
Research Article
Thromb Haemost Res. 2019; 3(2): 1027.
Combined Use of Rapid Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) Activity, VWF-Propetide and Classical VWF Assays for Improved Diagnosis of Von Willebrand Disease Type 1, 2N and 2E Due to Mutations in the D1, D2, D’, D3 and D4 Domains of the VWF Gene
Michiels JJ1,2,3*, Smejkal P1, Mayger K2, Moore G2, Budde U4, Berneman Z5, Vangenechten I5, Gadisseur A5, Blatny J6 and Penka M1
1Department of Clinical Hematology, University Hospital and Department of Laboratory Methods, Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic
2Department of Haemostsis & Thrombosis, Viapath Analytics at Guy’s & St Thomas’ Hospitals, UK
3Goodheart Institute in Nature Medicine & Health, Blood Coagulation and Vascular Medicine Center, European Free University Network, Netherlands
4Central Laboratory, Asklepios Kliniken, Germany
5Department of Hematology, University Hospital Antwerp, Belgium
6Department of Pediatric Hematology, Children’s University Hospital Brno, Czech Republic
*Corresponding author: Jan Jacques Michiels, Department of Clinical Hematology, University Hospital and Department of Laboratory Methods, Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University Brno, CZECH Republic, Goodheart Institute in Nature Medicine & Health2, Blood Coagulation and Vascular Medicine Center, Freedom of Science, Art and Education, European Free University Network, Netherlands, Department of Haemostsis & Thrombosis, Viapath Analytics at Guy’s & St Thomas’ Hospitals, London UK
Received: July 05, 2019; Accepted: August 02, 2019; Published: August 09, 2019
Abstract
Introduction: The Brno Antwerp and London VWD investigators used a complete set of Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) assays for the diagnosis and classification of Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) according to European Clinical Laboratory and Molecular (ECLM) criteria (Clinical Applied Thrombosis/ Hemostasis 2017; 23: 518).
Aims: Thr Brno Antwerp London VWD investigators directly compared the rapid von Willebrand factor (VWF) assays VWF:GPIbM and VWF:GPIbR in Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) against the complete set of VWF assays using the ECLM criteria as the gold standard for VWD classification anno 2018. Between 2008 and 2018 we prospectively studied the Brno-Antwerp cohort with VWD type 1, 2N and 2 due to mutations in the D1, D2, D’and D3 domains of the vW gene.
Methods: The complete set of rapid and classical VWF assays include Platelet Function Analyser Closure Time (PFA-CT) Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) Antigen (Ag), Ristocetine Cofactor activity (RCo), Collagen Binding (CB), Propeptide (pp), Ristocetine Induced Platelet Aggregation (RIPA), the rapid VWF activity assay VWF: GPIbM based on glycoprotein Ib (GPIb) binding to particles coated with G233V and M239V mutants in the absence of ristocetin, the rapid VWF: GPIbR assay in the presence of ristocetine, and the responses to DDAVP of FVIII: C and VWF parameters to pick up secretion and/or clearance defects of VWF.
Results: The VWF: RCo/VWFAg, VWF: GPIbM/VWFAg and VWF: GPIbR/ VWF: Ag ratios are completely normal (above 0.7) in all variants of VWD type 1 and Low VWF. The VWF: RCo/VWF: Ag, GPIbR/VWF: Ag and GPIbM/VWF: Ag ratios vary around the cut off level of 0.70 in VWD due to multimerization defect in the D3 domain and therefore diagnosed as either type 1 E or type 2E VWD. Type 1 due to a heterozygous mutation in the D1 domain is featured by persistence of proVWF as the cause of VWF secretion/multimerization and FVIII binding defect mimicking VWD type 3 together with decreased values for VWFpp, VWFpp/Ag ratios. The majority of 22 different missense mutations in the D3 domain are of type 1 or 2 E multimerization defect usually associated with an additional secretion defect (increased FVIII: C/VWF: Ag ratio) and or clearance defect (increased VWFpp/Ag ratio). The majority of VWF mutations in the D4 and C1 to C6 are VWD type 1 SD with smeary (1sm) or normal (1m) multimers with no or a minor clearance defect. The heterozygous S2179F mutation in the D4 domain is featured by VWD type 1 Secretion and Clearance (SCD). The introduction of the rapid VWF:GPIbM or VWF:GPIbR assays as compared to the classical VWF: RCo assay did change VWD type 2 into type 1 in about 10 to 12%.
Conclusion: A complete set of sensitive FVIII: C and the VWF assays VWF; Ag, VWFGPIbM ot GPIbR, VWF: PP and VWF multimer analysis are mandatory for a correct diagnosis and classification of VWD type 1, 2N and 2 E due to mutations in the D1, D2, D’and D3 domains of the VWF gene.
Keywords: Von willebrand disease; Von willebrand factor; Antigen
Introduction
The ISTH classification of VWD patients in Europe clearly distinct VWD 2A (lumping IIA, II E, IIC, IID) with loss of large and increased triplet banding of VWF multimers and VWF ratio ‹ 0.7; from 2B with loss of large and increased triplet banding of VWF multimers, VWF:RCo/Ag ratio ‹0.7 but increased RIPA; 2M with decreased RIPA and normal or smeary vWF multimers, from 2N with FVIII: C/VWF Ag ration ‹0.5 (Figure 1) [1-12]. The ECLM criteria as the gold standard for VWD classification anno 2018 in Table 1 use a complete set of VWD disease related assays including PFA-CT, VWF: Ag, VWF: RCo, VWF: GPIbM and or VWF: GPIbR, VWFpp, the ratios for FVIII: C/VWF: Ag, VWF: RCo/Ag, VWF: GPIbM/ Ag, VWF: GPIbR/Ag, VWFpp/Ag, VWF multimeric analysis in low medium to high SDS resolutaion gel, and detection of the molecular defect (Table 1) [1-12].
