
Research Article
Adv Res Text Eng. 2017; 2(1): 1013.
Usage of Core and Dual-Core Yarns Containing Tungsten for Electromagnetic Shielding
Telli A¹, Daşan Y¹, Babaarslan O¹* and Karaduman S²
¹Cukurova University, Department of Textile Engineering, Turkey
²Calik Denim Textile R&D Center, Turkey
*Corresponding author: Osman Babaarslan, Cukurova University, Department of Textile Engineering, Turkey
Received: September 20, 2016; Accepted: January 18, 2017; Published: January 20, 2017
Abstract
Textile materials having electrically conductive features come to the forefront in the development of electromagnetic shielding products in the literature. Yarns and fabrics containing high-conductivity and low surface/volume resistivity metal wires among these textile materials became important. However, no research has been found about yarns containing tungsten wires and fabric structures composed of these yarns. Point of origin of this study consisted of tungsten having similar electrical resistivity and electrically conductive properties with metals used for electromagnetic shielding such as silver, nickel and copper. The aim of this paper was to evaluate and validate fabrics composed of tungsten with conductivity properties as an alternative electromagnetic shielding product. From this point of view, three different core yarns were produced using Inox, Copper and Tungsten wires. In addition to these core yarns, three different dualcore yarns were also produced with elastane and metal wires. Furthermore, 100% CO (Cotton) yarn and core yarn containing elastane were selected as the control group. Thus, obtained yarn set was used as weft material for the fabric production. The properties of produced yarns and fabrics were determined and EMSE performances were examined comparatively. The findings from this study indicate that the use of tungsten core yarn in the fabric structure can be an alternative to existing products for electromagnetic shielding. This research will serve about products containing tungsten for electromagnetic shielding as a base for future works.
Keywords: Tungsten; Metal wires; Core yarns; Dual-core yarns; Electromagnetic shielding
Introduction
Radiation is divided into two types: ionizing and non-ionizing. Alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ) radiation are types of ionizing radiation. The energy of ionizing radiation is high enough to remove electrons from atoms or molecules. And these rays are harmful unequivocally to human health. However, non-ionizing radiations such as various electromagnetic frequencies have relatively lowenergy radiation according to ionize atoms or molecules. More studies are required to find out effects of these frequencies containing non-ionizing radiation and devices using these frequencies on human health. Because, the technology integrated with our lives and the increasing usage of electrical and electronic devices for our daily works give rise to electromagnetic pollution.
In recent years, this pollution caused by electromagnetic waves has started to generate various problems threatening human mental and physical health. For instance, previous research has indicated that the Electro Magnetic (EM) radiations induce oxidative stress by injuring some ion channels and increasing the flow of Ca+2 within the cell [1]. Furthermore, it is a well-known fact that EM radiations cause a temperature rise in tissues. Therefore, it is foreseen that EM radiation has negative effects to human health in the long term or overexposure despite considering less dangerous than ionizing radiation [2]. These negative effects can show a change according to electromagnetic field intensity and exposure time or frequency and wavelength of EM radiation. Moreover, body sizes and electrical features of human can be also changed these effects. For this reason, several attempts have been made to reduce these effects in the literature. It was stated that textile products obtained from classic textile fibers have, Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness (EMSE) values below 5dB. And these structures cannot prevent electromagnetic waves in any frequencies due to the non-conducting properties. However, textile materials having electrically conductive features come to the forefront to the development of electromagnetic shielding products in the mentioned literature since textile materials occupy less volume and have lower cost than other products. Yarns and fabrics containing high-conductivity and low surface/volume resistivity metal wires among these textile materials became important. They are preferred by the reason of wash-resistant. Thus, they can be use quite a long time.
