Case Report
Austin J Surg. 2024; 11(3): 1331.
Innovative Therapy Unveiled - Proximal Medial and Lateral Locking Plates Combined with Drilled Reduction and Osteoinductive Implantation for Comminuted Upper Tibia Fractures
Wendong Xie²; Guangsu Zhang²; Chao Zhang¹*
¹Department of Orthopedics, Gansu Provincial Hospital, PR China
²Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, PR China
*Corresponding author: Chao Zhang, Department of Orthopedics, Gansu Provincial Hospital, No.204, DonggangWestRoad, Lanzhou, 730000, Gansu Province, PR China. Email: zc-315@163.com
Received: August 06, 2024 Accepted: August 27, 2024 Published: September 04, 2024
Abstract
In the modern field of orthopaedic treatment, comminuted fractures of the upper tibia have always been a challenging challenge. This type of fracture not only brings great pain to the patient, but also may lead to dysfunction due to improper treatment. In recent years, through continuous exploration and practice, our medical experts have successfully developed an innovative treatment method - proximal tibia medial and lateral locking plate combined with proximal tibia drilling and reduction and osteoinductive implantation.
Keywords: Comminuted fractures of the upper tibia; Medial and lateral locking plates of the proximal tibia; Tibial drilling and reduction; Osteoinduction; Surgical treatment; Rapid rehabilitation
Introduction
A comminuted fracture of the upper tibia is a severe fracture of the upper tibia in which the fracture line usually passes through the articular surface, resulting in destruction of the articular surface. This type of fracture is characterised by complex fracture lines and multiple fracture fragments, which makes it difficult to treat because the damage to the articular surface can seriously affect the patient's joint function. Traditional treatment methods such as plaster fixation, unilateral plate internal fixation, and intramedullary nail fixation can restore the stability of the fracture, but they are ineffective in repairing the articular surface, and are prone to leave behind problems such as dysfunction and stiffness of the joint [1].
Proximal tibial medial and lateral locking plate: it is a medial and lateral locking plate fixed to the proximal tibia medially and laterally, respectively.
The plate adopts double locking design, which can firmly fix the fracture end, reduce the displacement of the fracture end, and facilitate fracture healing [2,3].
Proximal tibial drilling and decompression: By drilling holes at the proximal end of the fracture, the intraosseous pressure and local soft tissue pressure at the fracture site can be reduced, and blood circulation can be improved to promote the healing of the fracture.
Osteoinductive implantation: A biologically active substance with osteoinductive effect is implanted into the fracture area to stimulate the growth and differentiation of osteoblasts and promote fracture healing. Commonly used osteoinductive substances include Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP), growth factors and so on [4].
Case Report
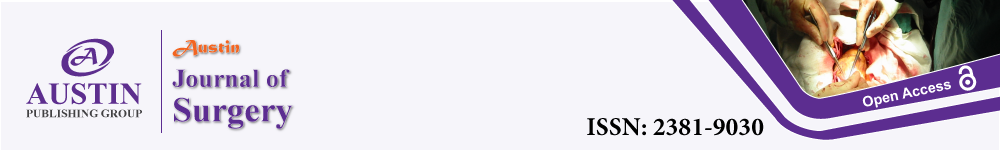
The patient was a 75-year-old male who had been in the hospital for 9 days due to pain, swelling, and limited movement of his right lower extremity. He reported that 2 hours prior to admission, he was injured in his right lower limb when he was hit by a car and was brought to our hospital by his family. Physical examination showed: swelling of the upper right lower leg, obvious pressure pain, palpable bone friction, obvious limitation of movement, normal sensation in the right lower limb, good pulsation of the right dorsalis pedis artery. CT scan showed: comminuted fracture of the right upper tibia, involving the articular surface, and swelling of the surrounding soft tissues (Figure 1).
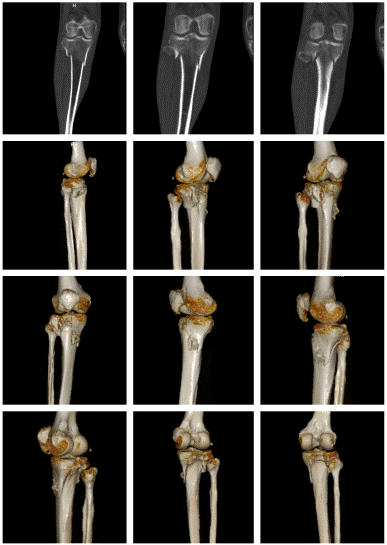
Figure 1: CT scan showed: comminuted fracture of the right upper tibia, involving the articular surface, and swelling of the surrounding soft tissues.
