Case Report
Austin J Surg. 2022; 9(3): 1293.
Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Peritoneum: An Unusual Location of A Rare Tumor
Lamghari M, Azzaoui IE, Sabur M, Aboulfeth EM, Najih M, Moujahid M, Bonchentouf SM, Kaoui HE and Bounaim A*
Department of visceral Surgery 1, Mohammed Military Hospital, Rabat, Morocco
*Corresponding author: Ahmed BounaimHead of Department, Department of visceral Surgery 1, Mohammed Military Hospital, Rabat, Morocco
Received: November 07, 2022; Accepted: December 15, 2022; Published: December 21, 2022
Abstract
Introduction: SFT is an uncommon tumor representing 3, 7% of all soft tissue sarcomas and mesenchymal tumor. The most common location is pleura followed by the abdomen.
Case Report: A 68 years old male patient was admitted to our department with abdominal pain and a mobile masse in his abdominal hypogastric area. CT-scan showed a well-defined mass with vividly homogenous enhancing features in both the arterial and venous phases. A complete resection of the tumor was performed thought a median sub-ombilical laparotomy. The histological examination showed a fibroblastic mesenchymal tumor with expression of CD34, CD99 and Bcl2 in the immunohistochemical study that is specific of the solitary fibrous tumor.
Discussion: SFT are anatomically ubiquitous mesenchymal tumors developed from fibroblasts. It is an uncommon tumor represents 3, 7% of all soft tissue sarcomas and mesenchymal tumors. The most common location is the pleura followed by the abdomen. Clinically, abdominal SFT is usually manifest as abdominal fullness, gastrointestinal obstruction, weight loss, jaundice, fever, or hypoglycemia. Immunohistochemistry, the cell of the SFT typically express the following markers: CD34, CD99 and Bcl2. Complete surgical removal of the tumor is the gold standard treatment which can be completed by adjuvant radiotherapy.
Conclusion: Primary SFTs in the peritoneum are extremely uncommon. Clinical symptoms and imaging manifestations are nonspecific whish make the diagnosis difficult. Treatment includes surgical resection, embolization therapy, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and anti-angiogenic agents.
Keywords: Solitary fibrous tumor; Peritoneum; Resection; Immunohistochemistry
Introduction
SFT is an uncommon tumor representing 3, 7% of all soft tissue sarcomas and mesenchymal tumor [1]. This neoplasm can present anywhere throughout the human body and has high risk of malignant transformation, the most common location is pleura followed by the abdomen [2,3].
SFT is usually presents as slow growing mass, its clinical symptoms are caused by local compression or metastasis [4-6] and its typically appears as a hypervascular tumor on CT-scan [7,8].
The commonest treatment is complete surgical excision which can be completed by radiotherapy [9].
Case Report
A 68 years old male patient was referred to our surgical department with abdominal pain without any transit disorder or digestive hemorrhage. Physical examination found a patient in good general condition, presenting a 20 diameter mobile masse in his abdominal hypogastric area.
The patient underwent an abdominal ultrasound, which revealed a well-defined and hyperechoic masse in the pelvic. CT-scan showed a well-defined mass measuring 27 x 19 cm, after contrast injection the mass presented with vividly homogenous enhancing features in both the arterial and venous phases, the appearance of this peritoneal tumor indicated benign behavior with no invasive sings or invasion of neighborhood organs (Figure 1).
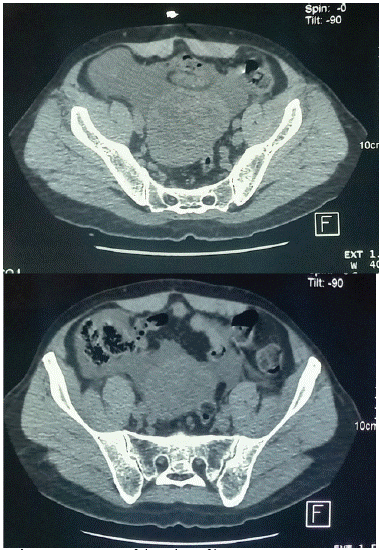
Figure 1: CT images of the solitary fibrous tumor
Surgical treatment was planned under general anesthesia, a complete resection of the tumor was performed thought a median sub-ombilical laparotomy (Figures 2). Outcome were uneventful and the patient was discharged 2 days after. Histological examination showed a fibroblastic mesenchymal tumor with expression of CD34, CD99 and Bcl2 in the immunohistochemical study that are specific of the solitary fibrous tumor. 18 months of surgery, the patient remained free of occurrence.