There is a large volume of published studies investigating with copper and stainless steel metal wires. Ueng ve Cheng (2001) pointed out that Electro Magnetic Shielding Effectiveness (EMSE) of the woven fabric can be tailored in a number of ways, including fabric structure, fabric density, and the amount of conductive core material. It has been shown that the increase of surface or volume resistivity of fabrics cause a decrease in EMSE results [3]. Su ve Chern (2004) examined the EMSE features of woven fabrics produced from three different hybrid yarns (core, covered and plied yarns) including stainless steel. It has been demonstrated that the metal wires lie in the inner region of the spun yarn in the core yarn structure. They are straight, and their distance is the shortest among these three hybrid yarns, so the core yarn has a lower electrical resistance, resulting in a good EMSE. In the plied yarn, the metal wire twists with the spun yarn. The distance is longer than core yarn. The metal wires cover the spun yarn along a helical line in the covered yarn. Their distance (metal wire length) is the longest, so it has a higher electric resistance, resulting in a lower EMSE [4]. Furthermore, the experimental results reveal that the plain weave has a higher EMSE than other weave types. Similar results were found in subsequent studies [5]. Cheng et al. (2006) reported that EMSE values of all the fabrics in the incident frequency range 0, 3–144 MHz was similar because of the diffraction of low frequency plane wave and skin effect of the woven fabric. EMSE values show an increase with an increase in the number of conductive fabric layers, warp density, and weft density in electromagnetic frequencies ranging from 144 to 3000 MHz. Furthermore, a decrease in EMSE has been observed with an increase in wire diameter [6]. In the literature, these results are also supported by other studies [7]. Moreover, several studies were conducted on the knitted and nonwoven fabrics for electromagnetic shielding in addition to woven fabrics [8-10]. There is also increasing concern on the measurements of EMSE. So far, there are four basic methods and different devices derived from these methods in the market [7,11-14].
However, no research has been found about yarns containing tungsten wires and fabric structures composed of these yarns in the literature. Point of origin of this study consisted of tungsten having similar electrical resistivity and electrically conductive properties with metals used for electromagnetic shielding such as silver, nickel and copper [15]. Tungsten and its substances are not acute toxicants, eye and skin irritants, or dermal sensitizers. Tungsten is rare and its compounds are generally inert. Tungsten in insoluble form is also resistant against physical weathering [16,17]. The aim of this paper was to evaluate and validate fabrics composed of tungsten with conductivity properties as an alternative electromagnetic shielding product. From this point of view, three different core yarns were produced using Inox, Copper and Tungsten wires with the same diameter. In addition to these core yarns, three different dual-core yarns were also produced with elastane and metal (Inox, Copper, and Tungsten) wires. Furthermore, 100% CO (Cotton) yarn and core yarn containing elastane were selected as the control group. Thus, obtained yarn set was used as weft material for the denim fabric production. The properties of produced yarns and fabrics were determined and EMSE performances were examined comparatively.
Materials and Methods
For this study, 55 Tex core and dual-core yarns in the twist coefficient of αe= 5 (αtex= 4787, 5) were produced in modified ring spinning system. Ring Spinning Frame was used with 8300 rpm spindle speed. 100% CO roving (990 Tex) was used as covering material. Eight different yarns were produced with 78 dtex elastane and metal (Inox, Copper, Tungsten) wires as core material. Wire diameter of these metals was 0, 035 mm. Compositions of produced yarns are given on Table 1. Denim fabrics were produced using eight different weft yarns in combination with same cotton warp yarns according to production details shown in Table 2. Singeing, causticizing, washing, softening finish, drying and sanforizing were performed respectively on all produced gray fabrics. Quality control tests according to universal standards were applied on engineered yarns and denim fabric samples obtained from these yarns.
Type
Roving
First Core
Second Core
R1
Cotton
-
-
R2
Cotton
-
Elastane
C1
Cotton
Inox
-
C2
Cotton
Copper
-
C3
Cotton
Tungsten
-
D1
Cotton
Inox
Elastane
D2
Cotton
Copper
Elastane
D3
Cotton
Tungsten
Elastane
Table 1: Yarn details.