After admission, under general anaesthesia, he underwent examination of the right upper tibia, internal fixation with medial and lateral locking plates for comminuted fracture of the right upper tibia, proximal tibia drilling and reduction, and osteoinductive implantation. Intraoperatively, a comminuted fracture of the right upper tibia was seen, with fracture of the articular surface and swelling of the surrounding soft tissues. Surgical procedure: after removing the blood clot, the fracture break was reset, Firstly, a suitable locking steel plate was selected, and the plate was fixed with a bone holder, while a number of small holes were drilled along the edge of the plate, and then a screw was implanted at each end of the plate for temporary fixation of the plate (Figure 2). Intraoperative X-ray examination showed that the fracture was in good alignment (Figure 3). The fracture alignment was found to be good and the plate was in good position, so the remaining screws were implanted sequentially (Figure 4). X-ray examination after implantation of the screws showed that the fracture was in good alignment and the internal fixation was in good position (Figure 5). After repeated rinsing with saline, a drain was placed (Figure 6). Finally, osteoinduction was implanted at the fracture site (Figure 7). Two days after the operation, the patient's symptoms were significantly relieved and his mental state recovered significantly, and he could gradually walk on the ground. Follow-up of the patient's condition was continued.
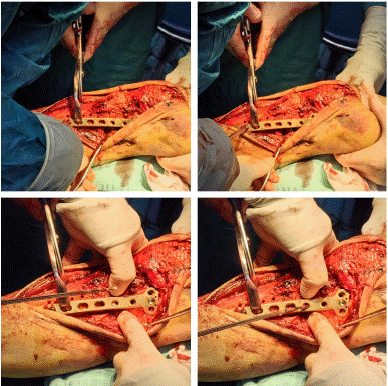
Figure 2: Firstly, a suitable locking steel plate was selected, and the plate was fixed with a bone holder, while a number of small holes were drilled along the edge of the plate, and then a screw was implanted at each end of the plate for temporary fixation of the plate.
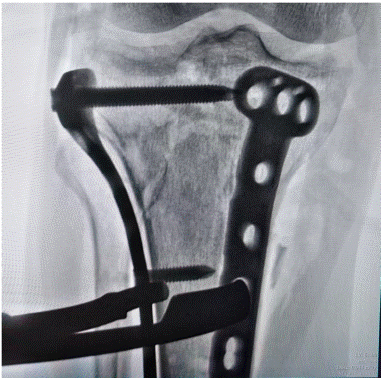
Figure 3: Intraoperative X-ray examination showed that the fracture was in good alignment.
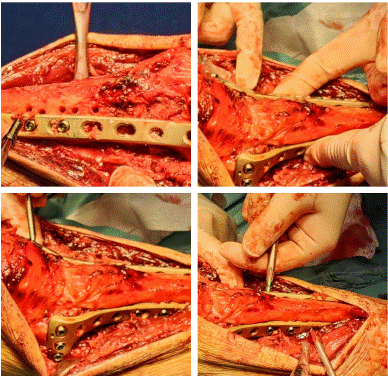
Figure 4: The fracture alignment was found to be good and the plate was in good position, so the remaining screws were implanted sequentially.
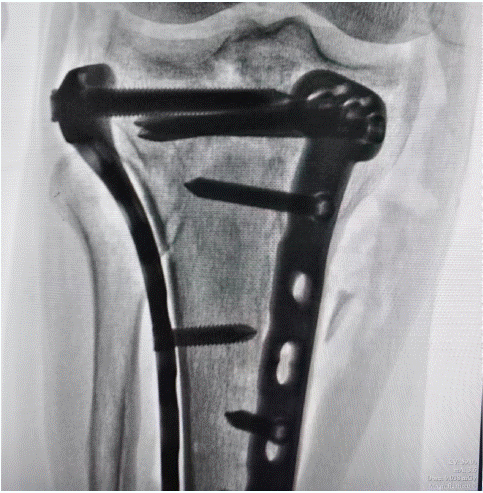
Figure 5: X-ray examination after implantation of the screws showed that the fracture was in good alignment and the internal fixation was in good position.
