Research Article
Austin J Surg. 2022; 9(1): 1283.
Principles and Surgical Techniques in the Management of Intraoperative Retroperitoneal Vascular Injury
Yu F#, Jun Z#, Baohua Z#, Rui C, Kai D, Xiang F* and Lin-Hui W*
Department of Urology, Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China #Co-First Authors
*Corresponding author: Feng Xiang, Department of Urology, Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China
Wang Linhui, Department of Urology, Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China
Received: February 17, 2022; Accepted: March 12, 2022; Published: March 19, 2022
Abstract
Objective: To assess the surgical techniques and ideas in the treatment of the intraoperative retroperitoneal vascular injury.
Methods: Between Oct 2017 and Dec 2019, 85 retroperitoneal tumor patients with retroperitoneal vascular injury intraoperatively in Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University were analyzed retrospectively. Among them, the arterial injury occurred in 52 patients, the venous injury occurred in 49 patients, and 16 patients had both arterial and venous injuries. Main disease diagnosis, common types of vascular injury, different management methods, and results of vascular injury were analyzed.
Results: The most common type of diagnosis is a retroperitoneal primary malignant tumor, followed by metastatic malignant tumor and retroperitoneal benign tumor. The most frequent injury arteries were the aorta (12 patients) and common iliac artery (12 patients), followed by the external iliac artery (6 patients) and superior mesenteric artery (6 patients). The most frequent injury vein was inferior vena cava (10 patients), followed by internal iliac vein (7 patients), external iliac vein (6 patients), inferior mesenteric vein (6 patients), and common iliac vein (4 patients). A total of 19 patients received artificial vessels replacements, including aortic replacement (4 patients), renal artery replacement (1 patient), superior mesenteric artery (2 patients), common iliac artery (5 patients), external iliac artery (3 patients), inferior vena cava (1 patient), Right renal vein (1 patient), common iliac vein (1 patient) and external iliac vein (1 patient). The remaining patients underwent ligation and sutures to achieve hemostasis. All patients attained hemostasis in the operating room and were admitted to medical wards or the medical ICU. After artificial vessels replacements, one patient died of DIC postoperatively, other patients had an uneventful perioperative course, no anastomotic bleeding was reported.
Conclusion: In the management of intraoperative retroperitoneal vascular injury, it is important to assess the extent of injury, select reasonable remediation methods, and adopt artificial vessels replacements when necessary.
Keywords: Retroperitoneal sarcoma; Intraoperative; Complications; Surgical techniques
Introduction
Because the retroperitoneal area is characterized by rich soft tissue and little nerve distribution, patients with retroperitoneal tumors often have nonspecific clinical manifestations. While the vast majority of retroperitoneal tumors are poorly sensitive to radiation and chemotherapy as well as other adjuvant treatments, surgical resection is the most popular treatment for retroperitoneal tumors [1]. The retroperitoneal area harbors many important blood vessels including the abdominal aorta, inferior vena cava, renal arterioles, and veins, while primary malignant tumors of the retroperitoneum, primary benign tumors of the retroperitoneum, and other primary diseases of the retroperitoneum can invade the retroperitoneal vessels, which makes the operation difficult and carries the risk of blood vessel injury due to the possibility of intraoperative damage to the important blood vessels of the retroperitoneum [2]. Retroperitoneal metastatic malignancies, such as testicular, colorectal, urothelial cancer often develop retroperitoneal lymph node metastasis and are also prone to vascular injury when surgical dissection is performed [3,4]. Previously, although a small number of studies has reported the management methods of intraperitoneal large vessel injury, such as resection and replacement of inferior vena cava invasion [5], resection and replacement of abdominal aorta and iliac artery [6]. However, because the number of reported cases is relatively small, and clinical studies guiding physicians in preoperative planning and intraoperative management are lacking, this study focuses on analyzing the ideas and techniques for the management of intraoperative vascular injury in retroperitoneal tumors.
