
Research Article
Adv Res Text Eng. 2016; 1(1): 1007.
Options for Enhancing Functional Properties of Knitted Cotton Fabrics
Ibrahim NA¹*, Ibrahim DF², Elzairy WM², Eid BM¹ and Tawfik TM³
¹Textile Research Division, National Research Centre, Egypt
²Printing, Dyeing and Finishing Department, Helwan University, Egypt
³Printing, Dyeing and Finishing Department, Benha University, Egypt
*Corresponding author: Nabil A. Ibrahim, Textile Research Division, National Research Centre, Egypt
Received: October 03, 2016; Accepted: December 04, 2016; Published: December 07, 2016
Abstract
In this study, single jersey knitted cotton fabrics were treated with different finishing formulations to impart new and durable functional properties as well as to extend their potential applications. Anti-bacterial agent based on organosilane-quaternary ammonium compound or AgCl/TiO2, UV-protecting agent based on an oxanilide, water/oil repellent agent based on polymeric hyperbranched hydrocarbon dendrimers, as well as hand modifying agent based on acid cellulose or amino-siloxane micro-emulsion, have been individually applied on the cotton knits using proper treatment methods. Individual utilization of the nominated bio-active agents exhibits high antibacterial activity against the G +ve (S. aureus) and G –ve (E. coli) pathogenic bacteria. The UV-protection factor of the treated fabrics has been enhanced remarkably to attain the maximum grade >50+. Water and oil repellency of the finished samples has been improved significantly to attain 80/5 rate. Anti-pilling and softness properties are improved by using the acid-cellulases or the silicon softener.
Keywords: Cotton knits; Durable functional finishes; Anti-bacterial; UVprotection; Water/oil repellent; Soft-handle
Introduction
Cotton cellulose is the most abundantly used textile fibers in apparel industry due to its biodegradability, comfortability, hydrophilicity, softness and remarkable coloration. Cotton cellulose has three hydroxyl groups per repeating anhydroglucose unit, one C-6 primary and two C-2 and C-3 secondary, which are responsible for the chemical reactivity, i.e. in chemical modification, coloration and chemical finishing [1,2]. The extent of modification, coloration and∕or functionalization of cotton cellulose structure depends on the relative amount of the amorphous/crystalline phases. On the other hand, the quality of knitted fabric is governed by the kinds of chosen knitting yarn, knitting technology as well as finishing treatments.
Recently, several studies have been carried out to improve the existing properties and/or to impart and create additional and innovative functional properties such as antibacterial, UV- protection, self cleaning, anti-pilling and ∕or softness to the cotton- based textiles [3-11] to cope with the ever-growing of consumer demands for hygienic, protective and active wear clothing as well as to increase the value addition and potential applications.
Therefore, the major objective of this research work is to assess and investigate the influence of certain finishing treatments such as antibacterial, UV-protection, water & oil repellent, bio-and soft - finishes on some performance and functional properties of 100% cotton single Jersey knitted fabrics taking in consideration both the consumer and industrial demands.
Experimental
Materials
Mill - scoured and bleached weft knitted fabrics Single Jersey I (yarn count: 24/1 Ne, weight: 180 g/m²), Single Jersey II (yarn count: 30/1 Ne, weight: 140 g/m²) and Single Jersey III (yarn count: 30/1 Ne, weight: 120 g/m²) were used in this study.
Chemicals
Precosoft® SM40 (nonionic softener based on amino polysiloxane micro emulsion, Schill - Seilacher, Germany) and Iogen® DR-802 (liquid acid cellulase enzyme, Iogen® Bio-products, Canada) were used.
Rucofin® DRY DHY (cationic water repellent agent, based on polymeric hyperbranched dendrimers in a hydrocarbon matrix including F6- fluoro chemical product, Rudolf Chemie, Germany), UV-Sun® CE liq (UV-absorber based on oxalaniline, anionic, Huntsman, Germany), Polyprotec® BBC (permanent antimicrobial agent, cationic, based on organosilane-coupled quaternary ammonium, Polysistec, Barcelona) and Sanitized®T27-22 Silver (weakly anionic antibacterial agent based on silver chloride/titanium dioxide combination, Clariant, Switzerland) were used in functional finishing treatments.
Fixapret®ECO (low formaldehyde reactant resin, based on modified dimethyloldihydroxyethylene urea, BASF, Germany) was of commercial grade.
Citric Acid (CA), Magnesium Chloride Hexahydxate (MgCl2.6H2O), Na-Hypophosphite (SHP, NaH2PO2.H2O), acetic acid, Na-carbonate and Glauber salt were of laboratory grade chemicals.
Treatment methods
Table 1 illustrates the actual experimental formulations and conditions of the post-finishing treatments.