Weft yarn count (tex)
≈55
Warp yarn count (tex)
≈42
Warp Ends / cm
≈26
Picks / cm
≈18
Fabric Structure
Twill 3/1 Z
Table 2: Fabric production details.
All of yarn/fabric performance the tests were carried out after conditioning in standard atmospheric conditions according to TS EN ISO 139. Tensile strength and elongation at break of the yarns were carried out using TITAN tensile testing device in conformity with TS 245 EN ISO 2062 standard. Twenty results per yarn type were determined as tenacity (cN/tex) and elongation at break (%). Hairiness of the yarns was carried out using “Zweigle G 567” instrument in measurement speed of 50 meters per minute for 100 meters of yarn. Ten results per yarn type were determined as Zweigle hairiness (S3).
Mass per unit area determination of fabrics was done according to ASTM D3776. Breaking strength tests were carried out in weft and warp direction according to ASTM D5034 with grab method. Tear strength tests were also fulfilled according to ASTM D1424. Circular bending rigidity tests were performed using ASTM D 4032 standards with Chatillon Digital Pneumatic Stiffness Tester. The Electro Magnetic Shielding Effectiveness (EMSE) of various woven denim fabrics was obtained using a coaxial transmission line holder in the frequency range of 0,05- 4,4 GHz according to ASTM D 4935- 99. The average of three measurements from each sample was taken for EMSE. Furthermore, the results were statistically evaluated with variance analysis for the most widely used frequencies (800, 900, 1800, 1900, 2100, 2450, 2600 and 3000 MHz) in daily life. The analysis was carried out according to 95% confidence level. All the statistical analysis was performed on a computer using the SPSS (Statistical Package of Social Science) packet program.
Results and Discussion
Tensile strength (cN/tex), elongation at break (%) and Zweigle hairiness (S3) results of the eight different yarns and each of their averages are given in Table 3, 4 presents the measurement results obtained from denim fabrics. It can be seen from the data in Table 3 that the use of metal wires as the core in the yarn structure affected negatively on yarn tensile strength when analyzed yarn results.
Design Code
Core
Tensile Strength (Cn/tex)
Elongation at Break (%)
Zweigle Hairiness (S3)
R1
-
19, 18
9, 00
3791
R2
Elastane
17, 44
9, 20
3364
C1
Inox
19, 00
8, 12
3432
C2
Copper
16, 88
7, 51
4033
C3
Tungsten
17, 27
5, 33
5690
D1
Inox+ Elastane
13, 42
7, 04
4543
D2
Copper+Elastane
11, 70
7, 82
4207
D3
Tungsten+Elastane
9, 16
2, 28
5943
Table 3: The averages of test results obtained from yarns.
Properties
R1
R2
C1
C2
C3
D1
D2
D3
Fabric width (cm)
147
138
153
150, 3
161
147, 3
139
161, 5
Fabric width after washing (cm)
144
118, 5
145
144
149
120
113, 5
139
Mass per unit area (g/m2)
Gray
370
375
353
350
355
355
423
320
Finished
397
475
394
395
371
457
491
389
Circular bending rigidity (kg)
1, 45
2, 4
1, 55
1, 7
1, 15
1, 5
1, 6
1, 35
Breaking Force
(kgf)
Warp
97
105
91
92
94
113
120
97
Weft
60
51
47
46
40
41
43
26
Tear Strength
(grf)
Warp
6524
6328
6524
6459
6524
6524
6524
6524
Weft
5872
6393
5611
5089
4045
4306
4632
3458
Table 4: The averages of test results obtained from fabrics.
