Case Report
Austin J Surg. 2014;1(1): 1003.
Relative vs. Absolute Cerebral Oximetry: does a Skin Pigmentation Effect Normal values on cardiopulmonary Support?
Christine Feldmeier, Harrison Pitcher, Hitoshi Hirose*, Nicholas Cavarocchi
Department of Surgery, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA, USA
*Corresponding author: Hitoshi Hirose, Department of Surgery, Thomas Jefferson University, 1025 Walnut Street, Suite 605, Philadelphia, PA, 19107, USA
Received: December 30, 2013; Accepted: January 27, 2014; Published: February 21, 2014
Abstract
Introduction: Real–time cerebral oximetry has been used to monitor perfusion in the brain. Two types of oximetry devices employed at our institution are: INVOS (Covidien, Mansfield, MA) and FORESIGHT (CAS Medical Systems, Branford, CT) which are relative and absolute cerebral oximetry, respectively. We have observed inaccuracy with relative oximetry compared to absolute oximetry in patients with dense melanin pigmentation.
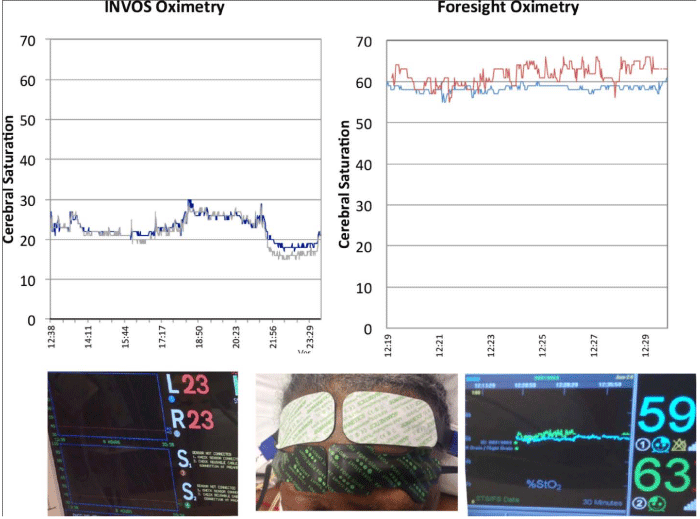
Case Presentation: A 71 year–old African American female without carotid disease underwent coronary artery bypass. Baseline cerebral saturations with relative oximetry were ˜ 40–45% immediately after induction of anesthesia, decreasing consistently to 20–30% during the procedure. Attempts to increase cerebral oximetry during CPB included volume expansion, increase flow and vasopressors. Upon arrival to the ICU, simultaneously tracings of cerebral oximetry from relative (INVOS) and absolute (FORESIGHT) were obtained. The cerebral saturations using FORESIGHT were found to be adequate >60 bilaterally (>50 = normal). Vasopressor support was weaned quickly and theabsolute cerebral saturations were maintained. The patient had no neurologic deficits or mental status changes postoperatively.
Conclusions: An inaccurate reading using relative oximetry was most likely produced by the dense presence of melanin in the patient⁄s skin, as melanin has a similar absorption spectrum as hemoglobin. Absolute oximetry uses a fiber optic laser light source with four wavelengths (690, 780, 810, and 880nm), while relative oximetryutilize two wavelengths (730 and 810nm) and an LED light source. The four wavelengths used by absolute oximetry have been proven necessary for accurate measurement of oxy and de–oxy hemoglobin in determining absolute cerebral saturation by accounting for interference from other background light absorbers, including melanin.
Introduction
Real–time cerebral oximetry is non–invasive monitoring of perfusion changes of cerebral oxygenation [1]. We have been using two different oximetry devices: INVOS System (Covidien, Mansfield, MA) and FORESIGHT Cerebral Oximeter (CAS Medical Systems, Branford, CT) in our practice [2,3]. We have observed differences in these oximetry devices in patients with darker skin, specifically those on various types of advanced cardiopulmonary support. Persistent decreases in cerebral saturations seen on relative oximetry have caused additional interventions to correct or diagnose the drop in saturation in our patients. However when directly compared to the saturations calculated by absolute oximetry, we have found the absolute saturations to be consistently adequate. We report our experience with differences in cerebral oximetry with respect to skin color variation in our patient on cardiopulmonary support.
