Case Report
Austin J Surg. 2022; 9(1): 1286.
Primary Hydatid Cyst of Gluteal Muscle, an Anusual Location: A Case Report and a Literature Review
Lamghari M, Aboulfeth EM, Sabur M, Maazouz A, Azzoui IE, Najih M, Kaoui HE and Bounaim A*
Department of Visceral Surgery, Mohammed Military Hospital, Rabat, Morocco
*Corresponding author: Ahmed Bounaim, Head of Department, Department of Visceral Surgery, Mohammed Military Hospital, Rabat, Morocco
Received: July 04, 2022; Accepted: August 01, 2022; Published: August 08, 2022
Abstract
Introduction: Hydatid disease is a zoonosis caused by an infection with the larvae of the tapeworm echinococcus granulosus, it mostly involves liver and lungs but it may exceptionally affect muscle.
Case Report: we report the case of a 22 years old man who was admitted to our surgical clinic with a primary hydatid cyst in gluteal muscle diagnosed by clinic examination, imaging and serological testing. The treatment was a complete pericystectomy and chemotherapy by antiparasit drugs.
Discussion: Hydatid disease it‘s an endemic disease in sheep-producing regions, In human, this disease involves usually the liver and the lungs and exceptionally the muscle. The diagnosis may be challenging, as it should consider arguments such as history, physical examination, imaging and serological testing.
The best treatment is pericystectomy with perioperatory chemotherapy to reduce risk of occurrence.
Conclusion: The hydatid cyst of gluteal muscle is exceptional even in endemic area, the diagnosis may be challenging and the surgery is the gold standard of treatment.
Keywords: Hydatid cyst; Gluteal muscle; Perikystectomy
Introduction
Hydatid disease is a zoonosis caused by an infection with the larvae of the tapeworm echinococcus granulosus, it‘s an endemic disease in sheep-producing regions of southern Europe, Mediterranean, Africa, Australia, Asia and the Middle East. It mostly involves liver and lungs, but it can appear anywhere in the body, the primary and isolated muscle location of echinococcosis remains exceptional.
Investigations using serological test and imaging modalities do not provide formal arguments but only a presumptive diagnosis. Only histopathological examination can deliver a definitive diagnosis [1].
We report an unusual location of this condition: a hydatid cyst of the gluteal muscles which illustrates well the diagnostic challenge and the treatment’s modality of this pathology.
Case Report
A 22 years old man, who lived in rural Moroccan area, with no medical history presented to our surgical clinic for a slowly growing swelling mass in his left gluteal area which appeared 3 years ago with no fever or weight loss.
Physical examination found a patient in good general condition, presenting a 13 cm diameter mobile masse in his upper lateral quadrant of the left gluteal without erythema, tenderness or warmness. Neurological examination was normal and nodes areas were free.
Ultrasound revealed a round, anechoic, well-circumscribed, 15x13 x9 cm cyst lesion with a thick wall and posterior reinforcement. CTscan showed in the medius gluteus muscl a well-defined hypodense and homogenous multivesicular cyst measuring 15x10x9 cm with cortical destruction of the iliac bone, suggested a cyst lymphangioma or hydatid cyst (Figures 1a & 1b).