Especially, yarn tensile strength was affected more negatively in the dual-core yarn structure containing elastane in addition to metal wires. There was a clear trend of decreasing for elongation at break in core and dual-core yarns like tensile strength. In particular, the lowest elongation at break was observed in yarn (D3) produced with elastane and Tungsten wires as core material. This study confirms that tensile strength values are shown a decrease associated with the increase of the core ratio. The rate of utilization of sheath fibers and the amount of staple fibers in the yarn structure was decreased by the increase as the core ratio. However, the findings of this study do not support the previous research in relation to elongation at break. Earlier findings point out that elastane core has positive contribution for elongation at break [18,19]. The present findings seem to be consistent with another research in the core yarn containing only elastane (B). Expected contribution was observed in this yarn (R2) according to yarn coded as “R1” but different results were determined in dualcore yarns (D1, D2 and D3). Dual-core yarn containing elastane and copper coded as D2 has higher elongation at break value than core yarn (C2) containing only copper as core material. Other dual-core yarns (D1 and D3) showed a decrease according to their core yarn types (C1 and C3) in terms of elongation at break. It can be said that elastane did not provide expected positive contribution to dual-core yarns containing metal wires with regards to mechanical properties.
It is apparent from Table 3 that S3 values showed an increase in the dual-core yarn when analyzed hairiness results. The highest S3 value was also found in dual-core yarn (D3) containing elastane and tungsten. Hairiness values showed an increase depending upon the increase of the yarn number (Ne) although there was no significant difference in thicker yarn when used metal wires as core material in previous studies [20]. Similarly, the most important effect on the yarn unevenness in earlier works was observed with the increase of yarn number (Ne). It was indicated that the trend of proper and uniform effect of staple fibers on core material in yarn center in terms of cohesion was decreased with the increase of yarn number (Ne). This condition is related with the decrease of the staple fiber amount within yarn cross-section [18].
It can be seen from the data in Table 4 that yarn properties reflected to fabric results. Fabrics containing metal wires have lower breaking force and tear strength values among all fabrics in weft direction. All produced fabrics provided minimum expectable requirements from a stand art denim fabric for mentioned fabric mass per unit area except from fabric coded as “D3”. The most negative fabric characteristics was determined in fabric coded as “D3” as in yarn results. There were no significant differences between fabrics containing metal wires and others in respect to rigidity. EMSE test results (dB) obtained from eight different fabrics are compared in Figure 1- 4. The averages of EMSE values of fabrics in the selected frequencies are presented in Table 5.
Mhz
800
900
1800
1900
2100
2450
2600
3000
R1
6, 68
7, 02
0, 00
0, 00
0, 00
0, 20
0, 76
1, 49
R2
5, 26
5, 58
0, 00
0, 00
0, 00
0, 00
0, 50
1, 34
C1
14, 66
13, 84
6, 51
12, 30
24, 20
30, 14
26, 10
16, 85
C2
13, 25
12, 63
5, 79
11, 50
25, 88
31, 39
28, 92
18, 56
C3
13, 29
15, 19
7, 24
9, 51
22, 90
36, 51
26, 72
19, 46
D1
13, 66
14, 51
6, 95
9, 2
20, 63
29, 36
28, 20
17, 37
D2
14, 06
14, 62
9, 57
12, 08
23, 04
33, 32
28, 41
16, 28
D3
17, 12
16, 76
6, 12
10, 16
20, 52
34, 06
27, 59
18, 10
Table 5: The averages of Electro Magnetic Shielding Effectiveness (EMSE) of fabrics in the selected frequencies.
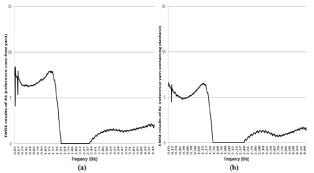
Figure 1: (a) EMSE results of R1 (reference core-free yarn) and (b) R2 (reference yarn containing elastane).