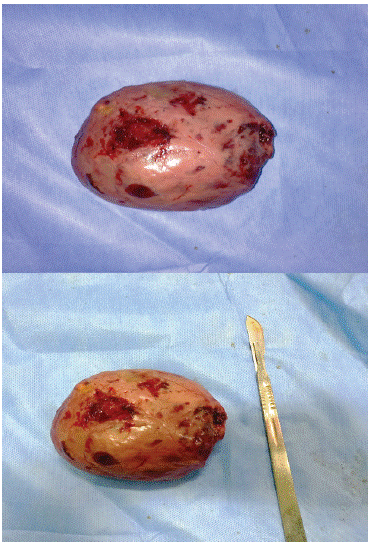
Figure 2: Postoperative images of the solitary fibrous tumor.
Discussion
First described by Klemperer and Rabin in 1931, SFT are anatomically ubiquitous mesenchymal tumors developed from fibroblasts. Subdivided by the fifth edition of the WHO classification of fibroblastic/myelofibroblastic tumors into benign, intermediate and malignant, they have the same clinical, histological, immunohistochemical and radiological characteristics regardless of their location. It is an uncommon tumor represent 3, 7% of all soft tissue sarcomas and mesenchymal tumors [1,10].
SFT occurs in patients during the 5th and 6th decades with no gender predilection. The most common location is the pleura followed by the abdomen. Pleural involvement is usually seen in older patients (56-60 years old) but abdominal location is seen in younger patients (fourth decade) [2,3].
Immunohistochemistry, the cell of the SFT typically express the following markers: CD34, CD99 and Bcl2 [11]. However, anti-STAT6s is a new marker more specific for the diagnosis and rarely positive in other types of tumors [12].
Clinically, abdominal SFT is usually manifest as abdominal fullness, gastrointestinal obstruction, weight loss, jaundice, fever, or hypoglycemia [4-6]. These symptoms are the result of adjacent organs compression by the tumor or the overproduction of insulin-like growth factor-2 (Doege-Potter syndrome) [13-15].
Computed Tomography (CT) is the first line imaging exam. It can show SFT as a well-circumscribed, hypervascular masses containing necrosis zone or calcification, with compression of nearby organs [7,8]. On Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) SFT has intermediate signal intensity on T1-weighted images and heterogeneous low signal intensity with flow voids on T2-sequence. However, central focus of heterogeneity and variable contrast enhancement on CT or MRI are signs of malignancy [16].
Complete surgical removal of the tumor is the gold standard treatment. In case of positive margins (R1/R2), a second resection should be discussed. Otherwise, adjuvant radiotherapy is a reasonable option. Conservative attitude may be adopted in selected cases to preserve organ function when postoperative RT can be delivered, given a favorable long-term outcome.
Neoadjuvant RT may be an option in specific cases to improve tumor respectability or when wound complications are a concern [9].
No prospective study is available on the activity of chemotherapy activity in SFT [17].
Angiogenesis is an important feature involved in tumor growth and metastatic spread of SFT. Therefore, inhibition of angiogenesis pathways has been suspected to be a key therapeutic target to inhibit tumor cell proliferation. Given the angiogenic properties of FSTs, several case reports and clinical trials have investigated various angiogenesis inhibitors with promising activity in FSTs [9].
After complete resection, these tumors show a good prognosis, and the 10-year overall survival is in the order of 54% to 89%. However, recurrence may occur in 10% to 25% of the cases at 10 years [18,19] and it is more frequent in cases of incomplete resection (R1/R2) [20]. The risk of 5-year metastatic recurrence in lung, liver and bone is up to 40% in high-risk patients with criteria for malignancy as large size, dissemination at presentation, pleomorphism, necrosis, and a mitosis rate = 4 per 10 high-power fields [20-23].
Conclusion
In conclusion, primary SFTs in the peritoneum are extremely uncommon. Clinical symptoms and imaging manifestations are nonspecific. Therefore, the diagnosis of SFTs can be challenging and relies on histological and immunohistochemical study. Treatment includes surgical resection, embolization therapy, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and anti-angiogenic agents.
References
- De Pinieux G, Karanian M, Le Loarer F, Le Guellec S, Chabaud S, Terrier P, et al. Nationwide incidence of sarcomas and connective tissue tumors of intermediate malignancy over four years using an expert pathology review network. PLoS One. 2021; 16: e0246958.
