
Research Article
Thromb Haemost Res. 2019; 3(1): 1020.
Plateletpheresis: A Comparative Study Between Haemonetics MCS Plus and Spectra Trima
Heba N and Noha BH*
Department of Clinical Pathology (Central Blood Bank), Ain Shams University, Egypt
*Corresponding author: Hassan NB, Clinical Pathology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Abassia, Egypt
Received: January 25, 2019; Accepted: February 26, 2019; Published: March 05, 2019
Abstract
Background and Aim: Platelet collection by apheresis techniques has rapidly increased recently owing to its advantages as reduced disease transmission, alloimmunization, in addition to storage characteristics. In this study we compared two apheresis instruments (Haemonetics MCS plus and Spectra Trima) with regard to Platelet (PLT) yield, Collection Rate (CR), White Blood Cell (WBC) and Red Blood Cell (RBC) contamination for selecting equipment for apheresis units.
Materials and Methods: Eighty data obtained by Haemonetics MCS plus and Spectra Trima systems (40 for each) were randomly selected among donors attending to the Central blood bank of Ain Shams university for blood donation. Platelet yield/session, number of therapeutic doses, collection rate and WBC/ RBC contamination were recorded for each session.
Results: No significant difference was found between 2 instruments regarding pre-apheresis variables; however PLT yield/unit, therapeutic dose and CR showed a higher significant difference (p<0.0001) (p=0.004), being higher with Trima [7.6±1.26 (×1011), 3.47±0.57 and 0.089±0.019 (platelet × 1011/ min)]. RBC contamination was significantly higher in Haemonetics’ products (p=0.0005) in contrast to WBC contamination (p=0.1995).
Conclusion: We concluded that CR and PLT yield values were more by Trima machines than Hemonetics, with no WBC contamination of both instruments’ products.
Keywords: Haemonetics MCS plus; Spectra trima; Collection rate; Plateletpheresis; Platelet yield
Introduction
Platelet Concentrates (PC) derived from whole blood or Single Donor Platelets (SDP) obtained by apheresis (using automated cell separation equipment) are indicated to treat acute hemorrhage secondary to thrombocytopenia or to provide prophylaxis from hemorrhage in patients with bone marrow aplasia [1]. Advances in apheresis technology have made SDP easier to obtain and therefore more plentiful. Some of SDP advantages including reduced disease transmission, alloimmunization, in addition to storage characteristics [2].
The use of apheresis equipment for platelet collection has rapidly increased in recent years, while improvements in apheresis technology are ongoing; some problems do remain, for example, the duration of the procedure and donor discomfort owing to the citrate used for anticoagulation. Therefore, some studies focusing on the comparison of different cell separators [3]. In this study we compared two apheresis instruments (Haemonetics MCS plus and Spectra Trima) with regard to Platelet (PLT) yield / efficiency, and Collection Rate (CR) in a retrospective study. The main goal of the study is to provide data that will be a guide in selecting equipment for apheresis units.
Single donor platelet therapeutic doses a leucocyte-depleted platelet component obtained by platelet apheresis of a single donor, which contains platelets in a therapeutically effective dose suspended in a mixture of plasma (30-40 per cent) and an additive solution (60- 70 percent). It should contain a minimum content of 2 × 1011 platelets [4].
Materials and Methods
Overall 80 data obtained by Haemonetics MCS plus and Spectra Trima systems (40 for each) were randomly selected among donors attending to the Central blood bank of Ain Shams university for blood donation between March 2018 to December 2018. All donors met the Council of Europe Guidelines and Recommendations for apheresis and the standard guidelines established by the AABB [5]. Details of plateletpheresis were explained to each donor who gave due consent before the procedure.
Criteria for eligibility for a single unit (= 2 × 1011) were as follows [5]:
- Weight more than 50 kg
- The interval between procedures of the platelet donations shall be at least 2 days but not more than twice per week.
- The total number of plateletpheresis donations must not exceed 24 times per year.
- Hemoglobin >12.5 g/dl
- Platelet count >150 × 103/μL
- Hematocrit must not be less than 38%.
- Absence of any illness.
- No consumption of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for last 48 hours.
- Negative test for HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and Syphilis.
- Donor weight (Kg).
- Donor height (Cm).
- Donor age.
- Total leucocytic count, hematocrit and platelet count from a pre-donation sample (3mL) collected from the donor in EDTA tube and examined on automated cell counter (Sysmex Corporation, Kobe, Japan).
- Time (minutes) consumed in each session.
- Platelet count from the sample pouch of the session’s final product after one -hour post- donation [6].
- Calculated volume of the product [Total weight-net weight of the bags] / 1.03.
- The following equations were calculated:
Vital signs were monitored at the beginning and end of each procedure; also the donors were monitored for adverse events during the procedures as hypotension and hypocalcaemia.