Post-treatment
Conditions
Antibacterial finish
- Portion of cotton knits was treated with Polyprotec®BBC (X% owf), CA (2%owf), SHP (1% owf), at pH(5), M/LR(1/10), 45°C for 30 min by the exhaustion technique, then padded to 80% wet-pickup, dried and polymerized at 150°C/3min, thoroughly rinsed and dried at 100°C/3min.
- Another set of knitted cotton fabrics were treated in finishing bath containing Sanitized® T27-22 silver (x% owf), CA (2% owf), SHP (1% owf) at PH (5), M/LR(1/10), 60°C for 45 min. using the exhaustion method, then padded to 80% wet pickup, fixed at 160°C /3min, thoroughly rinsed and dried at 100°C /8min.
UV – protection finish
Portion of knitted fabrics was treated with UV-Sun CEL (X% owf) only with Glauber salt (8g/L), soda ash (8g/L) at 45°C for 30min. in a pilot scale jet machine (M/LR: 1/10). Finally, the treated cotton knits were thoroughly rinsed and then dried at 100°C for 5 min.
Water & oil repellent finish
Another set of cotton knits was padded twice to a wet pickup of 80% with an aqueous solution of Rucofin® DRY DHY (X g/L), Fixapret®ECO (25 g/L) and MgCl2.6H2O (5g/L), then the treated fabrics were dried100°C /5min, cured at 150°C for 3 min. thoroughly rinsed and dried at 100°C for 5 min.
Bio –finish
Enzymatic treatment was carried out in a pilot scale jet machine according to the following conditions: Iogen® DP-802 dose (X% owf), pH (5) using a buffer solution, M/ LR (1/10) at 55°C for 45 min, then the bath temperature were raised up to 90°C, which was maintained for 10min to deactivate the used enzyme, thoroughly rinsed the fabric to wash away abraded fibers and loaded enzyme, squeezed and air dried.
Soft-finish
Soft- finishing treatment was performed in a pilot scale jet machine using Precosoft®SM40 (X% owf), pH (5), M/LR(1/10) at 45°C for 45 min, followed by hydro-extracting and drying at 120°C / 3min.
Table 1: Post-treatment formulations and conditions.
Fabric evaluation
Before and after finishing applications, the following tests are carried out to evaluate the performance and functional properties of knitted cotton fabrics. All measurements were conducted under standard testing conditions (20±2°C and 65±2% relative air humidity).
Weight loss or gain of fabric (W) was determined as the differences in weight between the referenced and the treated samples according to ASTM (D3776-79). Rate of Shrinkage (RS) was determined according to ASTM (D2120-96). Pilling Rate (PR) was assessed according to ASTM (D4970-2002). Surface Roughness (SR) was measured according to JIS B0031-1994 standard, using surface roughness measuring instrument (SE-1700, Japan). Stiffness (St) of knitted fabrics was evaluated according to ASTM (D3388-1996). Absorbency Time (AT) of knitted samples was assessed according to AATCC (79- 1992). Heat Transmittance (HT) was determined according to ASTM (D1518-85). Air permeability (AP) was tested according to ASTM (D737-96). Whiteness index (WI) was evaluated by using Color-Eye 3100 spectrophotometer according to ASTM (E313-2005). Water Repellency (WRR) and oil repellency (ORR) ratings were performed using the spray test method AATCC (22-1989) and (118-2007) respectively. Antibacterial activity of functionalized Knits against G+ve (S. aureus) and G-ve (E.coli) bacteria was evaluated using agar diffusion test according to AATCC test method 147-1988. UV -Protection Factor (UPF) of functionalized cotton knits was assessed according to the Australian New Zealand standard method (AS/NZS 4366-1996). Durability to wash was performed according to AATCC 61(2A)-1996. Scan Electron Microscope (SEM) images and Energy Disperse X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) spectrums of selected samples were investigated using a JEOL, JXA-840A electron probe micro analyzer equipped with X-ray spectroscopy to clarify the changes in surface morphology and to prove the existence of elements onto the treated substrates respectively.
Results and Discussion
Enhancing antibacterial activity
To impart antibacterial activity to the nominated cotton knits (I, II, III), knitted fabric samples were treated with Polyprotec® BBC, as a permanent antimicrobial agent, (2-4% owf), along with Citric Acid (CA), as a formaldehyde free cross-linker, (2% owf), along with Na- Hypophosphite (SHP) as a catalyst (1% owf). The results in Table 2 revealed that increasing the antimicrobial agent concentration up to 4% owf is accompanied by an increase in add – on percentage, an enhancement in dimensional stability, an improve in fabric softness, a slight decrease in air permeability, a marginal increase in the water droplet absorption time along with a remarkable improvement in the antibacterial activity of the treated samples compared with the untreated ones and regardless of the used substrate. The extent of variation in the aforementioned performance and antibacterial functional properties is governed by type of substrate, i.e. fiber fineness, yarn count, weight, thickness as well as surface morphology [12] keeping other parameters constant.