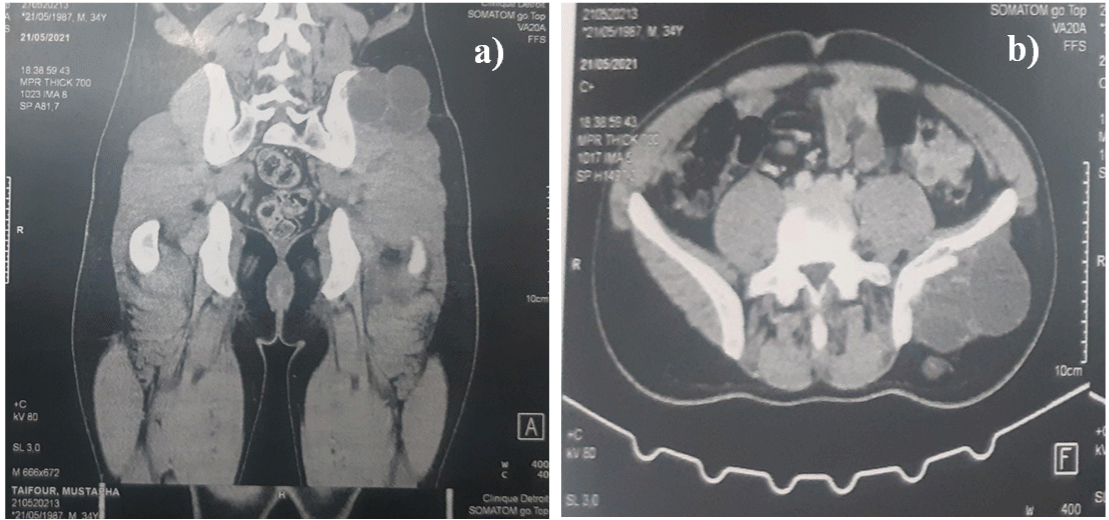
Figure 1: a), b) CT-scann image showing the hydatid cyst of the gluteal
muscle.
Thoraco-abdominal CT-scan did not show other location and hydatid serological test was positive.
Surgical treatment was planned under general anesthesia, a complete pericystectomy was performed with protection of the surgical field by draps soaked wit
H hypertonic saline (Figures 2a & 2b).
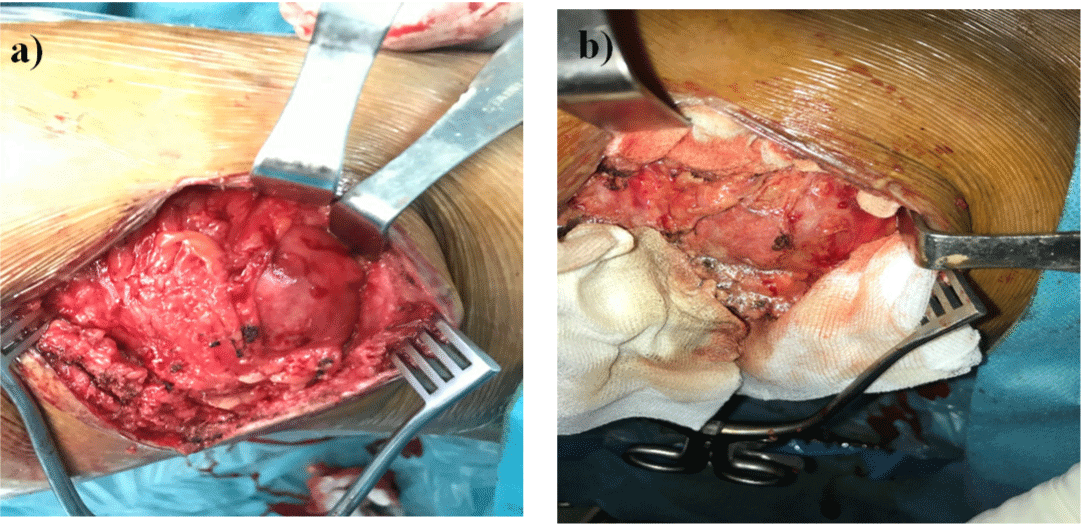
Figure 2: a), b) Opreatory image of the hydatid cyst in gluteal muscle.
Outcomes were uneventful though the patient was discharged 2 days after on albendazol for three months to prevent local recidive. Histological examination established the diagnosis of hydatic cyst.
A 2 years control examination found no sign of recidive and serological statut remains negative.
Discussion
Hydatidosis is an endemic disease in sheep-producing regions of southern Europe, Mediterranean, Africa, Australia, Asia and the Middle East [1]. In human, the liver is the most common site of cyst development, followed by lungs and much less commonly kidneys, spleen brain and soft tissue [3].