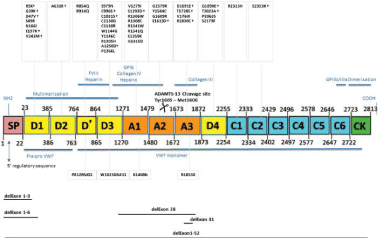
Figure 1: Structure and function of Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) protein and
localization of VWF mutations in the Brno cohort of VWD patients (Source
Vangenechten et al. [12]).
In this real field report Michiels, Smejkal, Mayger prospectively analysed the performance of the rapid von Willebrand INNOVANCE activity assay based on GPIb binding to particles coated with gain of function mutants G233V and M239V (VWF: GPIbM assay) in the absence of ristocetin and the rapid VWF: RCo HemoSIL (VWF: GPIbR) in the presence of ristocetin as compared to classical VWF ristocetine cofactor (VWF: RCo) and collagen binding (VWF: CB) ELISA assay in the large Brno cohort of VWD patients as the direct extension of two precious studies by Vangenechten et al. Between 2008 and 2018 we prospectively collected the Brno-Antwerp cohort of VWD patients and measured the rapid and classical VWF assays in 204 patients with suspected VWD from 95 families. VWD was diagnosed according to the ISTH/EAHAD and European Clinical Laboratory and Molecular (ECLM Table 1 Figure 1) criteria for the classification of all possible variants of VWD. Molecular characterization and classification of VWD started in each patient started with the detection and location of the molecular defect to each of the D1, D2, D”, D3, A1, A2, A3, D4, C106 and the CK domains of the VWF gene are recently described by Inge Vangenegten (Figure 1) [11,12]. In these studies the Brno-Antwerp VWD investigators applied the complete set of all VWF parameters in one and the same blood sample of the individual patient (Table 1) [11,12]. Standardized molecular characterisation of VWD patients allows precise classification into the correct biological type of VWD, the identification of carriers of VWD type 3 and severe type 1 in familial genetic studies and any other molecular defect in the cohort of 204 cases with high suspicion of having VWD according tot he ISTH/ EAHAD criteria. The gold standard approach of the updated really 2020 nor 2018? ECLM classification in Table 1 wil become particularly relevant and even mandatory for genetic counselling for all variant of VWD with high bleeding risk, but particular in severe recessive type 1 and type 3 VWD. Moreover, the 2020 ECLM classification facilitates the evaluation of purified human or recombinant VWF concentrates for targeted prophylactic requirements, targeted treatment options of bleeding manifestations and clinical orientation in precision and personal medicine, particularly in risky situations like trauma and surgery for bleeding prevention.
Methods
Laboratory diagnosis, phenotyping and genetic analysis of vWD patients were performed by Vangenechten et al. (Figure 1 [11,12]) and principles of rapid von Willebrand activity assays VWF: GPIbM and VWF; GPIbR (Figure 2 Source Mayger et [13]) as described in great detail by Vangenegten et al. [11,12].
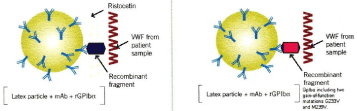
Figure 2: Principle of the HemosIL VWF:GPIbR assay (Werfen, Warrington,
UK) and the INNOVANCER VWF: G.PIbM assay (Sysmex UK, Milton Keynes,
UK) Source Katarzyna et al. [13].
Recessive von Willebrand Disease: VWD
Domain
Recessive severe type 3 double null mutation VWF gene
Double null
Recessive severe or pronounced type 1
Homozygous or Double missense
Recessive severe type 1 VWD-hemophilia A mimicking type 3
D1
Recessive 2N FVIII:c/VWF:Ag ratio <0.5. FVIII-VWF binding defect
D’-D3
Recessive 2C FVIII:C.VWF:Ag increased, secretion mulimerization defect
D2
Dominant von Willebrand Disease VWD
Domain
2E: type 1/2, loss of large multimers, no triplets and increased clearance
D3
2A: Loss of large MM due to increased VWF proteolysis, RIPA N or decreased
A2
2M: Decreased RIPA, VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag ratio, normal VWF:CB/VWF:Ag ratio
A1
2B: Increased RIPA (0.8mg/ml) and thrombocytopenia with VWD type 2
A1
2CBD Collagen type, VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag and VWF:CB/VWF:Ag ratio < 0.7
A3
1m or 1sm
D4 C1-6
2D: dimerization defect loss large MM intervening bands and absence of triplets
CK
Type 1: VWF:Ag‹ 0.30 U/mL normal VWF:CB/Ag and VWF:Rco/Ag ratio ›0.7 Low VWF type 1: VWF: Ag levels ›0.30-0.60 U/mL due to dominant mutations in the D4, C1-6 domain and carriers of null or missense mutation VWD recessive type 3 and 1 all over the VWF gene (blood group O dependent bleeding phenotype, Michiels et al. [2]. Type 2: Decreased VWF: RCo/VWF: Ag ‹ 0.7 for 2A, 2B, 2C, 2E, 2D and 2M equal to decreased VWF:GPIbR ot VWF: GPIbM ‹ 0.7 with some discrepancies in 2B and 2M Type 3: VWF: Ag and FVIII:C undetectable or very low double null VWF gene mutation. Severe type 1 hemophilia A phenotype due to mutations in the D1 domain (this report). Severe type 1 VWD VWF: Ag and VWF: RCo detectable, but increased FVIII:C/VWF ratio due to homozygous or double heterozygous missense mutation for a secretion defect.