Knitted
Fabric
Polyprotec®
(% owf)
Performance and functional properties
Add-on
(%)
aSh
(%)
SRb
(µm)
APc
(L/cm²/S)
ATd
(S)
WIe
ZI(mm)f
G
(+ve)
G
(-ve)
I
Untreated
0.00
6
22.85
166
2
76.0
0.0
0.0
II
0.00
8
22.66
244
1
76.8
0.0
0.0
III
0.00
10
22.41
368
1
77.3
0.0
0.0
I
2
1.11
5
22.81
160
3
75.8
17.0
16.0
II
1.43
7
22.60
235
2
76.5
18.0
16.5
III
2.50
9
22.35
360
2
77.0
19.5
17.5
I
3
2.78
5
22.76
152
4
75.4
20.0
18.5
II
3.57
6
22.56
230
3
76.0
21.0
19.0
III
4.17
8
22.28
352
3
76.4
23.0
20.0
I
4
3.89
4
22.70
145
5
74.0
22.5
19.0
II
4.28
5
22.50
225
4
75.3
24.0
22.0
III
5.00
7
22.22
345
4
76.0
25.5
23.0
I: Single Jersey24, II: Single Jersey30, III: Single Jersey 36
aSh: Shrinkage; bSR: Surface Roughness; cAP: Air Permeability; dAT: Absorbency Time; eWI: Whiteness Index; fZI: Zone of Inhibition, G+ve: S. aureus; G-ve: E. coli.
Table 2: Effect of Polyprotec® BBC concentration on some performance and antibacterial properties of finished cotton knits.
The increase in weight gain, the improve in dimensional stability and surface softness as well as the drastic increase in antibacterial efficacy of the treated fabric samples are a direct consequence of modification and/or ester-cross-linking of cotton cellulose structure (Equation 1) along with loading and immobilizing the used antimicrobial agent onto/ within the cellulose structure (Equation 2) as illustrated by the following chemical reactions:
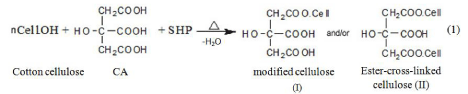
Equation 1:
On the other hand, the decrease in air permeability through the treated cotton knits, the marginal increase in absorption time as well as decrease in whiteness index properties are attributed to the deposition and fixation of the antimicrobial polymers onto/within the fabric surfaces thereby blocking of some hydrophilic active sites along with covering some of the voids between fibers and yarns [13].
From Table 2 it is obvious that the imparted antibacterial activity against the nominated bacteria follows the decreasing order: G+ve> G-ve, keeping other parameters fixed. This can be attributed to the differences between them in cell wall structure as well as extent of interruption of essential functions of the cell membrane and protein activity [14]. Moreover, the inhibition activity of the finished samples follows the descending order: III> II>I>> untreated, which could be discussed in terms of the difference among them in the extent of diffusion and penetration of the active ingredients, availability and accessibility of cellulose active sites , extent of modification of cellulose structure as well as extent of subsequent loading, fixing, and immobilizing the-bio-active agent, Polyprotec® BBC, into/ onto the cellulose structure via physical binding forces and via ionic interactions [15] between the positively active sites of the antimicrobial agent and the negatively charged carboxylate groups of the modified and/or crosslinked cellulose (Equation 2). The remarkable enhancement in the imparted antibacterial functionality reflects the ability of the loaded bioactive agent to damage the cell wall, disrupt the cytoplasmic membrane, facilitate the release of cytoplasmic constituents and finally to cause the death of the cell [16].