Muscular involvement is usually seen as secondary location of liver or lung’s hydatid cyst. However, it may be rarely seen as primary location even in endemic countries (2,3%) [3-5]. This atypical location may affect musculature of the chest wall, pectorals major, Sartorius quadriceps and exceptionally gluteus muscle [6-9].
Dog is the final host of Echinococcus Granulosis, and the sheep is the intermediate host, human may be infested by ingestion of the taeniae’s eggs contained in the feces of dogs, after ingestion, the eggs will be absorbed in the human intestine and pass into the portal system. The liver and the lung are considered as a filter of the venous system making the extra hepato-pulmonary location very uncommon [10].
The exceptional muscular involvement can be also explained by the high lactic level in muscle tissue, unfavorable for parasite survival and the muscular contraction that prevent fixation of larvae of the tissue [11].
Clinically, the muscular hydatid disease is often asymptomatic, it may be manifested as a painless slow-growing mass with normal overlying skin in patient with a good overall general condition like it was in our case. These nonspecific symptoms can simulate lipoma, hematoma, abscess or tumor. Which make the diagnosis of hydatid cyst in gluteal muscle very difficult, especially in patient without history of liver or lung location [12-15].
The diagnosis of hydatid cyst in muscle may be challenging, as it should consider arguments such as history, physical examination, imaging and serological testing. This diagnosis should be suspected in patients with history of dog’s contact and who are living in sheepraising or rural area [16].
Positivity of serological test can be useful in diagnosis but it’s inconstant because of frequency of false positive up to 50% of cases [17], however it may be helpful for patients follow up if it was initially positive [18]. In our case serological testing became negative throughout 2 years after surgery.
Ultrasound is the first line imaging exam with a sensitivity of 95 % in typical cases. It can detect the cyst membrane septa and hydatid sand. Ultrasonographic diagnosis can be difficult in solid, mixed or pseudotumoral lesion [19]. CT scan is not much superior in diagnosis than ultrasound in these locations however it can identify associated bone’s lesion and calcification with daughter cysts.
Magnetic resonance imaging is the gold standard of giant cyst even if it’s so expansive, it may evaluate with high performance the size of the cyst, the relationship with adjacent tissue and neurovascular structures [20]. In our case we didn’t perform MRI as the cyst was typical in US and CT scan.
Ultrasound or CT-scan guided needle biopsy can be helpful for diagnosis [21]. We believe as like some authors that’s not recommended because of the risk of cyst rupture and anaphylactic reaction [22].
Surgical removal of the cyst and chemotherapy by antiparasit drugs are the treatment of muscle’s hydatidosis [23,24]. Before surgery it’s recommended to search other locations especially in the lungs because of the risk of rupture after general anesthesia [25].
The best technic is the pericystectomy without opening the cyst and protection of surrounding tissue by hypertonic saline to reduce the risk of occurrence [26].
Conclusion
The hydatid cyst of gluteal muscle is exceptional even in endemic area, it must be considered in front of any cystic mass especially when associated with other location. Diagnosis is very difficult in isolated forms. Pericystectomy with perioperatory chemotherapy is the best treatment to reduce risk of occurrence.
References
- Jan Z, Zeb S, Shoaib A, Ullah K, Muslim M, Anjum H, et al. Hydatid cyst involving right pectoralis majormuscle: a case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019; 58: 54-6.
- Combalia A, Sastre-Solsona S. Hydatid cyst of gluteus muscle. Two cases. Review of the literature. Joint, bone, spine : revue du rhumatisme. 2005; 72: 430-432.
- Lorenzetti L. Contribution to the knowledge of primary echinococcosis of the muscles. Gazz Int Med e Chir. 1962; 67:2775-95.
- Sakka SA. Primary hydatic cyst of the thigh has painful manifestation at the hip about a case and review of the literature. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Word. 1993; 79: 226-8.
- AlouiniMekki R, MhiriSouei M, Allani M, et al. Hydatic soft tissue kyste: MRI input. J Radiol. 2005; 86: 421-5.
- Alvarez-Sala R, Terreros FJGD, Caballero P. Echinococcus cyst as a cause of chest wall tumor. The Annals of thoracic surgery. 1987; 43: 689-690.