Case Report
A 71 year–old African American female underwent a coronary artery bypass for complex stenosis on the left anterior descending artery. She had no peripheral vascular disease or carotid disease. INVOS monitoring was placed on her scalp before induction of general anesthesia and baseline readings were recorded as being between 40–45%. Throughout the case, saturations dropped and were consistently 20–30%. Replacement of oximeter, leads, and adjustment of lead placement were all attempted but cerebral saturations remained <30%. Intervention taken in the OR included volume expansion, increase pump flow, vasopressors and 100% oxygen to increase cerebral perfusion, which were unsuccessful. Upon arrival to the ICU, report was given that the patient’s mean arterial pressure was kept above 100 to maintain adequate cerebral saturations, to the point of sacrificing cardiac output to increase cerebral perfusion with higher arterial pressures. INVOS and FORESIGHT sensors were placed to the patient’s forehead side by side and we found the oximetry reading of the FORESIGHT was in normal range compared to INVOS (Figure). The FORESIGHT reading was greater than 60 while INVOS was lower than 30. Based on this finding, vasopressors were weaned quickly and the patient was extubated without neurologic issues.
Discussion
The case presented demonstrates the importance of reliable cerebral oximetry measurement, as unnecessary interventions were done to improve an inaccurate reading. We have encountered this situation repetitively in patients with dark skin in our practice with those on various support devices, including extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, total artificial heart, and biventricular assist device. In these patients, falsely low readings were found on relative oximetry (INVOS system), but were normal when measured by absolute cerebral oximetry (FORESIGHT system).
Figure 1 :Simultaneously tracings of cerebral oximetry from the INVOS (left) and FORESIGHT (right) obtained from a dark skin patient.
It is theorized that patients with a greater amount of skin pigmentation would have inaccurate results in relative cerebraloximetry [4], since melanin has a similar absorption spectrum as hemoglobin [5]. Absolute oximetry uses a fiber optic laser light source with four wavelengths (690, 780, 810, and 880nm), while relative oximetry uses an LED light source with two wavelengths (730 and 810nm) [6]. The four wavelengths used by absolute oximetry have been proven to be necessary for accurate measurement of oxy and de–oxy hemoglobin in determining absolute cerebral saturation by accounting for interference from other background light absorbers [3]. Although relative cerebral oxygenation monitoring focuses more on the amount of change from an established baseline cerebral oxygenation value, INVOS system saturations below 40% should be an alert for impending cerebral ischemia [7]. Readings below the normal limit can be seen in those with darker skin due to melanin’s attenuating effect on the reading.
In our practice we have experienced consistently low cerebral saturations using relative oximetry in numerous patients with dark skin compared to absolute oximetry. As depicted in this presentation, unnecessary interventions were performed due to inaccurate readings from the relative cerebral oximetry. Patients with such low readings were worked up using the flow diagram recently published by Wong et al. [8], but as our experience grew we have since started almost exclusively using absolute oximetry to avoid having to work up faulty low readings.
Conclusion
Because the accuracy in absolute oximetry is greater than that of relative oximetry in patients with darker skin, we now exclusively use absolute cerebral oximetry to guide us in ensuring adequate cerebral perfusion in darker skinned patients.
References
- Henson LC, Calalang C, Temp JA, Ward DS. Accuracy of a cerebral oximeter in healthy volunteers under conditions of isocapnic hypoxia. Anesthesiology 1998; 88:58-65.
- Baikoussis NG, Karanikolas M, Siminelakis S, Matsagas M, Papadopoulos G. Baseline cerebral oximetry values in cardiac and vascular surgery patients: a prospective observational study. J Cardiothorac Surg 2010; 24:5-41.
- FischerGW. Recent advances in application of cerebral oximetry in adult cardiovascular surgery. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2008; 12:60-69.
- Murkin, JM and Arango, M. Near-infrared spectroscopy as an index of brain and tissue oxygenation. Br J Anaesth 2009; 103: I3-I13.
- Fiener JR, Severinghaus JW, Bickler PE. Dark skin decreases the accuracy of pulse oximeters at low oxygen saturation: the effects of oximeter probe type and gender. Anesth Analg 2007; 105:S18-23.
- Moerman A, Vandenplas G, Bové T, Wouters PF, De Hert SG. Relation between mixed venous oxygen saturation and cerebral oxygen saturation measured by absolute and relative near-infrared spectroscopy during off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting. Br J Anaesth 2013; 110:258-65.
- Elser HE, Holditch-Davis D, Brandon, DH. Cerebral oxygenation monitoring: a strategy to detect IVH and PVL. Newborn Infant Nurs Rev2011; 11:153–159.
- Wong JK, Smith TN, Pitcher HT, Hirose H, Cavarocchi NC. Cerebral and lower limb near-infrared spectroscopy in adults on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Artif Organs 2012; 36:659-667.