The maximum EMSE value was observed as 33, 05 dB in 2, 33 GHz for fabrics coded as “C1” as can be seen from Figure 2 (c). EMSE values above 20 dB was
measured within the frequency range of 2, 07- 2, 98 GHz for “C1”. Table 5 also shows that 2100 MHz, 2450 MHz and 2600 MHz have EMSE result above 20 dB
within the selected frequencies for “C1”. Furthermore, EMSE values above 30 dB was determined in the frequency range of 2, 22- 2, 45 GHz for “C1”. However, it
appears that EMSE values after 2, 98 GHz frequency has declined dramatically without over again rise.
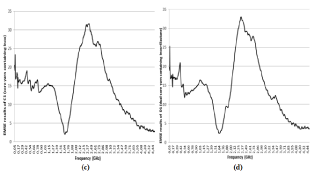
Figure 2: (c) EMSE results of C1 (core yarn containing Inox) and (d) D1 (dual-core yarn containing Inox + Elastane).
Figure 2 (d) provides that the highest EMSE result was measured as 31, 65 dB in 2, 42 GHz for fabrics coded as “D1”. EMSE values above 20 dB was measured
within the frequency range of 2, 09- 2, 92 GHz for “D1”. 2100 MHz, 2450 MHz and 2600 MHz have EMSE result above 20 dB within the selected frequencies for
“D1” as can be seen from Table 5. Moreover, EMSE values above 30 dB was observed in the frequency range of 2, 25- 2, 45 GHz for “D1”. However, it is apparent
that EMSE values after 2, 92 GHz frequency has declined dramatically without over again rise.
As shown in Figure 3 (e), the maximum EMSE value was found as 34, 42 dB in 2, 34 GHz for fabrics coded as “C2”. EMSE values above 20 dB was measured
within the frequency range of 2, 02- 2, 87 GHz for “C2”. Table 5 also presents that 2100 MHz, 2450 MHz and 2600 MHz have EMSE result above 20 dB within the
selected frequencies for “C2”. Furthermore, EMSE values above 30 dB was observed in the frequency range of 2, 20- 2, 58 GHz for “C2”. However, it appears that
EMSE values after 2, 87 GHz frequency has decreased dramatically without over again increase.
It can be seen from the data in Figure 3 (f) that EMSE reached a peak with 34, 37 dB in 2, 43 GHz for fabrics coded as “D2”. EMSE result above 20 dB was found
in the frequency range of 2, 06- 2, 90 GHz for “D2”. 2100 MHz, 2450 MHz and 2600 MHz have EMSE values above 20 dB within the selected frequencies for “D2”
as shown in Table 5. In addition to this, EMSE results above 30 dB was determined in the frequency range of 2, 38- 2, 56 GHz for “D2”. On the other hand, Figure
3 illustrates that EMSE values after 2, 90 GHz frequency has declined dramatically without over again increase.
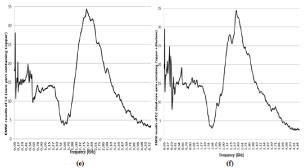
Figure 3: (e) EMSE results of C2 (core yarn containing Copper) and (f) D2 (dual-core yarn containing Copper + Elastane).
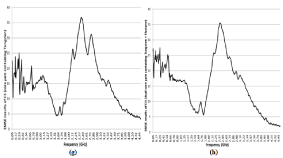
Figure 4: (g) EMSE results of C3 (core yarn containing Tungsten) and (h) D3 (dual-core yarn containing Tungsten + Elastane).
The maximum EMSE value was observed as 36, 82 dB in 2, 44 GHz for fabrics coded as “C3” as can be seen from Figure 4 (g). This was the highest EMSE value
among all fabric samples. EMSE values above 20 dB was measured within the frequency range of 2, 06- 2, 99 GHz for “C3”. Table 5 also shows that 2100 MHz,
2450 MHz and 2600 MHz have EMSE result above 20 dB within the selected frequencies for “C3”. However, it appears that EMSE values after 2, 99 GHz frequency
has declined dramatically without over again rise.