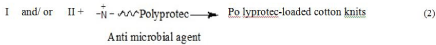
Equation 2:
Moreover, the effect of incorporation of Sanitized®T27-22 silver, as antibacterial agent, at various concentrations (0.4%- 08% owf) along with other ingredients was studied (Table 3). As shown in Table 3, increasing the bioactive agent concentration from (0.4% to 0.8% owf ) results in: i) An improvement in add-on %, dimensional stability, expressed as shrinkage %, and fabrics stiffness as well as a noticeable increase in the imparted antibacterial activity against G+ve and G-ve bacteria compared with the untreated substrate and ii) A slight decrease in air permeability, as well as a marginal decrease in wettability and degree of whiteness, regardless of the used cotton knit. The changes in the aforementioned properties are governed by type of substrate , surface morphology, availability and accessibility of its active sites and micro-pores, extent of modification and /or ester cross-linking, extent of loading and fixing the antibacterial agent onto /within the fabric structure in addition to the extent of leaching and controlled releasing Ag+ ions and the data presented in Table 3 also show that: i) The increase in the antibacterial activity of treated substrates is most significant in the light–weight fabric and follows the decreasing order: III > II >I >> untreated, regardless of the used bacteria, ii) Incorporation of citric acid as a binding/ester cross linking agent along with its proper catalyst , SHP, in the finishing formulation would be expect to promote further fixation of the antibacterial agent onto the modified cellulose structure during the thermo-fixation step as follows: (Equation 3)
Knitted fabric
Sanitized®
T 27-22
( % owf )
Performance and functional properties
Add-on
(%)
aSh
(%)
bSt
(mg.cm)
cAP
(L/m²/S)
dAT
(S)
eWI
f ZI(mm)
G (+ve)
G (-ve)
I
Untreated
0.00
6
896
166
2
76.0
0.0
0.0
II
0.00
8
804
244
1
76.8
0.0
0.0
III
0.00
10
643
368
1
77.3
0.0
0.0
I
0.4
0.59
6
910
163
3
75.3
15.5
14.0
II
0.76
8
816
242
2
76.0
16.5
15.0
III
0.98
10
657
365
2
76.4
18.5
17.0
I
0.6
1.25
6
915
158
3
75.0
18.5
17.0
II
1.53
7
822
238
2
75.4
20.0
18.0
III
1.75
9
661
360
2
76.0
21.5
19.0
I
0.8
2.38
5
930
152
4
74.6
21.0
18.5
II
2.95
6
839
230
3
75.0
22.0
20.0
III
3.53
8
681
352
3
75.4
23.5
21.5
aSh: Shrinkage; bSt: Stiffness; cAP: Air Permeability; dAT: Absorbency Time; eWI: Whiteness Index; fZI: Zone of Inhibition, G+ve: S. aureus ; G-ve: E. coli.
Treatment condition: Sanitized® T 27-22 (X% owf) CA (2% owf); SHP (1% owf); pH (5.5); M/ LR (1/10), at 60oC for 45 min , them padded to a wet pickup of 80% , dried at 100oC/3min; thermofixed at 160oC / 3min, followed by washing and drying.
Table 3: Effect of Sanitized® T 27-22 concentration on some performance and functional properties of finished cotton Knits.
Knitted
Fabric
UV- SUN®
CEL
(% owf)
Performance and functional properties
Add – on
(%)
aSh
(%)
bSt
(mg.cm)
cAP
(L/cm²/S)
dAT
(S)
eWI
fUPF
I
Untreated
0.00
6
896
166
2
76.0
10
II
0.00
8
804
244
1
76.8
7
III
0.00
10
643
368
1
77.3
6
I
0.20
0.38
6
903
161
2
75.7
20
II
0.58
8
809
242
1
76.6
25
III
0.74
10
647
363
1
77.0
29
I
0.40
0.81
5
910
159
2
75.4
36
II
1.21
7
815
236
1
76.3
44
III
1.48
9
654
359
1
76.8
50
I
0.60
1.27
5
916
154
3
75.0
54
II
1.65
7
821
230
2
76.0
58
III
2.08
8
660
355
2
76.4
65
Treatment condition: UV - SUN® (x % owf); Glauber’s salt (8 g/L); Na – carbonate (8 g/L); M/LR (1/10); at 95oC /30 min, then rinsed and dried at 100oC for 5 min.
fUPF: UV- Protection factor.
For explanation of abbreviations see footnote to Table 1.
Table 4: Effect of UV- SUN® concentration on some performance and functional properties of finished cotton Knits.
Knitted
Fabric
Rucofin®
(g/L)
Performance and functional properties
Add – on
(%)
aSh
(%)
bPR
cSR
(µm)
dAP
(L/Cm²/S)
eWI
fWRR
gORR
I
Untreated
0.00
6
4
22.85
166
76.0
00
2
II
0.00
8
3
22.66
244
76.8
00
1
III
0.00
10
3
22.41
368
77.3
00
1
I
80
2.08
5
3
22.79
162
75.4
60
4
II
2.52
7
2
22.58
239
76.0
50
3
III
3.15
9
2
22.35
360
77.0
50
3
I
100
5.75
4
2
22.70
154
74.0
70
5
II
6.55
6
1
22.45
232
74.8
60
5
III
7.48
8
1
22.18
354
76.4
60
5
I
120
7.75
4
1
22.58
150
72.5
80
5
II
9.02
5
1
22.20
226
73.5
80
5
III
9.85
7
1
22.00
350
74.0
80
5
Treatment condition: Rucofin® DRY-DHY, (Xg ∕ L), Fixapret® ECO (25 g ∕ L) MgCl2.6H2O , (5 g ∕ L); pH(5); wet pick- up (80%); dried at 100oC for 5 min, curing at 150oC ∕ 5min, thoroughly rinsed and dried.
bPR: Pilling Rate; fWRR: Water Repellent Rating; gORR: Oil Repellent Rating
For explanation of other abbreviations see footnote to Table 1.