For each session, we recorded the following data:
Platelet Yield/ Session=Volume of the product (ml) × Product count (platelet/μl) × Conversion factor volume (1000 μL/ mL)
Number of therapeutic doses = Platelet yield / Therapeutic dose (2 × 1011) [4].
Collection rate (CR) = Platelet yield/separation time [7].
Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism 8.0.0 program as employed to fit our data. Data were expressed as the median (range) or mean ± Standard Deviation (SD). The devices were compared using an unpaired t-test or the Mann-Whitney U-test with regard to pre- and post-apheresis blood variables and product variables. The level of significance was set at P <0.05.
Results
The general donors’ characteristics, pre-apheresis laboratory data (platelet count and hematocrit) in addition to platelet apheresis procedure and product of in total 80 donors (number=40 in each instrument; haemonetics and trima) are given in (Table 1).
Parameters (Mean±S.D)
Haemonetics (N=40)
Trima (N=40)
P-value
Significance
(a) Donors’ characteristics and pre-apheresis laboratory data:
Age, years
30.5±7.2
29.7±6.7
0.5443
NS
Weight, kg
83.4±13.5
85.3±20
0.6197
NS
Height, cm
173.3±6.8
172±18.3
0.6802
NS
Hct %
44.5±2.5
45±2
0.3517
NS
PLT count(×103/μL)
262±35
263±42
0.8875
NS
(b) Plateletpheresis procedure and product data:
Plasma volume collected, mL
410.6±72.14
505±84.38
Platelet count in product (×103/μL)
1314±226
1536±220
PLT yield (×1011)
5.28±1.18
7.67±1.26
<0.0001
HS
Therapeutic dose
2.37±0.54
3.47±0.57
<0.0001
HS
Cycle time, min
87.4±9.7
84.6±12.56
0.2683
NS
Collection rate (PLT×1011/min)
0.06±0.015
0.089±0.019
0.0436
S
WBC (×106/unit)**
0.032±0.013-0.089)
0.031(0-0.05)
0.1995*
NS
RBC (million/cmm3)**
0.1(0.05-0.2)
0.057(0.01-0.097)
0.0005*
S
Hct: Hematocrit; PLT: Platelet, WBC: White Blood Cells; RBC: Red Blood Cells, **: median (interquartile range), S.D: Standard Deviation; NS: Non-Significant; HS: Highly Significant; S: Significant; *: Mann Whitney.
Table 1: Comparative parameters between the two platelepheresis instruments (Haemonetics vs Trima).
Comparison of pre-apheresis variables between the 2 groups revealed no statistical significant difference in terms of weight (P=0.6197), height (P=0.6802) and age (P=0.5443) of the donors, also there was no significant difference concerning pre-apheresis laboratory data (platelet count and hematocrit); p=0.8875 and 0.3517, respectively. Concerning procedure and product data between 2 groups; both platelet yield/unit and therapeutic dose showed a highly significant difference (p<0.0001 for each) being higher with trima compared to haemonetics; 7.6±1.26 (×1011) and 3.47±0.57 versus 5.28±1.18 (×1011) and 2.37±0.54, respectively. Although there was no significant difference in separation (cycle) time (p=0.26) between 2 groups but the Collection Rate (CR) was significantly (p=0.004) higher in trima compared to haemonetics; 0.089±0.019 (platelet × 1011/min) versus 0.06±0.02, respectively (Table 1) (Figure 1). On comparing the contamination of apheresis product with WBC and RBC between 2 groups, it was found that RBC was significantly higher (p=0.0005) in haemonetics’product than trima; with median 0.1 (million/cmm³) versus 0.057 (million/cmm³), respectively; however WBC contamination revealed no significant difference (p=0.1995) between 2 product groups.
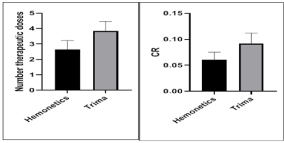
Figure 1: Therapeutic doses and CR by Hemonetics and Trima.
Discussion
SDP offers major advantages over RDP, particularly when improved patient care is given primary emphasis [8]. Although a variety of apheresis devices are currently available on the market for plateletpheresis procedures, there are scant studies that compared different machines with each other. In our study, we compared Haemonetics MCS plus and Trima Accel plus (Both are Singleneedle system) regarding Platelet (PLT) yield, Collection Rate (CR), WBCs and RBCs contamination. We also kept in consideration that donors’pre-apheresis variables such as platelet count, weight and height were not significantly different between the two groups. In today’s world, productivity, i.e. ‘doing more in less time’, is as key feature as yield when evaluating equipment [9]. So the collection rate was an important entity to be included in the study.