Figure 4 (h) provides that the highest EMSE reached a peak with 35, 48 dB in 2, 39 GHz for fabrics coded as “D3”. EMSE values above 20 dB was measured
within the frequency range of 0, 09- 0, 61 GHz and 2, 09- 2, 84 GHz for “D3” as well as more fluctuant measurements than other samples. 2100 MHz, 2450 MHz
and 2600 MHz have EMSE result above 20 dB within the selected frequencies for “D3” as can be seen from Table 5. Moreover, EMSE values above 30 dB was
also observed in the frequency range of 2, 31- 2, 54 GHz for “D3”. However, it is apparent that EMSE values after 2, 84 GHz frequency has declined dramatically
without over again rise.
Fabrics produced using R1 (reference core-free yarn) and R2 (reference yarn containing elastane) did not provide enough electromagnetic protection as might be expected. The minimum 20 desibel (dB) EMSE value is required to talk about electromagnetic shielding in daily usage [21]. The highest value was measured as 8, 4 dB in 0, 07 GHz for fabrics coded as “R1” as can be seen from Figure 1(a). Table 5 also shows that 900 MHz has maximum EMSE results with 7, 02 dB value within the selected frequencies for “R1”. Figure 1(b) presents that the highest value was measured as 6, 63 dB in 0, 06 GHz for fabrics coded as “R2”. 900 MHz has maximum EMSE results with 5, 58 dB value within the selected frequencies for “R2” as can be seen from Table 5. It can be said that metal-free fabrics (R1 and R2) did not provide electromagnetic shielding because they have lower EMSE results than 20 dB value.
When all results are analyzed as a whole, it was observed that electromagnetic shielding consisted of metal wires. Six fabrics (C1, C2, C3, D1, D2 and D3) containing metal wires have an inadequate and fluctuant shielding in low starting frequencies. Shielding effectiveness gradually increased after about 2 GHz frequencies. It began to drop rapidly after 3 GHz frequencies (Figure 2-4). We can see apparent that there were significant differences between fabrics containing metal wires and metal-free fabrics (R1 and R2) in terms of EMSE. However, no significant differences were found between each other of fabrics containing metal wires.
The results obtained from EMSE measurements were statistically evaluated with variance analysis for six fabrics (C1, C2, C3, D1, D2 and D3) containing metal wires in the selected frequencies. The analysis was carried out according to 95% confidence level. The Analysis of variance (ANOVA) table and the results (p values) of multiple comparisons obtained from variance analysis are summarized in Table 6.
MHz
Sum of Squares
df
Mean Square
F
Sig.
800
Between groups
31, 964
5
6, 393
0, 850
0, 541
Within groups
90, 300
12
7, 525
-
-
Total
122, 264
17
-
-
-
900
Between groups
28, 453
5
5, 691
1, 232
0, 353
Within groups
55, 410
12
4, 617
-
-
Total
83, 863
17
-
-
-
1800
Between groups
27, 470
5
5, 494
0, 330
0, 885
Within groups
199, 543
12
16, 629
-
-
Total
227, 013
17
-
-
-
1900
Between groups
36, 432
5
7, 286
0, 677
0, 649
Within groups
129, 118
12
10, 760
-
-
Total
165, 550
17
-
-
-
2100
Between groups
64, 267
5
12, 853
2, 336
0, 106
Within groups
66, 033
12
5, 503
-
-
Total
130, 300
17
-
-
-
2450
Between groups
107, 489
5
21, 498
1, 709
0, 207
Within groups
150, 934
12
12, 578
-
-
Total
258, 423
17
-
-
-
2600
Between groups
17, 166
5
3, 433
0, 218
0, 948
Within groups
188, 821
12
15, 735
-
-
Total
205, 987
17
-
-
-
3000
Between groups
20, 410
5
4, 082
0, 567
0, 724
Within groups
86, 408
12
7, 201
-
-
Total
106, 819
17
-
-
-
Table 6: Analysis of variance (ANOVA) test results and significant (p) values.