Table 5: Effect of Rucofin® DRY -DHY concentration on some performance and functional properties of finished cotton knits.

equation 3:
i.e. the –COOH chelating group on the modified cellulose acting as coordination sites for Ag+ and TiO2 ions, iii) The inhibition effect against the nominated bacteria decreases according to the following sequence: G +ve > G -ve, v) The slight decreases in the whiteness index of the finished fabrics is suggested to be due to the immobilized Ag/TiO2 onto the fabric surface and its optical properties [16], iv) The presence of inhibition zones around the treaded samples clearly confirmed that the biocidal action of Ag/TiO2-loaded fabric samples were attributed to the leached Ag+ ions, which in turn leads to denaturation and inactivation of proteins via reaction with nucleophilic amino acid residues causing cell death as well as the photo catalytic activity of TiO2 [16].
Improving UV - protection ability
Within the range examined, (0.2% - 0.6% owf ), the results in Table 4 revealed that increasing the UV-absorber (UV-SUN®CEL) concentration up to (0.6% owf) brings about an increase in the weight gain, an improve in dimensional stability expressed as area shrinkage, a marginal increase in fabric stiffness along with a slight decrease in air permeability without significantly affects both the wettability and whiteness index properties in comparison with the untreated ones. The results also demonstrated that the anti –UV properties, expressed on UPF values, have improved significantly up to 50+ by increasing the UV-absorber concentration up to (0.6% owf) in the finishing bath, irrespective of the used substrate. The higher the concentration of the UV-absorber is, the better the UV- protection ability. The imparted UV-protection functionality to the treated cotton knits follows the decreasing order: III > II > I>> untreated ones. On the other hand, the variation in UV –blocking efficiency upon using different cotton knits could be discussed in term of differences among them in: weight, thickness, porosity, compactness, cover factor, shrinkage percentage, as well as extent of loading the UV-absorber onto /within the fabric structure [6,10,17,18].
Imparting water & oil repellency
In this part, the effect of using Rucofin® DRY- DHY, as a water & oil repellent agent (80-120g/L), along with Fixapert® ECO, as a crosslinking agent (25g/L) and MgCl2.6H2O, as a catalyst (5 g/L) using pad-dry technique on some performance and functional properties of the treated knitted fabrics were examined. The data presented in Table 5 show that: i) The weight-gain values were significantly increased by increasing the water repellent concentration, ii) Treated fabric samples exhibited better dimensional stability than that of the untreated samples, iii) Finished cotton knits exhibited better pilling resistance than the untreated ones, iv) both air permeability and whiteness index of the treated samples were slightly decreased by increasing the finishing agent concentration up to 120 g/L, v) treated fabric samples exhibited outstanding water & oil repellency compared with the untreated fabrics, and vi) the variation in the abovementioned properties is governed by type of substrate, surface morphology, extent of cross-linking, loading of the water & oil repellent film as well as its extent of fixation onto the finished substrates. This clearly reflects the positive impacts of coating and covering the fabric surfaces with the repellency film by the agent and in the presence of the cross-linker during the curing step on : i) Increasing the weight of fabric, ii) Fixing the surface fuzz and protruding fibers and yarns more tightly in the fabric construction, i.e. reduced pilling tendency, iii) Enhancing the dimensional stability via cross-linking as well as hindering the diffusion and penetration of aqueous solution within the treated structure as well as iv) Imparting new and remarkable hydrophobic and lipophobic functional properties to the treated cotton knits as direct consequence of the change in their surface composition as well as the reduction in free energy at the fiber surface [6,19]. On the other hand the marginal decrease in the whiteness index of the treated fabrics compared with the untreated ones can be attributed to the change in fabric surface properties as well as deposition of repellency film onto the surfaces.
Modifying surface properties
From Table 6, it is clear that as the enzyme dose increases up to (0.35% owf) in the enzymatic treatment bath, the percentage loss in weight, the shrinkage tendency, air permeability and the whiteness index values of the treated cotton knits increase compared with that of the untreated fabrics, while the pilling tendency, surface roughness and absorption time values decrease. The extent of increase or decrease in the tested properties is governed by the type of substrate, e.g. weight, compactness, surface morphology , surface area, amount of microfibers at the surface, substrate binding sites, availability and accessibility to the soluble enzyme as well as subsequent extent and efficient of enzymatic attack [5,20].