- Abdel-Khaliq RA, Othman Y. Hydatid cyst of pectoralis major muscle. Case report and note on surgical management of muscleechinococcosis. Acta Chir Scand. 1986; 152: 469-71.
- Rask MR, Lattig GJ. Primary intramuscular hydatidosis of the sartorius. Report of a case. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume. 1970; 52: 582-584.
- Ozkoc G, Akpinar S, Hersekli MA, Ozalay M, Tandogan R. Primary hydatid disease of the quadriceps muscle: a rare localization. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2003; 123: 314-6.
- Saidi F. Surgery of Hydatid Disease. London: WB Saunders Co. 1976; 31-59.
- Orhan Z, Kara H, Tuzuner T, Sencan I, Alper M. Primary subcutaneous cyst hydatic disease in proximal thing: an unusual localisation: a case report. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2003; 4: 25.
- Chigot JP, Ben Hamida M, Mercadier M. About a case of muscle hydatic cyst. Gaz Med Fr. 1974; 81: 5313-7.
- Meunier Y, Danis M, Nozais JP, et al. Muscle Hydatidosis about two cases. Sem Hop. 1983; 59: 2785-6.
- Mseddi M, Mtaoumi M. Dahmene. Muscle hydatic cyst. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2005; 91: 267-71.
- Emy P, Lebas P, Master F, et al. Muscle hydatic cyst insulates from the abdominal wall. Rev Med Intern. 1989; 10: 152-3.
- Durakbasa CU, Tireli GA, Sehiralti V, Sander S, Tosyali AN, Mutus M. An audit on pediatric hydatid disease of uncommon localization: incidence, diagnosis, surgical approach and outcome. J Pediatr Surg. 2006; 41: 1457- 1463.
- Kammerer WS, Schantz PM. Echinococcal disease. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1993; 7: 605-18.
- Stojkovic M, Rosenberger K, Kauczor H, Junghanss T, Hosch W. Diagnosing and Staging of Cystic Echinococcosis: How Do CT and MRI Perform in Comparison to Ultrasound?. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 2012; 6.
- Thursky K, Torresi J. Primary muscle hydatidosis of the thigh: management of a complicated case with combination adjunctive albendazole and praziquantel chemotherapy. Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2001; 32: e65-e68.
- Von Sinner WN. New diagnostic signs in hydatid disease; radiography, ultrasound, CT and MRIcorrelated to pathology. Eur J Radiol. 1991; 12: 150- 159..
- Filice C, Perri GD, Strosselli M, Pirola F, Brunetti E, Dughetti S, et al. Parasitologic findings in percutaneous drainage of human hydatid liver cysts. The Journal of infectious diseases. 1990; 161: 1290-1295.
- Ozkoc G, Akpinar S, Hersekli MA, Ozalay M, Tandogan R. Primary hydatid disease of the quadriceps muscle: a rare localization. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2003; 123: 314-6.
- Ormeci N, Idilman R, Akyar S, Palabiyikoglu M, Coban S, Erdem H, et al. Hydatid cysts in muscle: a modified percutaneous treatment approach. International journal of infectious diseases: IJID: official publication of the International Society for Infectious Diseases. 2007; 11: 204-208.
- Ferrandez HD, Gomez-Castresana F, Lopez-Duran L, Mata P, Brandau D, Sanchez-Barba A. Osseous hydatidosis. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume. 1978; 60: 685-690.
- Hammami T, Noomane F, Ketata M, Ganneme Y, Nasr M, Zouari K et al. Hydatid cyst of the thigh: three cases. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2002; 88: 193-196..
- Kazakos CJ, Galanis VG, Verettas DAJ, Polychronidis A, Simopoulos C. Primary Hydatid Disease in Femoral Muscles. Journal of International Medical Research. 2005; 33: 703-706.
- Bonitacino A, Carino R, Caratozzolo M. L’e´chographie dans l’hydatidose. Symposium international sur l’hydatidologie. Med Chir Dig. 1989; 18: 301-12.