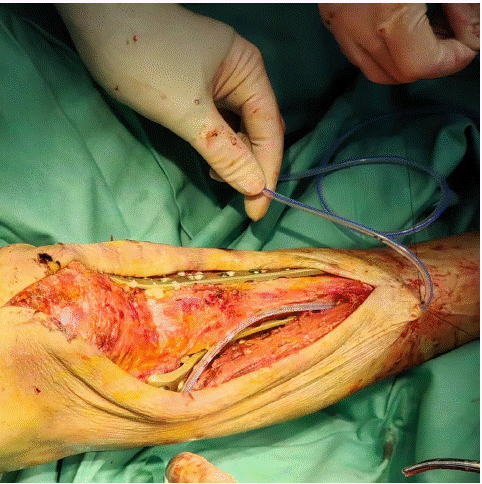
Figure 6: A drain was placed.
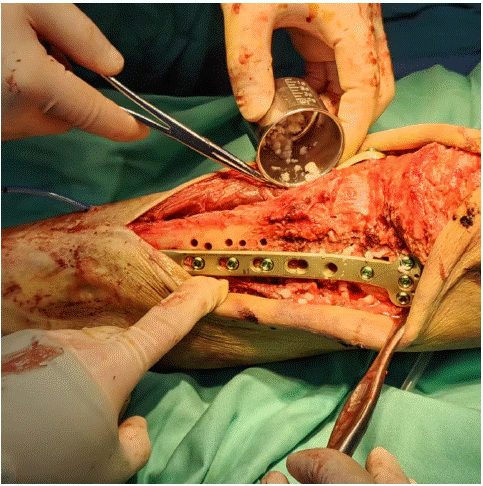
Figure 7: Osteoinduction was implanted at the fracture site.
Discussion
Proximal medial and lateral locking plates combined with proximal tibial drilling and reduction and osteoinductive implantation for the treatment of comminuted fractures of the upper tibia is an innovative and efficient treatment. It has the following advantages [5]:
(1) Reliable fixation: double locking plates can firmly fix the fracture end, reduce fracture displacement, and facilitate fracture healing.
(2) Promote fracture healing: drilling and decompression can improve local blood circulation, and osteoinductive implantation can stimulate the growth and differentiation of osteoblasts, which together promote fracture healing.
(3) Reducing complications: It reduces the incidence of complications.
(4) Wide range of indications: it is suitable for all types of comminuted upper tibia fractures.
In conclusion, proximal medial and lateral locking plates combined with proximal tibial drilling and reduction and osteoinductive implantation for the treatment of comminuted upper tibia fracture has the advantages of reliable fixation, promotion of fracture healing, and reduction of complications, which provides a better treatment option for patients. With the accumulation of clinical applications, this treatment method will be more widely promoted and applied in the future.
Author Statements
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no financial disclosures or other conflicts of interest to report related to the content of this article.
References
- Buckley JR, Caiach SM. External fixation in comminuted upper femoral fractures. Injury. 1993; 24: 476-8.
- Tírico LE, Demange MK, Bonadio MB, Helito CP, Gobbi RG, Pécora JR. Medial Closing-Wedge Distal Femoral Osteotomy: Fixation With Proximal Tibial Locking Plate. Arthrosc Tech. 2015; 4: e687-95.
- Oh JK, Hwang JH, Varte L, Ko JH, Oh CW, Jung DY, et al. Locking plate in proximal tibial fracture: a correlation between the coronal alignment of tibia and joint screw angle. Yonsei Med J. 2013; 54: 720-5.
- Perren SM, Cordey J, Rahn BA, Gautier E, Schneider E. Early temporary porosis of bone induced by internal fixation implants. A reaction to necrosis, not to stress protection? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988: 139-51.
- Thamyongkit S, Abbasi P, Parks BG, Shafiq B, Hasenboehler EA. Weightbearing after combined medial and lateral plate fixation of AO/OTA 41-C2 bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: a biomechanical study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022; 23: 86.