- Kim JM, Choi Y La, Kim YJ, Park HK. Comparison and evaluation of risk factors for meningeal, pleural, and extrapleural solitary fibrous tumors: A clinicopathological study of 92 cases confirmed by STAT6 immunohistochemical staining. Pathol - Res Pract. 2017; 213: 619–25.
- Ronchi A, Cozzolino I, Zito Marino F, Accardo M, Montella M, Panarese I, et al. Extrapleural solitary fibrous tumor: A distinct entity from pleural solitary fibrous tumor. An update on clinical, molecular and diagnostic features. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2018; 34: 142–50..
- Guglielmi A, Frameglia M, Iuzzolino P, Martignoni G, De Manzoni G, Laterza E, et al. Solitary fibrous tumor of the liver with CD 34 positivity and hypoglycemia. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1998; 5: 212–6.
- Vennarecci G, Ettorre GM, Giovannelli L, del Nonno F, Perracchio L, Visca P, et al. Solitary fibrous tumor of the liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2005; 12: 341–4.
- Chithriki M, Jaibaji M, Vandermolen R. Solitary fibrous tumor of the liver with presenting symptoms of hypoglycemic coma. Am Surg. 2004; 70: 291–3.
- Chun HJ, Byun JY, Jung SE, Kim KH, Shinn KS. Benign solitary fibrous tumour of the pre-sacral space: MRI findings. Br J Radiol. 1998; 71: 677–9.
- Kinoshita T, Ishii K, Higashiiwai H, Naganuma H. Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumour of the Peritoneum: Case Reports. Clin Radiol. 2000; 55: 157–60.
- De Bernardi A, Dufresne A, Mishellany F, Blay JY, Ray-Coquard I, Brahmi M. Novel Therapeutic Options for Solitary Fibrous Tumor: Antiangiogenic Therapy and Beyond. Cancers (Basel). 2022; 14: 1064.
- Kallen ME, Hornick JL. The 2020 WHO classification: What’s new in soft tissue tumor pathology? Am J Surg Pathol. 2021; 45: 1–23.
- Yoshida A, Tsuta K, Ohno M, Yoshida M, Narita Y, Kawai A, et al. STAT6 immunohistochemistry is helpful in the diagnosis of solitary fibrous tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014; 38: 552–9.
- Geramizadeh B, Marzban M, Churg A. Role of immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis of solitary fibrous Tumor, a review. Iranian Journal of Pathology. 2016; 11: 195–203.
- Zafar H, Takimoto CH, Weiss G. Doege-Potter syndrome. Med Oncol. 2003; 20: 403–7.
- Steigen SE, Schaeffer DF, West RB, Nielsen TO. Expression of insulin-like growth factor 2 in mesenchymal neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 2009; 22: 914–21.
- Le Roith D. Tumor-Induced Hypoglycemia. N Engl J Med. 2008; 341: 757–8.
- Haaga JR. CT and MRI of the Whole Body. 5th ed. 2008; 1: 2734.
- Stacchiotti S, Libertini M, Negri T, Palassini E, Gronchi A, Fatigoni S, et al. Response to chemotherapy of solitary fibrous tumour: A retrospective study. Eur J Cancer. 2013; 49: 2376–83.
- Salas S, Resseguier N, Blay JY, Le Cesne A, Italiano A, Chevreau C, et al. Prediction of local and metastatic recurrence in solitary fibrous tumor: construction of a risk calculator in a multicenter cohort from the French Sarcoma Group (FSG) database. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. 2017; 28: 1979–87.
- England DM, Hochholzer L, McCarthy MJ. Localized benign and malignant fibrous tumors of the pleura. A clinicopathologic review of 223 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1989; 13: 640–58.
- Baldi GG, Stacchiotti S, Mauro V, Dei Tos AP, Gronchi A, Pastorino U, et al. Solitary fibrous tumor of all sites: outcome of late recurrences in 14 patients. Clin Sarcoma Res. 2013; 3: 1–7.
- Gholami S, Cassidy MR, Kirane A, Kuk D, Zanchelli B, Antonescu CR, et al. Size and Location are the Most Important Risk Factors for Malignant Behavior in Resected Solitary Fibrous Tumors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017; 24: 3865–71.
- Demicco EG, Wagner MJ, Maki RG, Gupta V, Iofin I, Lazar AJ, et al. Risk assessment in solitary fibrous tumors: validation and refinement of a risk stratification model. Mod Pathol. 2017; 30: 1433–42.
- Robinson LA. Solitary fibrous tumor of the pleura. Cancer Control. 2006; 13: 264–9.