Results
Recessive double heterozygous severe type 1 and heterozygous/WT type 1 VWD due to mutations in the D1 domain
The double heterozygous G39R/P812Rfs and G197/P812Rfs and homozygous P812Rfs/P812Rfs due to mutations in the D1 and D’domain are diagnosed as VWD type 3 with detectable FVIII: C and VWF: Ag levels (Table 2). The heterozygous D1 mutations G39R/ WT, D47V/WT, S49R, and N166I/WT in the VWF gene could be diagnosed as VWD type 1 or 2 irrespective of blood group (Table 2) had decreased values for VWF: RCo (0.06-0.45), VWFpp (0.15-0.50), the VWFpp/Ag ratios were decreased between 0.63-0.99 and below 1.0 with one exception. The PFA-CT times in heterozygous/WT mutation in the D1 domain were prolonged to strongly prolonged with values above 300 seconds in all (Table 2). VWD type 1 due to a heterozygous mutation in the D1 domain is featured by a secretion/ multimerization defect with the persistence of proVWF in rVWF expression studies (Figure 1). Four of 12 VWD type cases with heterozygous D1 mutations had decreased ratios for VWF: RCo/ VWF: Ag indicating type 2 VWD, but 12 of 13 cases had normal ratios for VWF: GPIbM/Ag and VWF: GPIbR consistent with type 1 VWD.
Mutation
FVIII:C
VWF:Ag
VWF:RCo
GPIbM/R
VWF:pp
RCo/Ag
GPIbM/R
VWFpp/
PFA-CT
ISTH/ECLM
D1 Domain
U/dL
U/dL
U/dl
U/dL
U/dl
CB/Ag
Ag ratio
Ag ratio
EPI ADP
Blood Group
G39R/P812fs
0.03
0.02
.
.
zero
na
na
na
nt
type 3
E197K/P812fs
0.02
0.03
.
.
zero
na
na
na
nt
type 3
P812Dfs/hom
0.03
0.02
.
.
zero
na
na
na
nt
type 3
G39R/WT
0.58
0.31
0.45
nt/nt
0.22
1.45
nt
0.70
nt
type 1 O
G39R/WT
0.55
0.52
0.40
0.47/0.47
0.42
0.77
0.90/0.90
0.80
>300/199
type 1 B
G38R/WT
0.34
0.48
0.30
0.31/0.33
0.33
0.63
0.64/0.69
0.69
>300/nt
type 2 B
D47V/WT
1.14
0.55
0.39
0.40/0.41
0.28
0.71
0.73/0.74
0.51
221/176
type 1 B
D47V/WT
0.52
0.26
0.18
0.20/0.24
0.21
0.69
0.80/0.93
0.81
284/198
type 2/1 O
S49R/WT
0.99
0.81
0.60
0.69/0.84
0.51
0.74
0.85/1.04
0.63
261/118
type 1 B
S49R/WT
0.47
0.45
0.35
0.22/0.37
0.39
0.78
0.74/0.81
0.87
262/252
type 1 O
N166I/WT
0.52
0.39
0.37
0.39
0.95
0.99
>300/196
type 1 A
N166I/WT
0.37
0.15
0.18
0.22
1.20
1.45
212/165
type 1 .
N166I/WT
0.16
0.15
0.06
0.15
0.40
0.89
>300/292
type 2 .
N166I/WT
0.93
0.45
0.37
0.36/0.32
0.34
0.82
0.80/0.71
0.76
>300/161
type 1 B
N166I/WT
1.09
0.43
0.27
0.41/0.43
0.39
0.51
0.75/0.81
0.74
>300/>300
type 2/1 O
E197K/WT
1.83
0.82
0.81
0.78/0.78
0.56
0.99
0.95/0.95
0.68
nt
type 1 A
Table 2: Results of VWD type 3 due to double heterozygous mutations in the D1/D’domain and in heteroygous/WT VWD duet o mutations in the D1 domain of the VWF gene. Results of VWD type 3 patients and heterozygous carriers for a D1 Domain mutation.
The heterozygous G39R/WT, D47V/WT, S49R/WT, N166I/WT and 197/WT mutations are diagnosed as VWD type 1 with decreased VWF: pp values, decreased VWFpp/VWG: Ag ratios beow 1.00 (one exception) and have pronounced prolongation of the PFACT irrespective of blood group O vs Non-O (Table 2). The E197K/ WT mutation was diagnosed as normal (Table 2). The V343M/WT mutation in the D1 domain reported with dominant mild VWD type 1m (Table 3). The V343M heterozygous/WT mutation in the D1 domain is diagnosed s VWD type 1with dereased VWF: PP values and near normal pFA-CT (Table 3).
FVIII:C
VWF:Ag
VWF:RCo
GPIbM/R
VWF:pp
RCo/Ag
VWF:CB/
VIII/VWF
PFA-CT
ISTH/ECLM
D1 Domain
U/dL
U/dL
U/dl
U/dL
U/dl ratio
CB/Ag
Ag ratio
Ag ratio
EPI ADP
VWD type
V343M/WT
0.46
0.38
0.32
0.32 0.29
0.42 1.10
0.84 1.19
0.85 0.76
1.21
nt
1 M Fig
V343M/WT
0.50
0.38
0.30
0.32 0.31
0.56 1.60
0.86 1.10
0.90 0.87
1.32
168 134
1 M
D2 Domain
A631R/WT
0.28
0.34
0.11
0.19 0.26
0.44 1.30
0.32 0,68
0.55 0.76
0.82
>301 >300
2C Fig
A631R/WT
0.32
0.34
0.02
0.18 0.18
0.57 1.67
0.06 0.74
0.53 0.54
0.94
nt
2C
Table 3: Results of dominant VWD 1 due to V343M/WT mutation in the D1 and dominant VWD 2C due to A631R/WT mutation in the D2 domain of the VWF gene.