We found that Trima had a significantly higher CR (0.089±0.019 vs. 0.06±0.015). Similarly Yin et al [10] reported that the CR was higher with the Trima device than the Haemonetics (0.052±0.0133 vs. 0.038±0.0083 × 1011/min). On the other hand Keklik et al [7] stated that the CR was significantly higher with the Haemonetics compared to the Trima (0.076±0.016 vs. 0.065±0.015 (PLT × 1011/min) respectively; P <0.001). They also stated that the PLT yield/unit was higher with the Haemonetics (4.4±0.8 vs. 3.9±0.8 × 1011, P=0.001). On the contrary our PLT yield was (5.28±1.18 vs. 7.67±1.26, <0.0001). In another study for evaluating the Haemonetics cell separator; Keklik et al [11] stated that the machine efficiently collected apheresis platelets with median PLT yields of 3.7 × 1011, and mean CR of 0.063±0.013 × 1011/min. Also, they mentioned that the device allowed the collection of White Blood Cell (WBC) reduced plateletpheresis with mean 0.07±0.15 × 106 WBC content with no serious donor or recipient reactions occurred. Furthermore, in other literature for evaluating the Trima cell separator, The Trima Accel cell separator efficiently collected platelets with median PLT yields of 3.7×1011 and mean CR of 0.096±0.012 × 1011/min [12].
In addition to PLT yields and CR, consistent leukoreduction is a key element in platelet pheresis [13]. There are no previous literatures that compared Tima and Hemonetics as regard the RBCs and WBCs contamination. Both machines gave leuco-depleted products (<1×106) as mentioned by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) [14], with no statistical significant difference between them. On the other hand, we found that RBC was significantly higher (p=0.0005) in haemonetics’ products than trima.
Conclusion
Although we concluded that CR and PLT yield values were more by Trima machines than Hemonetics, it’s preferable that the price/ therapeutic dose should be calculated. So we recommend that further future studies should include the price in the comparison.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge the art-work of Dr. Wael Mahmoud, the manager of Central Blood Bank, Faculty of medicine, Ain Shams University.
References
- Ness P, Braine H, King K, Barrasso C, Kickler T, Fuller A, et al. Single-donor platelets reduce the risk of septic platelet transfusion reactions. Transfusion. 2001; 41: 857-861.
- Chirag A, Snehal G, Kamal A, Amrish N, Mayur A, Jitendra N, et al. Transfusion effect of random donor platelet and single donor platelet in thrombocytopenic patients at tertiary care hospital of South Gujarat. International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences. 2017; 5: 3033-3037.
- Das SS, Chaudhary RK, Shukla JS. Factors influencing yield of plateletpheresis using intermittent flow cell separator. Clin Lab Haematol. 2005; 27: 316-319.
- Guide to the preparation, use and quality assurance of blood components, 18th European Committee, 2015.
- Price TH. Provision of single donor platelet transfusions: Patient and procedure perspectives. In: Apheresis: Principals and Practice. McLeod BCPT, Weinstein R, eds. Bethesda: AABB Press. 2003; 185-197.
- Council of Europe Guide to the preparation, use and quality assurance of blood components, 10th Strasbourg: Council of Europe Press, 2004.
- Keklik M, Keklik E, Kalan U, Ozer O, Arik F, Sarikoc M. Comparison of Plateletpheresis on the Haemonetics and Trima Accel Cell Separators. Ther Apher Dial. 2018; 22: 87-90.
- Tendulkar A, Rajadhyaksha SB. Comparison of plateletpheresis on three continuous flow cell separators. Asian J Transfusion Science. 2009; 3: 73-77.
- Slichter SJ. Evidence-Based Platelet Transfusion Guidelines. Hematology. 2007; 2007: 172-178.
- Yin G, Xu J, Shen Z, Wang Y, Zhu F, Lv H. The relationship of platelet yield, donor’s characteristic and apheresis instruments in China. Transfusion and Apheresis Science. 2013; 49: 608-612.
- Keklik M, Keklik E, Korkmaz S, Aygun B, Arik F, Kilic O, et al. Effectiveness of the haemonetics MCS cell separator in the collection of apheresis platelets. Transfusion and Apheresis Science. 2015; 53: 396-398.
- Keklika M, Korkmaza S, Kalanb U, Sarikocc M, Keklik E. Effectiveness of the Trima Accel cell separator in the double dose plateletpheresis. Transfusion and Apheresis Science. 2016; 55: 240-242.
- Edwin A, Jeffrey L, Alvaro A. Paired comparison of Gambro Trima Accel versus Baxter Amicus single-needle plateletpheresis. Transfusion. 2004; 44: 1612-1620.
- Hardwick J. Blood processing. ISBI science series; 2008; 3: 148-176.