Rapid Communication
Austin J Surg. 2016; 3(3): 1090.
Left Side Robotic Approach for Extended Thymectomy: Surgical Technique and Preliminary Experience
Pardolesi A* and Spaggiari L
Division of Thoracic Surgery, University of Milan School of Medicine, Italy
*Corresponding author: Pardolesi A, Division of Thoraci Surgery, European Institute of Oncology, University of Milan School of Medicine, Via Giuseppe Ripamonti 435, 20141 Milan, Italy
Received: September 14, 2016; Accepted: October 13, 2016; Published: October 19, 2016
Abstract
Background: Most published reports regarding minimally invasive approach for non invasive thymoma have focused on the right approach. In our early experience with robot-assisted thymectomies we adopted a left side three ports approach. We report our surgical technique for robotic extended thymectomy for early stage thymoma and early surgical outcome.
Method: We retrospectively reviewed all patients undergoing robotic thymectomy for clinical early-stage thymoma at the European Institute of Oncology, Milan Italy.
The preoperative work up included a Chest Computer Tomography scan and PET scan in all patients.
Results: From January 2010 to December 2015, 20 robotic extended thymectomies were performed. All patients were approached from the left side. There was no major post-operative complications only one case of atrial fibrillation (1 out of 20 patients).
Conclusion: The results of our initial experience showed that the left side robotic approach is a safe procedure and oncologically feasible for non-invasive thymomas.
Keywords: Human; Myasthenia gravis; Thymoma; Minimally invasive surgery; Robotic surgery; RATS
Introduction
Over the past 10 years video-assisted thoracoscopic approach, and more recently robot-assisted surgery, has replaced median sternotomy for resectable anterior mediastinal mass, including thymoma [1,2].
In our early experience with robot-assisted thymectomies we adopted a left side three ports approach. The left sided approach provide a clear view of the surgical field and the anatomical landmarks, phrenic nerves, in nominate vein and superior cava vein, are easily identifiable [3].
The aim of this “how to do it” is to describe our robotic extended thymectomy technique for early stage thymoma and to report early surgical outcome.
Surgical Technique
Patient selection
a. Nonthymomatous myasthenia gravis
b. Small (< 2cm) intrathymicthymoma
c. Large well encapsulated thymoma (preferably <4cm)
d. Minimally invasive thymoma
Patient positioning and port placement
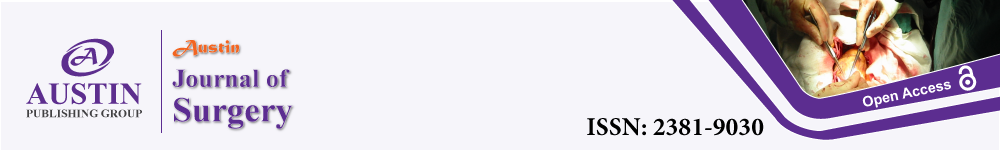
Under general anesthesia with double lumen intubation, patient is positioned in a 30 degree semi-supine position, left side up, with a roll placed under the left shoulder for a better left chest exposition. The right arm is right extended on a padded board. This approach allows access to the right side in case of need (Figure 1).
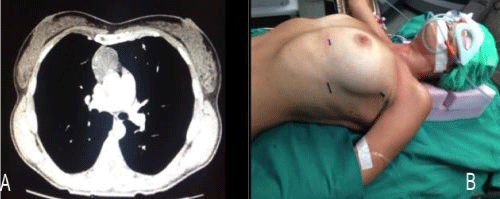
Figure 1: A) 4 cm thymoma. B) Patient positioning.
First incision (camera port) is generally performed in the fifth intercostals space at the anterior axillary line. The two “operative” ports are performed at the anterior axillary line in the third intercostals space and at the fifth intercostals space at the mid-clavicular line.
Operative steps
After performing the first incision (Camera port) the endoscope (12mm in diameter, 30° Lens) is inserted to explore the chest cavity and confirm that the lesion is resectable.