The A631R heterozygous mutation in the D2 domain is diagnosed as VWD 2C with decreased VWF: pp values and prolonged PFA-CT (Table 3).
VWD 2N due to VWF D’ domain mutations
The heterozygous/WT D’ mutation P812rfs/WT mutation in nine were diagnosed as VWD type 1 in seven and type 2 in two using the classical VWF assays and diagnosed as type 1 in eight and type 2 in one using the VWFGPIbR and VWF:GPIbM assays (Table 4). The heterozygous P812Rfs/WT mutation is featured by decreased VWF: Ag values (0.31-0.53 U/dL), normal VWFpp/Ag ratios (0.64-1.19) and moderate to pronounced prolonged PFA-CT. In contrast, four cases of heteozygous R854Q/WT carriers of FVIII binding defect mutations had normal VWF values diagnosed as normal with normal PFA-CT. Interestingly double heterozyosity of R854W/Y1584C was associated with symptomatic type 1 VWD in two patients respectively with decreased VWF:RCo (0,28- 0.49 U/dL) and prolonged PFA-CT (Table 4).
Mutation
FVIII:C
VWF:Ag
VWF:RCo
GPIbM/R
VWF:pp
RCo/Ag
GPIM/Ag
Blood
PFA-CT
ISTH/ECLM
D' domain
U/dL
U/dL
U/dl
U/dL
U/dl Ratio
VIII/Ag r
GPIR/Ag
group
EPI ADP
VWD type
P812rfs/
homozyg
0.03
0.01
nt
nt
3
P812rfs/WT
0.30
0.53
0.63
0.43 0.46
0.45 0.85
1.19
0.81 0.87
nt
nt
1
P812rfs/WT
0.78
0.39
0.31
0.40 0.39
0.55 1.41
0.79
1.03 0.99
O
nt
P812rfs/WT
0.23
0.32
0.35
0.32 0.33
0.25 0.83
1.09
0.99 1.04
B
nt
1
P812rfs/WT
0.88
0.31
0.29
0.36 0.31
0.29 0.69
0.94
1.18 0.99
O
257 168
1
P812rfs/WT
0.83
0.36
0.23
0.30 0.28
0.23 0.72
0.64
0.82 0.78
O
275 177
21
R812rfs/WT
0.50
0.30
0.21
0.22 0.28
0.37 1.19
0.70
0.74 0.93
O
>300 259
1
P812rfs/WT
0.64
0.42
0.28
0.41 0.32
0.32 0.89
0.67
0.98 0.77
O
258 157
21
R812rfs/WT
0.49
0.38
0.43 0.45
0.78
0.88 0.92
A
186 154
1
P812rfs/WT
0.48
0.53
0.29 0.33
1.10
0.60 0.68
O
>300 >300
12
P812rfsR854Q
0.12
0.28
0.28
0.22 0.31
0.25 0.89
0.96 0.43
0.92 1.12
O
290 223
2N
P812rfsR854Q
0.23
0.49
0.51
0.54 0.52
0.39 0.96
1.04 0.47
1.10 1.06
nt
nt
2N
P812rfsR854Q
0.22
0.61
0.44
0.61 0.63
0.36 1.02
0.72 0.32
1.01 1.04
nt
nt
2N
R854Q/WT
0.79
0.68
0.61 0.62
0.74 0.94
0.86
0.77 0.79
O
126 nt
Carrier 2N
R854Q/WT
0.71
0.80
0.81
0.84 0.80
0.70 0.81
1.01 0.89
1.05 1.00
O
139 nt
Carrier 2N
R854Q/WT
0.58
0.58
0.66
0.62 0.68
0.52 0.89
1.14 1.00
1.07 1.18
nt
nt
Carrier 2N
R854Q/WT
0.61
0.71
0.57
0.75 0.66
0.57 0.81
0.80 0.86
1.06 0.93
nt
nt
Carrier 2N
R854QY1584C
0.35
0.30
0.28
0.26 0.31
0.93 1.17
0.87 1.03
A
277 nt
1
R854QY1584C
0.42
0.46
0.49
0.54.6 0.53
1.07 0.91
1.17 1.15
O
277 nt
1
Table 4: Results of dominant heterozygous mutated VWD in the D’ domain.
The VWF: PP values are decreased in 9 cases heteozygous/WT for P812Rfs/WT (range 0,25-0.55) and in 3 VWD 2N cases double heterozygous for P812rfs/R854W (range 0.25-0.39) as compared to heterozygous R854W/WT mutation (range -.52-0.70).
VWD type 1, 1C, 2E and 2E clearance type (2E C) due to VWF D3 domain mutations
Using a complete set of six sensitive VWF assays (VWF: Ag, VWF: RCo, VWF: CB, VWF: GPIbM, VWF: GPIbR, VWFpp and medium resolution VWF multimeric analysis) VWD patients with the mutation W1144G/WT in 6 patients and Y1146C/WT in two patients are diagnosed as pronounced type dominant VWD 1 E or 2 E according to multimeric pattern associated with increased clearance (C) as documented by increased VWFpp/Ag ratios above 2.1 (Table 5). The performances of the VWF: RCo and VWF: CB versus VWF: GPIbM and VWF; GPIbR in typing VWD 1 or 2 did not essentially differ from each other regarding to the classification type 1 or 2 according to ISTH and ECLM classifications (Table 1).