Materials and Methods
Study subjects
The clinical data of 85 patients who underwent retroperitoneal tumor surgery at Changhai Hospital affiliated with Navy Military Medical University from October 2017 to December 2019 were retrospectively reviewed, including 52 patients with arterial injury and 49 patients with venous injury, and 16 patients with both arterial and venous injuries. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Changhai Hospital affiliated with Navy Military Medical University, and all patients gave written informed consent (ethics number: chec2019-142)
Preoperative imaging
All patients had contrast-enhanced CT, 7 patients did not undergo contrast-enhanced MR because of contraindications such as the presence of intracorporeal implanted metal implants.
Surgical approach options
Eighty of the 85 patients included in this study underwent a median abdominal incision approach, 3 a subcostal oblique incision approach, and 2 a combined abdominosacral approach.
Processing techniques and materials of injured vessels
For vascular repair and vessel replacement, sutures with different specifications, such as 4-0 or 5-0, were selected based on suture vessel size and specific circumstances using specialized vascular instruments and proline or CV vascular sutures.
Analytical methods
Analysis of different vessel types of intraoperative injury, recapitulate management strategies for different vascular injuries, introduce vascular injury management techniques, and evaluate vascular injury management outcomes.
Results
Common disease diagnoses
The most common diagnostic category was primary malignancy of the retroperitoneum (44 patients), which mainly included soft tissue sarcoma, lymphoma, malignant pheochromocytoma; Followed by 24 cases of metastatic malignancies, including retroperitoneal metastases from colorectal malignancies or urinary tumors; And 17 cases of benign tumors of the retroperitoneum, such as ganglioneuroma or retroperitoneal fibrosis (Table 1).
Disease Category
Disease Name
Case
Primary malignant tumor
Soft tissue sarcoma
38
Lymphoma
2
Malignant pheochromocytoma
4
Metastatic malignant tumor
Colorectal cancer
8
Urothelial carcinoma
9
Testicular cancer
2
Adrenocortical carcinoma
3
Adenocarcinoma of unknown primary
2
Benign tumor and disease
Ganglioneuroma
15
Retroperitoneal fibrosis
1
1
Total
85
Table 1: Types of diagnosis in retroperitoneal operation.
Common injury vessel types
The most commonly injured arteries during surgery in the retroperitoneal region were the aorta (12 patients), common iliac (12 patients), and external iliac (6 patients), superior mesenteric (6 patients), internal iliac (5 patients), and renal arteries (3 patients) (Table 2).
Artery
Replacement
Repairment
Ligation
Total
Aorta
4
8
0
12
Renal Artery
1
2
0
3
Superior Mesenteric Artery
2
4
0
6
Common Iliac Artery
5
7
0
12
External Iliac Artery
3
3
0
6
Internal Iliac Artery
0
2
3
5
Celiac Trunk (branches)
0
3
0
3
Inferior Mesenteric Artery
0
0
5
5
Total
15
29
8
52
Table 2: Types and treatments of injury arteries.
The most commonly injured veins were the inferior vena cava (10 patients), common iliac vein (4 patients), external iliac vein (6 patients) and internal iliac vein (7 patients), inferior mesenteric vein (6 patients), splenic vein (4 patients), left renal vein (3 patients), and right renal vein (4 patients) (Table 3).
Vein
Replacement
Repairment
Ligation
Total
Inferior Vena Cava
1
8
1
10
Right Renal Vein
1
3
0
4
Left Renal Vein
0
2
1
3
Superior Mesenteric Vein
0
0
5
5
Common Iliac Vein
1
3
0
4
External Iliac Vein
1
3
2
6
Internal Iliac Vein
0
3
4
7
Splenic Vein
0
4
0
4
Inferior Mesenteric Vein
0
0
6
6
Total
4
26
19
49
Table 3: Types and treatments of injury veins.
Management outcomes of injured vessels
A total of 19 patients underwent prosthetic vessel replacement, including 4 with aortic replacement, 1 with renal artery replacement, 2 with superior mesenteric artery, 5 with common iliac artery, 3 with external iliac artery, 1 with inferior vena cava, 1 with right renal vein, 1 with common iliac vein, and 1 with external iliac vein. All patients had smooth hemostasis in the operating room, all patients had smooth admission to the ICU or the recumbent ward, after artificial vascular replacement, all patients smoothly spent the perioperative period, and no postoperative complications such as bleeding from vascular anastomoses occurred, but 1 patient died due to DIC after operation, and the remaining patients were discharged from hospital smoothly (Figure 1).
