kayser R, Stegeman H, De Groot D, Fritsche E, et al. Neural progenitor cells as models for high-throughput screens of developmental neurotoxicity: state of the science. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2010; 32: 4-15.
- Kodavanti PR. Neurotoxicity of persistent organic pollutants: possible mode(s) of action and further considerations. Dose Response. 2006; 3: 273-305.
- Poland A, Knutson JC. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982; 22: 517-554.
- Dipple A. Reactions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with DNA. IARC Sci Publ. 1994; : 107-129.
- Alexeyenko A, Wassenberg DM, Lobenhofer EK, Yen J, Linney E, Sonnhammer EL, et al. Dynamic zebrafish interactome reveals transcriptional mechanisms of dioxin toxicity. PLoS One. 2010; 5: e10465.
- Teraoka H, Ogawa A, Kubota A, Stegeman JJ, Peterson RE, Hiraga T. Malformation of certain brain blood vessels caused by TCDD activation of Ahr2/Arnt1 signaling in developing zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol. 2010; 99: 241-247.
- Bello SM, Heideman W, Peterson RE. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin inhibits regression of the common cardinal vein in developing zebrafish. Toxicol Sci. 2004; 78: 258-266.
- Yamauchi M, Kim EY, Iwata H, Shima Y, Tanabe S. Toxic effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in developing red seabream (Pagrus major) embryo: an association of morphological deformities with AHR1, AHR2 and CYP1A expressions. Aquat Toxicol. 2006; 80: 166-179.
- Liu J, Fraser SD, Faloon PW, Rollins EL, Vom Berg J, Starovic-Subota O, et al. A betaPix Pak2a signaling pathway regulates cerebral vascular stability in zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104: 13990-13995.
- Takeuchi A, Takeuchi M, Oikawa K, Sonoda KH, Usui Y, Okunuki Y, et al. Effects of dioxin on vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production in the retina associated with choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009; 50: 3410-3416.
- Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S, Poltorak Z. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. FASEB J. 1999; 13: 9-22.
- Simka M, Majewski E. The social and economic burden of venous leg ulcers: focus on the role of micronized purified flavonoid fraction adjuvant therapy. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003; 4: 573-581.