Mutation
VWF:Ag
VWF:RCo
VWF:CB
GPIbM
GPIbR
RCo/Ag
GPIbM/Ag
VWFpp/
ECLM
GPIbM
D3
U/dL
U/dL
U/dL
U/dL
U/dL
vs CB/Ag
GPIbR/Ag
Ag ratio
diagnosis
GPIbR
ratios
ratios
R1205H
0.10
0.06
0.29
0.05
0.09
0.60 2.90
0.50 0.90
7.20
1C
1C
R1205H
0.15
0.10
0.26
0.05
0.09
0.67 1.76
0.35 0.59
4.87
1C
1C
W1144G
0.76
0.62
0.72
0.88
0.83
0.82 0.95
1.16 1.10
0.86
1E
1E
W1144G
0.24
0.16
0.20
0.17
0.19
0.67 0.82
0.70 0.79
2.25
1/2 EC
1EC
W1144G
0.13
0.07
0.06
0.06
0.59 0.46
0.49
3.19
2 EC
2EC
W1144G
0.19
0.14
0.12
0.10
0.18
0.74 0.61
0.54 0.94
3.20
1/2 EC
2/1 EC
W1144G
0.22
0.04
0.14
0.15
0.18
0.18 0.63
0.69 0.80
2.57
2EC
2/1 EC
W1144G
0.32
0.12
0.17
0.15
0.22
0.37 0.54
0.47 0.67
2.79
2EC
2 E C
Y1146C
0.18
0.09
0.07
0.09
0.12
0.50 0.39
0.51 0.67
2.78
2EC
2 E C
Y1146C
0.14
0.11
0.09
0.13
0.16
0.78 0.93
0.94 1.13
4.43
1EC
1 E C
S2179F D4
0.12
0.06
0.09
0.10
0.11
0.50 0.74
0.84 0.95
3.92
1mC
1mC
Mutation
VWF:Ag
VWF:RCo
VWF:CB
GPIbM
GPIbR
RCo/Ag
GPIbM/Ag
VWFpp
ECLM
GPIbM
U/dL
U/dL
U/dL
U/dL
U/dL
vs CB/Ag
GPIbR/Ag
/Ag rat
diagnosis
GPIbR
S979N
0.52
0.34
0.37
0.22
0.28
0.63 0.66
0.41 0.53
2.00
2E
2E
S979N
0.44
0.23
0.28
0.18
0.24
0.38 0.86
0.40 0.56
2.04
2E
2E
S979N
0.24
0.15
0.16
0.17
0.14
0.29 0.32
0.73 0.60
1.09
2E
1E 2E
S979N
0.26
0.10
0.22
0.10
0.16
0.65 0.71
0.61 0.77
1.20
2E
2E 1E
S979N
0.35
0.10
0.11
0.14
0.16
0.52 0.64
0.40 0.47
1.41
2E
2E
S979N
0.37
0.08
0.26
0.18
0.39
0.22 0.70
0.48 1.04
0.65
2E
2E 1E
S979N
0.37
0.05
0.17
0.19
0.18
0.46 1.38
0.52 0.49
1.38
2E
2E
BS/ECLM
ABO PFA-CT EPI vs ADP
R924Q
0.73
0.72
0.50
0.68
0.67
0.99 0.68
0.94 0.93
0.89
BS Zero/ N
nt nt nt
R924Q
0.57
0.50
0.45
0.48
0.51
0.88 0.80
0.83 0.83
1.35
BS2/ Low 1
O 150 nt
R924Q
0.41
0.41
0.26
0.37
0.33
1.00 0.64
0.89 0.80
2.08
BS2/ Low 1
O 150 nt
R924Q
0.89
0.90
0.71
0.91
0.77
1.01 0.80
1.01 0.87
1.00
BS Zero/ N
A 246 130
R924Q
0.84
0.88
0.82
0.92
0.79
0.98 1.01
1.10 0.94
1.01
BS Zero/ N
Nt 179 132
D4 Domain
P2063S/WT
0.57
0.53
0.53 0.51
0.59 1.03
0.93 0.79
1.15 1.13
1.19
O
146 nt
11m
Table 5: Results in VWD patients due to mutations in the D3 domain.
All VWD patients with the S979N/WT mutation were typed as 2E with normal VWFpp/VWF: Ag ratios (0.65-2.04) indicating the absence of a clearance (C) defect (Table 5). The R924G/WT mutation in 5 asymptomatic cases with low or normal Bleeding Score (BS) had variable VWF values between 0.26 to 0.89 U/dL but normal VWFpp/ Ag and VWF:RCo/Ag ratios and normal or near normal PFA-CT. This observation is in line with the UK Arg924Gln mutation study.
As shown in Table 4, out of 51 cases with Low VWF or normal VWF but no causative VWF mutation detectable or no evidence for VWD related to PFA-CT and blood group O vs non-O four cases (8%) changed from phenotype 2 to 1 using the VWF: GPIbM/Ag or VWF: GPIbR/Ag ratio compared to the classical VWF: RCo/Ag ratio.