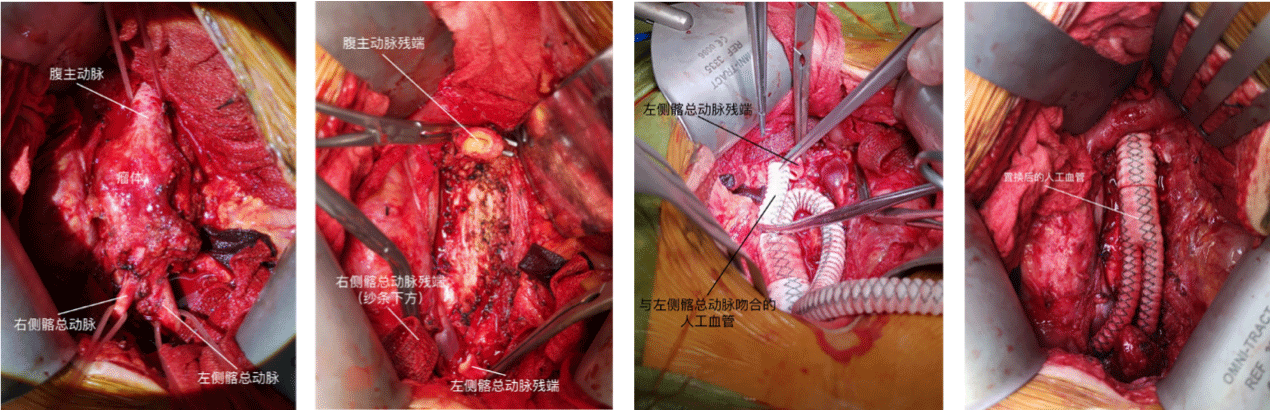
Figure 1: Artificial vessels replacements of the aorta and bilateral iliac arteries after the vascular injury during the operation of retroperitoneal metastatic malignant
tumor.
Processing techniques and materials of injured vessels
For vascular repair and vessel replacement, sutures with different specifications, such as 4-0 or 5-0, were selected based on suture vessel size and specific circumstances using specialized vascular instruments and proline or CV vascular sutures.
Vascular repair techniques and methods
When vascular injury was mild, suturing with vascular sutures could be employed, with suturing essentials including evenly selecting the entry point along the circumference of the injury point with a 1mm-2mm spacing, slowly adducting the line after each needle was withdrawn, simply pulling the pair gently to start suturing, and never tightening it with force. When the tissue to be sutured was slightly more and was able to withstand a certain amount of tensile force, slowly tightened again. If the vessel defect exceeded 1cm, reverse suturing could reduce tension.
Artificial vessel replacement techniques and methods
Artificial vessels were often used for replacement when repair was not possible or when the vessel needed to be removed because it was too widely invaded. When replacing, it was firstly important to design the location of the anastomosis, which usually requires reserving an approximately 1cm free space on the distal and proximal ends of the vessel to be anastomosed, trying to free the anastomotic surface sufficiently for better access. Secondly, to plan the length and path of the artificial vessels that need to be replaced, avoiding being influenced by other organs in the abdomen.
Discussion
The key points for successful management of vascular injury are as follows: comprehensive and careful preoperative assessment, reasonable incision selection and adequate exposure, maintaining a calm mind, accurately judging the degree of hemorrhagic vascular injury, reasonable choice of surgical method, and skilled suturing basic work.
Preoperative evaluation
At present, the diagnosis of retroperitoneal tumor mainly relies on imaging examination, different examination methods are selected according to the patient’s specific situation, it is vital to ultimately obtain more precise diagnosis, and to make an individualized surgical plan according to the perfect examination results. CT has imaging characteristics such as little interference from intestinal gas, bone, and adipose tissue, high resolution, no overlap with other images, and can accurately localize the lesion site, size, morphology, and visceral involvement with surrounding tissues, while contrastenhanced scanning can further show the relationship between the tumor and surrounding organs and blood vessels [7]. But in practical application, for some large retroperitoneal tumors, the localization of CT can be very difficult [8]. Enhanced MRI examination could be combined to further clarify the diagnosis of retroperitoneal tumor [9]. All patients included in this study were evaluated preoperatively with either contrast-enhanced CT or contrast-enhanced MRI so that the location of the tumor, the vessel at which site of invasion and the severity of the disease could be determined to facilitate the choices of surgical incision sites, surgical instruments, and repairment methods after vascular injury.