Under thoracoscopic view we perform the two operative ports. The daVinciTM Robotic System (Surgical Intuitive, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) is than introduced in the surgical field. The right robotic arm has a hook with electric cautery function to perform dissection, whereas the left arm has a Cadiereforceps (Endo Wrist; intuitive Surgical). We routinely use Ultracision (Ethicon) for dissection and for small vessels division.
Before proceeding with dissection, we start insufflating carbon dioxide (CO2) with a 6l/min flow and 8mmHg pressure.
Usually dissection starts from the inferior border at the pericardial reflection proceeding lateral to medial across the midline. When the right pleura and the right phrenic nerve are reached the dissection is directed cephalad parallel to the nerve. Once the pleural dissection has been completed in circumferential nature the thymus is mobilized and retracted laterally and dissected off of the underlying pericardium (Figure 2). The bilateral upper gland is than stripped down from the neck I order to reveal the thymic vein. The removed thymus and fat tissue is finally placed in a specimen bag and taken out.
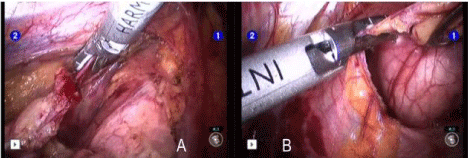
Figure 2: A) Thymic vein division with Ultracision device. B) Extended
thymectomy: dissection proceeds from left to right phrenic nerve.
At the end of the procedure we introduce a 24 or 28CH chest tube trough the operative port at the fifth intercostals space (Video 1).
Results
From January 2010 to December 2015, 20 robotic extended thymectomies were performed. All patients were approached from the left side. Mean age was 62 years (range 27-76 years); mean duration of surgery was 101 minutes (range 60 to 148 minutes).
Chest tube was always removed in the second post-operative day and mean duration of hospital stay was 2 days. There was no major post-operative complications only one case of atrial fibrillation (1 out of 20 patients).
Comment
Tips and considerations
The results of our initial experience showed that the three ports left side approach for the treatment early stage thymoma is a feasible and safe procedure and oncologically sound for non-invasive thymoma [3-5].
Robotic assisted thymectomy for thymoma should be generally confined to small intrathymic and encapsulated tumors as there are oncological concerns of possible breach of the tumor capsule with the risk of tumor seeding.
From our experience with robotic assisted, left side, approach we found some points that we fell enhanced the conduct of the operation and allow minimizing the risk of capsular breakage and tumor seeding:
- Well encapsulated tumors screened on CT scan thorax are ideal for robotic approach.
- Tumor >4 in diameter and radiological suspect of brachiocephalic vein invasion should be excluded.
- Tumor should be approached from the side of the tumor (right/ left approach) so that dissection is done under direct vision.
- The tumour should be dissected last using a no touch technique. The non tumorous part of the gland is always dissected first and used for grasping and traction.
The Robotic assisted extended thymectomyis “simple” and safe and facilitates mediastinal mass resection with no need of extra incisions. Dedicated instruments (robotic instruments that enabled precise instrument articulation and control) that articulate inside the chest cavity increase precision of dissection and reach any target inside the chest.
References
- Sugarbaker DJ. Thoracoscopy in the management of anterior mediastinal masses. Ann thorac Surg. 1993; 56: 653-656.
- Ng CS, Wan IY, Yim AP. Video-assisted thoracic surgery thymectomy: the better approach. Ann thoracic Surg. 2010; 89: S2135-S2141.
- Li Y, Wang J. Left-sided approach video-assisted thymectomy for the treatment of thymic diseases. World J Surg Oncol. 2014; 12: 398.
- Marulli G, Rea F, Melfi F, Schmid TA, Ismail M, Fanucchi O, et al. Robotaided thoracoscopic thymectomy for early-stage thymoma: a multicenter European study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012; 144: 1125-1130.
- Rea F, Marulli G, Bortolotti L, Feltracco P, Zuin A, Sartori F. Experience with the “da Vinci” robotic system for thymectomy in patients with myasthenia gravis: report of 33 cases. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006; 81: 455-459.