An electromagnetic shielding at the desired level (above 20 dB) was not detected in 800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 1900 MHz and 3000 MHz among selected frequencies. Moreover, the ANOVA showed that these results were not statistically significant. No relevant differences were found in 800 MHz (p=0, 541), 900 MHz (p=0, 353), 1800 MHz (p=0, 885), 1900 MHz (p=0, 649) and 3000 MHz (p=0, 724). An electromagnetic shielding at the desired level was observed in 2100 MHz, 2450 MHz and 2600 MHz among selected frequencies. Furthermore, the ANOVA showed that these results were not statistically significant. No significant differences were found in 2100 MHz (p=0, 106), 2450 MHz (p=0, 207) and 2600 MHz (p=0, 948). The effect of type of metal type and dual-core yarn structure was not determined on electromagnetic shielding.
Conclusion
Developing technology was caused negative side effects. Electromagnetic pollution is not appearing, however, it triggers the diseases in the long term. We are exposed to electromagnetic pollution of our environment even if not direct as it was passive smoking. In recent years, wireless technology is taking the place of wired communication. In this study, the most successful EMSE result was measured in 2, 45 GHz. These frequencies are used for wireless connections. Additionally, their usage is on the increase. A frequency of 2, 45 GHz that is known as the best frequency of the water molecules vibrate is the frequency of the microwave oven. Water molecules are heated by vibrating at high frequencies. Because of this feature (50- 70% of the human body is comprised of water), it can be said that a wireless modem in frequency of 2, 45 GHz will become dangerous to human health as many base stations if it uses at close range and long time. The findings from this study make several contributions to protect against frequency of 2, 45 GHz. The findings from this study indicate that the use of tungsten core yarn in the fabric structure can be an alternative to existing products for electromagnetic shielding.
This research will serve about products containing tungsten for electromagnetic shielding as a base for future works. The obtained results can be summarized as follows.
1. It can be said that elastane did not provide expected positive contribution to dual-core yarns with regards to esthetics properties. Especially, the most negative features were detected in yarn/fabric coded as “D3”. “D3” has the lowest elongation at break and the highest S3 value in comparison to all yarns. The lowest breaking force and tear strength among all fabrics were also determined in “D3” containing tungsten and elastane.
2. There was a clear trend of decreasing for yarn tensile strength depending upon the use of metal wires as the core in the yarn structure. Yarn tensile strength was affected more negatively in the dual-core yarn structure containing elastane in addition to metal wires.
3. Electromagnetic shielding was only obtained with metal wires. In this study, an electromagnetic shielding at the desired level (above 20 dB) was found in the most widely used frequencies (2100 MHz, 2450 MHz and 2600 MHz) in daily life. Fabrics have an inadequate and fluctuant shielding in low starting frequencies. Shielding effectiveness gradually increased after about 2 GHz frequencies. It began to drop rapidly after 3 GHz frequencies.
4. It was apparent that there were significant differences between fabrics containing metal wires and metal-free fabrics (R1 and R2) in terms of EMSE. However, no significant differences were found statistically between each other of fabrics containing metal wires according to the results of variance analysis.
5. Fabrics, including tungsten wires were produced for electromagnetic shielding by providing esthetics and comfort desired from a garment. These fabrics may have also anti-static, antibacterial and anti-stress characters such as copper. Moreover, it is recommended that further research be undertaken in the different fabric structure and design such as the use of tungsten wires in warp direction as well.
References
- Naziroglu M, Tokat S, Demirci S. Role of Melatonin on Electromagnetic Radiation Induced Oxidative Stress And Ca2+ Signaling Molecular Pathways in Breast Cancer. Journal of Receptors and Signal Transduction. 2012; 32: 290-297.