Choice of intraoperative surgical incision
Since the majority of patients were in advanced or relapse stage, and their retroperitoneal tumors were generally larger and the extension of the involvement was wide at admission, adequate exposure of the surgical field is one of the keys in determining the success of surgery for retroperitoneal tumors involving large vessels. Skin incisions are mostly performed with a median abdominal incision, which allows for extended incisions up or down as needed intraoperatively to achieve adequate exposure. Fewer and fewer surgeons now choose rectus abdominis incision because both the superior or inferior epigastric artery and splanchnic branches communicate, which may affect collateral circulation function if the ventral process injures the superior or inferior epigastric artery. If the tumor is located in the basin, an abdominosacral or abdominoperineal approach may be considered [10], the incision can be selected depending on the location of the tumor: for example, adrenal, renal, epigastric tumors or tumors involving the upper end of the inferior vena cava, an oblique incision below the costal margin may be chosen intraoperatively; Of course, for smaller retroperitoneal tumors, the extraperitoneal approach can be chosen for surgery, which is able to reduce the effect of surgery on abdominal viscera, and achieve the goal of rapid recovery, but the extraperitoneal route has narrow space, this adds to the technical difficulty of the operation. With the development of science and technology, the surgical approach is also not limited to open surgery; maruyamat et al considered that tumors with a volume less than 10 cm and a clear boundary with the surrounding can be treated with minimally invasive surgery [11]. Minimally invasive surgery offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, such as faster recovery, less trauma, and shorter hospital stay.
Management of intraoperative vascular injury
Firstly, retroperitoneal large vessel injury is often accompanied by massive hemorrhage, and the most important thing is to judge whether the bleeding vessel is the rupture or broken of a large vessel, or other small arterioles and veins. The choice of an appropriate surgical approach can only be made with an accurate judgment of the source of the bleeding; Only with an accurate judgment of the extent of vascular injury can one determine whether the repair suture or the vascular replacement is followed.
Try not to coagulate hemostasis when encountering injured small vessels, injured small vessels should be sutured. Partial transverse eversion suture should be tried when suturing damaged vessels, as longitudinal sutures can predispose to vessel stenosis. In principle, the diameter of the lumen after suturing cannot be less than onehalf of normal, so that it can avoid creating inadequate blood supply or increasing the risk of thrombosis. Local heparinization can be performed simultaneously during the suture to reduce thrombosis; blind clamping should be avoided during the suture, which can damage the vessel wall, and moist the suture when knotting to reduce the damage to the vessel. Because retroperitoneal tumors have the characteristics of invasive growth, if the surgical field is not good due to persistent bleeding caused by inadvertent injury of blood vessels during separation, gauze compression can be given for hemostasis; if the involved blood vessels of the tumor need to be removed, vascular occlusion bands can be placed in advance in the upper and lower positions of the abdominal aorta, veins and other blood vessels, and the occlusion band can be lifted to control bleeding during massive hemorrhage. For some giant retroperitoneal tumors, piecemeal resection can be performed when en bloc resection is difficult, thereby improving the safety of surgery and reducing intraoperative bleeding; so that some seemingly unresectable tumors can eventually be removed and the prognosis is not significantly different from that of en bloc resection [12], and it is necessary to change the surgical strategy in time to obtain more complete resection [13].