Knitted
Fabric
Iogen®DP-82
(%owf)
Performance and functional properties
aWL
(%)
bSh
(%)
cPR
dSR (µm)
eAP
(L/cm²/S)
fAT
(S)
gWI
I
Untreated
0.00
6
4
22.85
166
2
76.0
II
0.00
8
4
22.66
244
1
76.8
III
0.00
10
3
22.41
368
1
77.3
I
0.15
1.11
6
3
22.72
172
1
76.6
II
1.45
9
3
22.44
250
<1
77.2
III
1.72
11
2
22.18
374
<1
77.6
I
0.25
2.38
7
2
22.54
179
<1
77.0
II
3.46
10
2
22.30
257
<1
77.6
III
3.80
12
1
21.85
380
<1
78.1
I
0.35
3.88
8
1
22.28
185
<1
77.5
II
5.58
11
1
22.08
261
<1
78.2
III
5.85
13
1
21.69
385
<1
78.4
Treatment condition: Iogen®DP-802 (X % owf); pH (5); M ∕ LR (1 ∕ 10); at 55oC for 45 min.
aWL: Weight Loss.
For explanation of abbreviations see footnote to Table 4.
Table 6: Effect of enzyme concentration on some performance and functional properties of finished cotton knits.
The synergistic action of acid cellulases and mechanical action results in bio-polishing of the fabric surface thereby upgrading pilling resistance, improving surface smoothness and softness, enhancing wettability as well as decreasing the light scattering and increasing its reflection via cleaning the fabric surface according to the following equation (Equation 4) [21-24].

Equation 4:
The results in Table 7 revealed that increasing the silicone softener (Precosoft® SM40) concentration up to 1.5% owf has significant positive impacts on the weight-gain, dimensional stability, anti-pilling and softness performance properties in comparison with the untreated fabric samples. This can be attributed to the deposition of considerable amount of the nominated softener onto/within the cotton cellulose structure and the formation of softener film on both the outer surface and the inner parts of the fabric yarns. This in turn results in building up higher amount of softener on/into the fabric, blocking some hydrophilic active sites and micro-pores between fibers and yarns, anchoring protruding microfibers emerged from the fabric surface, as well as acting as a lubricant thereby reducing the friction between the fibers and yarns in the fabric and imparting outer and inner softness to the treated substrates [25-27]. Table 7 also reveals that increasing softener concentration from 0.5% to 1.5% owf brings about a marginal decrease in air permeability ,an increase in absorption time along with slight decrease in the whiteness index values of the treated cotton knits compared with the untreated ones, which could be discussed in terms of shortage in hydrophilic active sites, -OH groups, partial blocking of air passages within the softened fabric structure, partial reduction in its surface energy as well as surface and/or inner deposition of softener film thereby affecting surface morphology/composition and causing a slight decrease in the fabric whiteness.
Knitted
Fabric
Softener
(% owf)
performance and functional properties
Add – on
(%)
aSH
(%)
bPR
cSR
(µm)
dAP
(L/m²/S)
eAT
(S)
fWI
I
Untreated
0.00
6
4
22.85
166
2
76.0
II
0.00
8
4
22.66
244
1
76.8
III
0.00
10
3
22.41
368
1
77.3
I
0.5
2.33
4
4
21.79
162
6
75.0
II
2.68
7
4
21.50
240
5
75.6
III
2.95
9
3
21.10
360
4
76.1
I
1. 0
5.05
3
3
21.40
155
8
74.3
II
5.56
5
2
21.15
235
7
75.0
III
6.02
7
2
20.85
354
6
75.4
I
1.5
6.22
2
2
21.10
160
9
73.2
II
6.80
3
1
20.85
239
8
74.3
III
7.30
5
1
20.55
358
7
74.8
Treatment condition: Precosoft®SM40 (X% owf); pH (5); M ∕ LR (1/10); at 40oC for 45 min, followed by hydro-extracting and drying at 120oC /3 min.
For explanation of abbreviations see footnote to Tables 1 & 4.
Table 7: Effect of softener concentration on some performance and functional properties of finished cotton knits.
Durability to wash
The data in Table 8 demonstrated that increasing the washing cycles up to 15 results in a reasonable decrease in the imparted functional properties, regardless of the used finishing agent. The extent of decrease is governed by type of finishing agent, extent of loading and fixation onto / within the cellulosic substrate.