Discussion
Yin et al. documented that homozygous and double heterozygous mutations in the D1 domain including G39R, D141N, D141Y, K157E, C379G do not split off VWFpp from proVWF that retains in the ER result in a severe secretion defect and loss of D’D3 multimerization with the clinical phenotype of severe VWF and FIII: C deficiency [14]. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of double heterozygous mutations G39R/D141N, K157E/C1165R in the D1 domain in the study of Yin et al. [14] are featured by recessive severe type 1 VWD (Rec 1) secretion defect and FVIII binding defect. Mutations in the D1 domain do not split off VWFpp from proVWF and retain proVWF in the Endoplasmatic Reticulum (ER), which is associated with severe secretion and intracellular multimerization defect and no binding of FVIII: C in their homozygous or double heterozygous mutated state. This combined recessive severe type 1 VWD/haemophilia a phenotype is distinct from VWD type 3, VWD type 2C and from dominant type 1 secretion caused by heterozygous C379G/WT in the D1 domain (Table 2). The persistence of proVWF in recombinant VWF (rVWF) of mutated G39R, D141N, K157E and C379G of the D1 domain is associated with the lack of FVIII binding to VWF the D’ domain (‹5%) and complete lack of multimerization of G39R, D141N and K157E mutants and partial lack of of multimerization of the C379G mutant. The missense rVWF D141N, K157E and C379G mutants showed a less severe but pronounced secretion and multimerization defect with a bold pro-VWF protomer as compared to WT rvWF. In the study of Yin et al G39R/D141N D1-D1 mutation is associated with VWD severe type 1.HA due severe secretion en multimerization defect of pro-VWF with absence of VWF multimers in plasma due to multimerization defect of pro-VWF that retains in the ER as the explanation of severe secretion defect. The K157E/C1165R D1/D3 mutation is associated with severe type 1/HA due to severe secretion defect and multimerization defect. The mutation G39R/D141N and K157E/C1165R are associated with severe type 1/HA mimicking type 3 VWD [14]. Two brothers in the study of Yin et al with heterozygous C379G/WT mutated cases in the D1 domain are could be phenotyped as dominant type 1 secretion and multimerization defects with lack of large VWF multimers due to the persistence of pro-VWF [14]. Interestingly, dominant heterozygous rC379G/WT mutated VWD is associated with a secretion multimerization defect of pro-VWF that interferes with normal VWF as clearly demonstrated in two patients with heterozygous C379G/WT.
The Platelet Function Analyzer Closur Times (PFA-CT) in the Brno study are slightly prolonged in VWD type 1 Low VWF (0,30 and 0,50), and to a less extend or normal in Low VWF between 0.40 to 0.70 U/dL in 51 cases with the absence of a causative mutation in the VWF gene. The PFA-CT are strongly prolonged (›300 sec) in recessive VWD type 1 and 2C, and in dominant 2E and in pronounced type 1. The cut off level 0.70 was used for VWF: RCo/ Ag, VWF: GPIbM/Ag and VWF: GPIbR ratios to define VWD type 1 versus type 2 VWD [15]. In the present study we compared the VWF: GPIbM and VWF: GPIbR assays against ECLM criteria as the gold standard (Table 1) and assessed the role of FVIII: C/VWF: Ag ratio and the VWFpp/VWF: Ag ratio in all VWD type 1, 2N and 2 E due to mutations in the D1, D2, D’and D3 domains of the \VWF gene (Table 3). In the Brno study we used a complete set of Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) assays for the diagnosis of Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) according to ECLM criteria. The VWF: RCo/Ag, VWF: GPIbM/Ag and VWF: GPIbR ratios are normal (above 0.7) in VWD type 1 due to heterozygous/WT mutations in the D1 domain consistent with type 2 (Table 2). and mild VWD in LowVWF without a detectable underlying molecular defect (Table 6). The VWF: RCo/ Ag, GPIbR/Ag and GPIbM/Ag ratios are variable around the cut off level of 0.70 in VWD type 2 due to multimerization defect in the D3 domain and therefore diagnosed as either type 1E or type 2E. This study clearly demonstes that the combined use of FVIII: C, VWF; Ag, VWF: PP, VWF: GPIbM or VWF: GPIbR and VWF mulrimeric analysis are mandatory to make a correct diagnosis of VWD type 1, 1C, 1E, 2E or 2 EC caused by mutations in the D3 domain (Table 5). The heterozygous/WT S2179F in the D4 is diagnosed as featured by VWD type 1 Secretion and Clearance (SCD) similar as decribed. The heterozygous P2063S/WT in the D4 domain is diagnosed as mild VWD type 1m.