Secondly, because retroperitoneal tumors often enwrap blood vessels, it is necessary to identify what kind of vascular injury that occurs during surgery. Arterial: Repair or graft replacement is necessary when the aorta, common iliac artery, external iliac artery, celiac trunk, renal artery, and superior mesenteric artery are injured. In this study, there were 4 patients with aortic replacement and 8 patients with repair. There was 1 case of artificial blood vessel replacement and 2 cases of repair in patients with renal artery injury. Patients with superior mesenteric artery injury were relatively critical cases in this study. Because the superior mesenteric artery plays a crucial role, and there is a possibility of intestinal necrosis after vascular injury, it is necessary to complete the reconstruction as soon as possible. In patients with injury to the unilateral internal iliac artery and inferior mesenteric artery, ligation and hemostasis can be used as a salvage option when repair fails. In the present study, five patients with inferior mesenteric artery injury did not receive vascular reconstruction, but ligation was chosen for hemostasis. Venous: When the inferior vena cava and renal vein are injured, repair is tried first. When the repair is unsuccessful, most cases need reconstruction; when the unilateral common iliac artery is injured, reconstruction should also be performed as far as possible. If reconstruction failed, it may lead to unilateral lower limb edema. However, if the iliac vein is compressed due to tumor invasion and other reasons, ligation and hemostasis can be selected; when the left renal vein is injured, it can be selected not to be reconstructed when difficult, due to the presence of certain collateral circulation in the left renal venous system. In addition, organ resection can be performed when some vessels show severe injury, and resection of the spleen can be selected as an option if splenic artery injury occurs.
In summary, the key to management of vascular injury in retroperitoneal surgery lies in the extent and location of tumor involvement; preoperative imaging data need to be evaluated in detail to facilitate the reasonable selection of surgical incision and the evaluation of the degree of intraoperative vascular injury; the methods to deal with intraoperative retroperitoneal vascular injury needs to be reasonably selected according to the type and degree of the injury, the surgeon’s surgical experience, and surgical proficiency. If the tumor surrounds the blood vessels, in order to completely remove the tumor and reduce the possibility of recurrence, it is important to resect the tumor and use artificial blood vessel replacement when necessary.
References
- Van Dalen T, Hennipman A, Van Coevorden F, et al. Evaluation of a clinically applicable post-surgical classification system for primary retroperitoneal softtissue sarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2004; 11: 483-490.
- Schwarzbach MH, Hormann Y, Hinz U, Leowardi C, Böckler D, Mechtersheimer G, et al. Clinical results of surgery for retroperitoneal sarcoma with major blood vessel involvement. J Vasc Surg. 2006; 44: 46-55.
- Albany C, Kesler K, Cary C. Management of Residual Mass in Germ Cell Tumors after Chemotherapy [J]. Current oncology reports. 2019; 21: 5.
- Syan-Bhanvadia S, Bazargani ST, Clifford TG, et al. Midline Extraperitoneal Approach to Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection in Testicular Cancer: Minimizing Surgical Morbidity [J]. European urology. 2017; 72: 814-820.
- Niebisch S, Staab H, Ullrich S, et al. Retroperitoneal space-occupying lesion with displacement of the inferior vena cava [J]. International journal of surgery case reports. 2019; 57: 170-174.
- KL Mattox, JM Burch, R Richardson, et al. Retroperitoneal vascular injury. Surg Clin North Am. 1990; 70: 635-653.
- Mizuki Nishino, Katsumi Hayakawa, Manabu Minami, et al. Retroperitoneal cystic masses: CT, clinical, and pathologic findings and literature review. Radiographics. 2003; 23: 45-57.
- Prabhakar Rajiah, Rakesh Sinha, Carlos Cuevas, et al. Imaging of uncommon retroperitoneal masses. Radiographics. 2011; 31: 949-976.
- Nishino M, Hayakawa K, Minami M, Yamamoto A, Ueda H, Takasu K. Primary retroperitoneal neoplasms: CT and MR imaging findings with anatomic and pathologic diagnostic clues. Radiographics. 2003; 23: 45-57.
- T Susini, G Taddei, D Massi. Giant pelvic retroperitoneal liposarcoma. Obstet Gynecol. 2000; 95: 1002-1004.
- Maruyama T, Sugamoto Y, Miyagishima D, et al. Laparoscopic resection of a retroperitoneal schwannoma located in the hepatic hilus [J]. Surgical case reports. 2015; 1: 18.
- Gronchi A, Miceli R, Colombo C, et al. Frontline extended surgery is associated with improved survival in retroperitoneal low- to intermediategrade soft tissue sarcomas [J]. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23: 1067-1073.
- Olimpiadi Y, Song S, Hu JS, et al. Contemporary Management of Retroperitoneal Soft Tissue Sarcomas [J]. Current oncology reports, 2015; 17: 39.