Finishing agent
Functional finish
Washing- cycle (number)
Substrates
Functional property
aAntibacterial (ZI)
bUPF
cWRR
dORR
ePR
fSR
(µm)
G
(+ve)
G
(-ve)
Polyprotec® BBC
(4% owf )
Antibacterial
1
Knit III
25.5
23.0
-
-
-
-
-
15
23.0
20.0
-
-
-
-
-
Sanitized® T27-22
(0.8% owf )
Antibacterial
1
Knit III
23.5
21.5
-
-
-
-
-
15
20.0
18.5
-
-
-
-
-
UV-Sun®
(0.6% owf )
UV- protection
1
Knit III
-
-
65
-
-
-
-
15
-
-
56
-
-
-
-
Rucofin® DRY DHY
(120 g /L )
Water / oil
repellent
1
Knit III
-
-
-
80
5
-
-
15
-
-
-
70
4
-
-
Iogen® DR-802
(0.35% owf)
Bio- finish
1
Knit III
-
-
-
-
-
1
21.69
15
-
-
-
-
-
2
22.40
Precosoft® SM40
(1.5% owf)
Soft- finish
1
Knit III
-
-
-
-
-
1
20.55
15
-
-
-
-
-
2
21.0
Table 8: Durability of the imparted functional properties to wash. For explanation of abbreviations see footnote to Tables 1&4.
SEM and EDX analysis
SEM images of selected substrates demonstrate the changes in the surface morphology for Single Jersey III in case of enzymatic treatment Figure1 (d) and a deposition of coating layer in case of treatment with Rucofin® Dry, Sanitized® T27-22, and Polyprotec® BBC Figure 1 (eg. i) compared with the untreated one Figure 1 (a) On the other hand, EDX spectrum shows change in carbon/oxygen ratio in enzymatic treated sample Figure 1 (c) while other EDX spectra confirm the existence of the following elements F Figure 1 (f), and Si, Ti and Ag Figure 1 (h), as well as N and Si Figure 1 (j) in case of using Rucofin® DRY DHY, Sanitized® T27-22, and Polyprotec® BBC respectively.
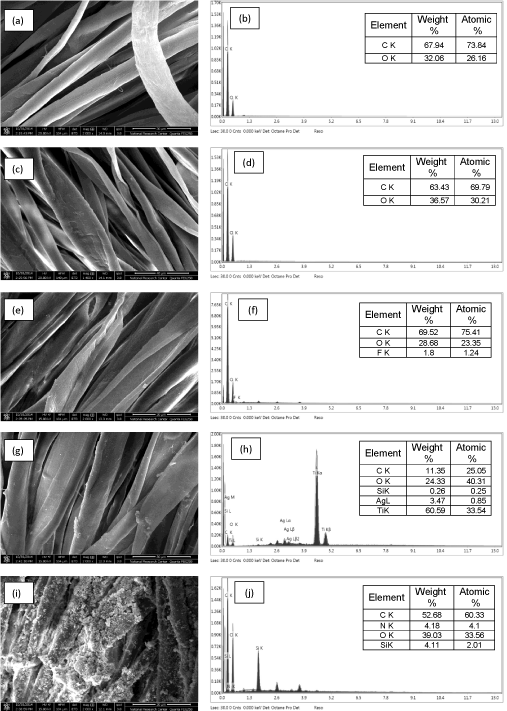
Figure 1: SEM and EDX spectra of: untreated Single Jersey III cotton (a&b), cotton fabric treated with acid cellulases (c&d), cotton fabric treated with Rucofin® DRY
DHY (e&f), cotton fabric treated with Sanitized®T27-22 Silver (g&h), cotton fabric treated with Polyprotec® BBC (i&j).
Conclusions
A new approach for imparting new functional properties to single Jersey knitted cotton fabrics was investigated. The obtained results showed that: i) Inclusion of Polyprotec® BBC (4% owf) or Sanitized® T27-22 (0-8% owf) along with CA (2% owf) and SHP (1%) in the finishing formulation, results in a significant improvement in the anti-bacterial efficacy of the treated cotton fabrics, ii) Increasing the UV-blocker concentration up to (0.6% owf) brings about a remarkable improvement in the ability of treated fabrics to block the harmful UV-radiation, iii) The water/oil repellency of the treated fabric samples using Rucofin® DRY - DHY (120 g/L) along with the ether-cross linking agent are much better than the untreated ones, iv) Anti- pilling and softness properties of the enzyme or silicone - softener treated fabric samples are better compared to the untreated fabrics, and v) All the functionalized fabric samples exhibit high durability to wash.
References
- Ibrahim NA. Dyeing of textile fibre blends. In: Handbook of textile and industrial dyeing, vol 2. Application of dyes. Editor. Clark M. Chapter 4. 2011; 147-172.
- Shamy R, Hussein T. Critical solutions in the dyeing of cotton textile materials. Textile Progress. 2005; 37: 1-84.