- Ongel K, Gumral N, Ozguner F. The Potential Effects of Electromagnetic Field: A Review. Cell Membranes and Free Radical Research. 2009; 1: 85- 89.
- Ueng TH, Cheng KB. The Leakage Power Density and Electromagnetic Shielding Conductive Woven Fabrics. Journal of Textile Engineering. 2001; 47: 70-76.
- Su CI, Chern JT. Effect of Stainless Steel-Containing Fabrics on Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness. Textile Research Journal. 2004; 74: 51-54.
- Bedeloglu A. Investigation of electrical, electromagnetic shielding, and usage properties of woven fabrics made from different hybrid yarns containing stainless steel wires. The Journal of the Textile Institute. 2013; 104: 1359- 1373.
- Cheng KB, Cheng TW, Nadaraj RN, GiriDev VR, Neelakandan R. Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of the Twill Copper Woven Fabrics. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites. 2006; 25: 699-709.
- Palamutcu S, Ozek A, Karpuz C, Dag N. Electrically conductive textile surfaces and their electromagnetic shielding efficiency measurement. Tekstil ve Konfeksiyon. 2010; 20: 199-207.
- Ozen MS, Sancak E, Beyit A, Usta I, Akalin M. Investigation of electromagnetic shielding properties of needle-punched nonwoven fabrics with stainless steel and polyester fiber. Textile Research Journal. 2013; 83: 849-858.
- Ortlek HG, Gunesoglu C, Okyay G, Turkoglu Y. Investigation of Electromagnetic Shielding and Comfort Properties of Single Jersey Fabrics Knitted from Hybrid Yarns Containing Metal Wire. Tekstil ve Konfeksiyon. 2012; 22: 90-101.
- Ozen MS. Investigation of the Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Carded and Needle Bonded Nonwoven Fabrics Produced at Different Ratios with Conductive Steel Fibers. Journal of Engineered Fibers and Fabrics. 2015; 10: 140-151.
- Jagatheesan K, Ramasamy A, Das A, Basu A. Fabrics and Their Composites for Electromagnetic Shielding Applications. Textile Progress. 2015; 47: 87- 161.
- Więckowski TW, Janukiewicz JM. Methods for Evaluating the Shielding Effectiveness of Textiles. Fibres & Textiles in Eastern Europe. 2006; 14: 18- 22.
- Tezel S, Kavusturan Y, Vandenbosch GA, Volski V. Comparison of electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of conductive single jersey fabrics with coaxial transmission line and free space measurement techniques. Textile Research Journal. 2014; 84: 461-476.
- Safarova V, Tunak M, Truhlar M, Militky J. A New Method and Apparatus for Evaluating the Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Textiles. Textile Research Journal. 2016; 86: 44-56.
- Electrical Resistivity and Conductivity, Resistivity And Conductivity Of Various Materials. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_resistivity_and_conductivity (23.04.2016).
- Tungsten https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tungsten. (13.01.2017).
- Lemus R, Venezia CF. An update to the toxicological profi le for water-soluble and sparingly soluble tungsten substances. Critical Reviews in Toxicology. 2015; 45: 388-411.
- Babaarslan O. Method of Producing a Polyester/Viscose Core-Spun Yarn Containing Spandex Using a Modified Ring Spinning Frame. Textile Research Journal. 2001; 71: 367-371.
- Ortlek HG. Influence of Selected Process Variables on the Mechanical Properties of Core-Spun Vortex Yarns Containing Elastane. Fibres and Textiles in Eastern Europe. 2006; 14: 42-44.
- Bedeloglu A, Sunter N, Yildirim B, Bozkurt Y. Bending and tensile properties of cotton/metal wire complex yarns produced for electromagnetic shielding and conductivity applications. The Journal of the Textile Institute. 2012; 103: 1304-1311.
- Committee for Conformity Assessment of Accreditation and Certification on Functional and Technical Textiles. Specified requirements of electromagnetic shielding textiles. 2003.