Diagnosis
VWF:Ag
VWF:RCo
GPIbM
GPIbR
RCo/Ag
GPIbM/Ag
GPIbR/Ag
Bleeding
PFA-CT
PFA-CT
Clinical Lab
U/dL
U/dl
U/dL
U/dL
ratio
ratio
ratio
Score ABO
EPI
ADP
No VWD N
1.07
0.90
0.69
0.66
0.84
0.64
0.62
4 nt
131
nt
Or1 1
0.30
0.25
0.34
0.26
0.83
1.12
0.85
2 O
nt
nt
Or1 1
0.34
0.43
0.41
0.39
1.26
1.19
1.15
3 O
239
136
No VWD N
1.18
1.19
1.22
1.01
1.14
1.03
zero A
140
nt
No VWD N
1.77
1.35
nt
1.55
0.76
0.84
0.88
zero A
145
nt
Or1 1
0.47
0.36
0.33
0.33
0.77
0.70
0.71
10 O
188
145
Or1 1
0.59
0.41
0.22
0.26
0.69
0.38
0.45
9 O
>300
136
1 1
0.73
0.52
0.67
0.65
0.71
0.92
0.89
zero
145
nt
Or1 1
0.72
0.43
0.25
0.24
0.60
0.35
0.34
8 O
177
188
1 1
0.47
0.37
0.38
0.38
0.79
0.80
0.81
2 A
>300
158
1 1
0.58
0.59
0.53
0.49
1.02
0.91
0.84
zero A
nt
nt
No VWD N
1.15
0.99
1.13
1.16
0.77
0.97
1.01
zero A
189
89
1 1
0.54
0.52
0.50
0.52
0.96
0.93
0.96
zero A
172
113
1 1
0.53
0.55
0.53
0.50
1.04
1.01
0.94
2 A
106
nt
No VWD N
0.78
0.88
0.74
0.71
1.13
0.95
0.91
1 O
100
nt
No VWD N
0.62
0.79
0.58
0.62
1.27
0.94
1.00
1 A
nt
nt
No VWD N
0.78
0.88
0.72
0.80
1.13
0.92
1.03
zero B
186
122
OrN
0.70
0.62
0.59
0.63
0.89
0.84
0.90
9 O
163
119
Or1 1
0.60
0.38
0.52
0.47
0.63
0.86
0.78
10 O
161
116
OrN
0.75
0.65
0.70
0.72
0.87
0.93
0.96
2 O
109
nt
1 1
0.58
0.46
0.49
0.46
0.79
0.84
0.79
15 O
190
179
1 1
0.45
0.33
0.38
0.32
0.73
0.84
0.72
11 O
215
131
Or1 1
0.71
0.54
0.58
0.55
0.76
0.82
0.78
11 O
199
140
Or1 1
0.77
0.52
0.98
0.68
1.41
1.28
6 O
166
140
1 1
1.16
0.62
1.13
0.53
0.89
0.98
2 B
125
nt
No VWD N
1.27
0.98
1.39
0.77
1.26
1.09
1 B
98
nt
Table 6: Result in 51 cases with no causative VWF mutation detectable or no evidence for VWD related to PFA-CT and blood group O vs non-O.
Or1 1
0.56
0.43
0.45
0.43
0.77
0.81
0.77
4 O
155
nt
1 1
0.58
0.30
0.48
0.46
0.52
0.83
0.80
2 A
146
nt
1 1
0.50
0.51
0.41
0.46
1.02
0.82
0.93
2 A
179
nt
1 1
0.57
0.62
0.54
0.53
1.09
0.95
0.94
2 A
104
nt
1 1
0.75
0.58
0.63
0.68
0.77
0.84
0.91
zero A
137
Or11
0.46
0.43
0.41
0.45
0.93
0.90
0.98
6 O
151
nt
Or1 1
0.62
0.49
0.48
0.41
0.79
0.77
0.66
4 O
124
Or1 1
0.53
0.60
0.58
0.52
1.13
1.10
0.96
zero O
179
127
Or11
0.31
0.31
0.27
0.31
1.00
0.86
1.01
1 O
229
138
1 1
0.49
0.40
0.45
0.38
0.82
0.91
0.77
3 A
205
nt
No VWD N
1.03
1.15
1.08
1.12
1.07
1.05
zero A
205
No VWD N
0.94
0.88
1.01
0.94
1.09
1.07
zero A
168
101
1 1
0.54
0.55
0.49
0.55
1.02
0.91
1.01
7 A
163
137
Or1 1
0.45
0.41
0.33
0.33
0.91
0.73
0.73
zero A
186
141
Or1 1
0.72
0.53
0.61
0.69
0.74
0.84
0.95
1 O
140
nt
No VWD N
0.93
0.93
1.18
1.00
1.18
1.26
7 O
139
nt
No VWD N
0.84
0.75
0.88
0.89
1.39
1.05
3 O
139
nt
No VWD N
1.03
1.10
0.76
0.89
1.07
0.74
0.87
zero
140
83
No VWD N
1.03
0.97
0.91
1.04
0.95
0.89
1.02
zero
139
nt
Or1 1
0.63
0.51
0.52
0.57
0.81
0.82
0.90
1 O
169
117
Or1 1
0.70
0.57
0.62
0.56
0.81
0.87
0.80
4 O
139
117
No VWD N
1.04
0.99
1.09
0.95
1.07
1.05
3 O
108
nt
Or1 1
0.59
0.59
0.52
0.54
1.00
0.88
0.92
7 O
>301
144
No VWD N
0.69
0.69
0.64
0.68
1.00
0.92
0.98
6 A
143
nt
No VWD N
0.88
0.64
0.67
0.82
0.73
0.76
0.93
6 B
160
nt
Table 6 of 1:
In a separate study we found that dominant VWD 2A and VWD 2B due to mutations in the A2 and A1 domain, the VWF: GPIbM/Ag and VWF: GPIbR/Ag ratios are pronounced decreased as compared to VWF: RCo/Ag and VWF: CB/Ag ratios due to the proteolytic loss of large and intermediate VWF multimers (manuscript in press). VWD 2M due to los of function mutation in the A3 domain is featured by decreased VWF: Rco/Ag ratio and normal VWF: CB/Ag ratio, but the VWF: GPIbR/Ag ratio (range 0.14-28) and the VWF: RCo/Ag ratio (range 0.10-0.33) were similar low but the VWF: GPIbM/Ag ratio somewhat higher (range 0.32 to 0.36) indicating the need to retain the VWF: CB assay to make a correct diagnosis of VWD 2M. The introduction of the rapid VWF: GPIbM or VWF: GPIbR assays as compared to the classical VWF: RCo assay will change VWD type 2 into type 1 in about 10 to 12%. VWD type 1 due to a heterozygous mutation in the D1 domain is featured by a persistence of proVWF as the cause of secretion/multimerization and FVIII binding defect mimicking VWD type 3, decreased valus for VWFpp, VWFpp/Ag ratios (0.51 to 0.99 with one exception) together with moderate to pronounced prolonged PFA-CT.