- Gao Y, Cranston R. Recent advances in antimicrobial treatments of textiles. Textile Research Journal. 2008; 78: 60-72.
- Holme I. Innovative technologies for high performance textiles. Coloration Technology. 2007; 123: 59-73.
- Ibrahim NA, Fahmy HM, Hassan TM, Mohamed ZE. Effect of cellulase treatment on the extent of post finishing and dyeing of cotton fabrics. Journal of Materials Processing and Technology. 2005; 160: 99-106.
- Ibrahim NA, Khalifa TF, El-Hossamy M, Tawfik TM. Effect of knit structure and finishing treatment on functional and comfort properties of cotton knitted fabrics. Journal of Industrial Textiles. 2010; 40: 49-64.
- Ibrahim NA, Refaie R, Ahmed AF. Novel approach for attaining cotton fabric with multifunctional properties. Journal of Industrial Textiles. 2010; 40: 65-83
- Ibrahim NA. Nanomaterials for antibacterial textiles. In: Nanotechnology in Diagnosis, Treatment and Prophylaxis of Infectious Diseases. Rai M, Kon K. (Editors). Elsevier Publisher. Chapter 10. 2015; 191-216.
- Ibrahim NA, Khalifa TF, El-Hossamy M, Tawfik TM. Factors affecting the functional and comfort related properties of reactive dyed cotton knits, Journal of Industrial Textiles. 2011; 41: 41-56.
- Kan CW, Au CH. Effect of biopolishing and UV-absorber treatment on the UV-protection properties of cotton knitted fabrics. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2014; 101: 451-456.
- Roy Choudhury AK, Chatterjee B, Saha S, Shaw K. Comparison of performances of macro, micro and nano silicone softeners. Journal of The Textile Institute. 2012; 103: 1012-1023.
- Behera BK. Comfort and handle behavior of linen-blended fabrics. AUTEX Research Journal. 2007; 7: 33-47.
- Montazer M, Hashemikia S. Application of polyurethane/ citric acid/ silicone softener composite on cotton/polyester knitted fabric producing durable soft and smooth surface. Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 2012; 124: 4141-4148.
- Simoneic B, Tomsic B. Structure of novel antimicrobial agents for textiles - A review. Textile Research Journal. 2010; 80: 1721-1737.
- Zhao T, Sun G. Antimicrobial finishing of cellulose with incorporation of aminopyridinium salts to reactive and direct dyed fabrics. Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 2007; 106: 2634-2639.
- Khalilabad MS, Yazdanshenas ME. Fabrication of superhydrophopic, antibacterial and ultraviolet-blocking cotton fabric. Journal of the Textile Institute. 2013; 104: 861-869.
- Ibrahim NA, Gouda M, Husseiny ShM, El- Gammal AR, Mahrous F. UV- protecting and antibacterial finishing of cotton knits. Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 2009; 112: 3589-3596.
- Wong W, Lam JKC, Kan C, Postle R. Influenced of knitted fabric construction on the ultraviolet protection factor of greige and bleached cotton fabrics. Textile Research journal. 2012; 27: 1-17.
- Ren Q, Zhao T. Synthesis and application of modified vegetables oils in water-repellent finishing of cotton fabrics. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2010; 80: 381-386.
- Ibrahim NA, EL-Hossamy M, Hashem MM, Refaie R, Eid BM. Novel pretreatment process to promote linen- containing fabrics properties, Carbohydrate Polymers. 2008; 74: 881-891.
- Cavaco-Paulo A & Gubitz G. Catalysis and processing. In Cavaco-Paulo A. and Gubtiz GM. (Editors). Textile processing with enzymes. Chapter 3, Wood head Publisher. Cambridge England. 2003; 86-119.
- Nierstrasz VA, Warmoeskerken MMCG. Process engineering and industrial enzyme applications. In: Cavaco- poulo A. Gubitz GM. (Editors). Textile processing with enzymes. Woodhead Publisher. Chapter 4, 2004; 120-157.
- Shaikh MA. Enzymes: a revolution in textile processing. 2010; 48-51.
- Yu C, Huimin T. Effect of cellulase on the modification of cellulose. Carbohydrate Research. 2002; 337: 1291-1296.
- Habered P, Bereck A. Softeners in textile processing. Part 2: silicon softeners. Review Progress in Coloration. 2002; 32: 125-137.
- Hashem M, Ibrahim NA, Refaie R, EL-Shafie A, Hauser P. An eco- friendly novel approach for attaining wrinkle free/soft hand cotton fabric, Carbohydrate Polymers. 2009; 78: 502-510.
- Wahle B, Falkowski J. Softeners in textile processing. Part 1: an overview, Review Progress in Coloration. 2002; 32: 118-124.