Borderline VWD
The result in 51 cases with no causative VWF mutation detectable or no evidence for VWD related to PFA-CT and blood group O vs non-O in Table 6 were tentatively diagnosed as VWD type 1 in 17, Blood group O related VWF deiciency in 20 and No VWD in 17 cases. The laboratory diagnosiswere mild VWD type 1 (LowVWF [16]) in 33 and Normal (N) in 17 cases. The PFA-CT closure times were normal or slighly prolonged in the majority of LowVWF cases and three cases had strongly prolonged PFA-CT for Epinephrine and much shorter values for PFA-CT.
Authors Contributions
JJM, PS, and KM initiated the study and wrote the manuscript on the direct compares two rapid VWF activity assays VWF: GPIbM and VWF: GPIbR in the Brno cohort of VWD patients against a complete set of FVIII: C and VWF parameters. PS, and JJM collected all clinical data and plasma and DNA samples. IV and AG performed the laboratory and molecular analysis. KM and GM measured the normal range of the two rapid VWF activity assays. ZB, UB, JB and MP served as scientific advisor.
References
- SadlerJE. A revised classification of von Willebrand disease. Thromb Haemostas. 1994; 71: 520-525.
- Sadler JE, Mannucci PM, Berntorp E, Bochkov N, Boulyjenkov V, Ginsburg D, et al. Impact diagnosis and treatment of von Willebrand disease. Thromb Haemostas. 2000; 84: 160-174.
- Sadler JE, Budde U, Eikenboom JC, Favaloro EJ, Hill FG, Holmberg L, et al. Update on the pathophysiology and classification of von Willebrand disease: a report of the Subcommittee on von Willebrand Factor. J Thromb Haemost. 2006; 4: 2103-2114.
- Meyer D, Fressinaud E, Hilbert L, Ribba AS, Lavergne JM, Mazurier C. Type 2 von Willebrand disease causing defective von Willebrand factor-dependent platelet function. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2001; 14: 349-364.
- Sadler JE. Von Willebranddisease type 1: a diagnosis in search of a disease. Blood. 2003; 101: 2089-2093.
- Michiels JJ, Berneman Z, Gadisseur A, van der Planken M, Schroyens W, van Vliet HHDM. Laboratory diagnosis and molecular basis of mild von Willebrand disease type 1. Acta Haematol. 2009; 121: 85-97.
- Schneppenheim R, Budde U, Ruggeri ZM. A molecular approach to the classification of von Willebrand disease. Best Practice Res Clin Haematol. 2001; 14: 281-298.
- Schneppenheim R, Budde U. Von Willebrand factor:the complex molecular genetics of a multidomain and multifunctional protein. J Thromb Haemostas. 2011; 9: 209-2015.
- Michiels JJ, Batorova A, Pricangova T, Smejkal P, Penka M, Vangenechten I, et al. Changing insights in the diagnosis and classification of recessive and dominant von Willebrand diseases. World J Hematol. 2016; 5: 61-74.
- Michiels JJ, Smjekal P, Penka M, Batorova A, Pricangova T, Budde U, et al. Diagnostic differentiation of von Willebrand disease type 1 and 2 by von Willebrand factor multimer analysis and DDAVP challenge test. Clin Applied Thromb Hemostas. 2017; 23: 518-531.
- Vangenechten I, Mayger K, Smejkal P, Zapletal D, Michiels JJ, Moore GW, et al. A comparative analysis of different automated von Willebrand factor GPIb-binding activity assays in well typed von Willebrand Disease patients. J Thromb Haemostas 2018; 16: 1268-1277.
- Vangenechten I, Smejkal P, Zapletal O, Michiels JJ, Berneman Z, Zavrelova J, et al. Analysis of von Willebrand Disease in the South Moravian population (Czech Republic): Results from the BRNO-VWD Study. Thromb Haemostas in press. 2019; 119: 594-605.
- Mayger K, Vangenechten I, Michiels JJ, Moore GW, Gadisseur A. Generation of reference intervals for two automated, new-generation von Willebrand factor activity assays on a large donor population. Abstract ISTH. 2015 Poster.
- Yin J, Ma Z, Su J, Wang JW, Zhao X, Ling J, et al. Mutations in the D1 domain of von Willebrand factor impair their propeptide-dependent multimerization, intracellular trafficking and secretion. J Hematol Oncol. 2015; 8: 73.
- Van Vliet HHDM, Kappers-Klunne MC, Leebeek F, Michiels JJ. PFA- 100 monitoring of von Willebrand factor (VWF) rsponses to DDAVP and FVIII?VWF concentrate in von Willebrand disease type 1 and 2. Thromb Haemostas. 2008; 100: 462-468.
- Lavin M, Aguila S, Schneppenheim S, Dalton N, Jones KL, O’Sullivan JM, et al. Novel insights into the clinical phenotype and pathophysiology underlying low VWF levels. Blood. 2017; 130: 2344-2353.
Citation: Michiels JJ, Smejkal P, Mayger K, Moore G, Budde U, Berneman Z, et al. Combined Use of Rapid Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) Activity, VWF-Propetide and Classical VWF Assays for Improved Diagnosis of Von Willebrand Disease Type 1, 2N and 2E Due to Mutations in the D1, D2, D’, D3 and D4 Domains of the VWF Gene. Thromb Haemost Res. 2019; 3(2): 1027.