
Short Communication
Thromb Haemost Res. 2022; 6(2): 1077.
Liposomes: A Promising Strategy to Treat Multidrug Resistance in Cancers
Kaur R¹, Mann S² and Hallan SS³*
¹State Institute of Nursing and Paramedical Sciences, Badal, India
²Surrey Memorial Hospital- Neurology, Canada
³Department of Chemical, Pharmaceutical and Agricultural Sciences, University of Ferrara, Italy
*Corresponding author: Supandeep Singh Hallan, Department of Chemical, Pharmaceutical and Agricultural Sciences, University of Ferrara, I-44121 Ferrara, Italy
Received: June 16, 2022; Accepted: July 19, 2022; Published: July 26, 2022
Introduction
Drug resistance has become a main concern in the cancer therapy worldwide. It can be a temporary or permanent potential of an organismto multiply even in the presence of the lethal drug concentration.Generally, multidrug resistance (MDR) is associated with the over-expression of P-glycoprotein(P-gp), resulting in amplified efflux of anticancer drug molecules from cancer cells [1]. Therefore, interrupting the P-gp efflux might be an effective strategy to resolve the MDR in cancer patients. Interestingly, smart nano-sized transporters can deliver the drug cargo at the proposed site and release the drug precisely to elicit desirable therapeutic response. Thanks to their small diameter, large surface area. Now a days, researchers have explored a smart drug delivery system known as polymer lipid hybrid nanoparticles, which are capable to combat various diseases [2,3].
Over expressed ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) transporters is frequently associated with MDR in cancer treatments. However, no approved anti-cancer drug molecules are available for clinical use in order to reverse MDR by obstructing P-glycoprotein. However, MDR is responsible for the low intracellular drug concentrations ultimately reduce the cytotoxicity of a broad spectrum of antitumor drugs including anthracyclines (e.g. DOX), vinca alkaloids (e.g. vincristine), podophyllotoxins (e.g. etoposide) and taxanes (e.g. taxol) [4].
Reversal of MDR
Numerous attempts have been made for the reversal of the MDR by the researchers worldwide. The most employed approaches include solid lipid nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles, mesoporous silica nanoparticles, nanoparticulated chemosensitizer and poloxamer, and magnetic nanoparticles [5]. Whilst, hydrophobic nature of chemotherapeutics leads to poor aqueous solubility and low bioavailability which can be overcome by nanocrystals, albumin based nanoparticles, liposomal formulation, polymeric micelles, cyclodextrin and chitosan based nanoparticles [6].
Limitations of Conventional Therapies
The limitations of existing approaches in the treatment of MDR have been presented in (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Limitations of existing therapies.
Non-specific targeting leads to damage of rapidly proliferating normal cells, limited aqueous solubility because most chemotherapeutics either from plant source or synthetic are hydrophobic and requires solvents to formulate the dosage form which contribute to severe toxicity. Moreover, lack of selectivity of anticancer drugs cause significant damage to rapidly proliferating normal cells and drug expulsion [7].
Liposomes in MDR
Liposomes are known as a one of the successful outcomes of the nanomedicine which have achieved clinical success. These are the bilayer arrangements compose of the phospholipids can move freely across the physiological barriers and employed in the numerous biomedical applications. Liposomes can be classified majorly on the basis of the surface charge, type of the lipid composition, dimensions and production process [8].
The liposomes can be modified in order to achieve precise drug release at specific target site such as cancer cells and can escape from the process of rapid clearance [9,10]. The process of clearing out of liposomes can be challenged by providing the PEGylation to the liposomes (Figure 2). This stealth property can increase the circulation time of liposomes within the human body by reducing their uptake by the Reticuloendothelial System (RES). Remarkably, the bio dispersal of PEGylated liposomes has been exploited successfully in the designing of doxorubicin-loaded liposomes commercially available as Doxil (Janssen Biotech, Inc., Horsham, USA) or Caelyx (Schering- Plough Corporation, Kenilworth, USA) for the treatment of solid tumors [11]. Furthermore, co-delivery of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drug moieties is also feasible in the liposomes as shown in (Figure 2). The use of cholesterol provides the strength and rigidity to the phospholipid chain. The liposomes used in the reversal of the MDR have been mentioned in (Table 1).
Drug (s)
Method
Type of cancer
Ref.
Resveratrol and Paclitaxel
Thin film hydration
Breast Cancer
[12]
Doxorubicin, Quinine, and Indocyanine
Thin film hydration
Colon cancer
[13]
Disulfiram and doxorubicin
Thin lipid film-hydration method
Breast Cancer
[14]
Tariquidar and doxorubicin
Thin film hydration method
Ovarian cancer
[15]
Paclitaxel and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin
Film dispersion method
Human lung adenocarcinoma
[16]
Table 1: Liposomes to treat MDR in various cancers.
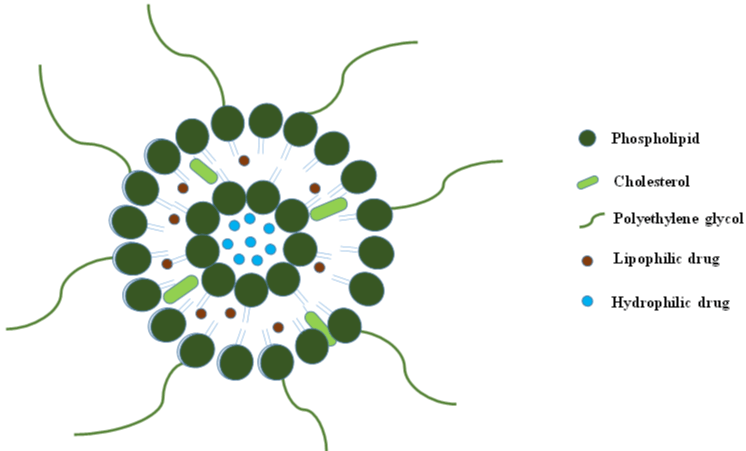
Figure 2: Stealth liposomes with prolonged circulation time.
Conclusion
The MDR is the main obstacle in the treatment of long stage cancers. The conventional treatment approaches are not efficient enough to resolve this issues. Therefore, biomimetic nano scale drug carriers have become the centre of the attraction for the researchers worldwide. Among the lipid nano-carriers, liposomes have been considered mostly for co-encapsulation of anticancer agents due to their capability to maintain optimum concentration at specific target site. They can circulate for the longer time in the physiological medium without undergoing degradation. However, the scale up manufacturing of the liposomes is still a major challenge.
References
- R W Robey, K M Pluchino, M D Hall, A T Fojo, S E Bates, et al. Revisiting the role of ABC transporters in multidrug-resistant cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018; 18: 452–464.
- S S Hallan, P Kaur, V Kaur, N Mishra, B. Vaidya. Lipid polymer hybrid as emerging tool in nanocarriers for oral drug delivery. Artificial Cells Nanomedicine and Biotechnology. 2016; 44: 334–349.
- S S Hallan, Nidhi, V Kaur, V Jain, N Mishra. Development and characterization of polymer lipid hybrid nanoparticles for oral delivery of LMWH. Artificial Cells Nanomedicine and Biotechnology. 2017; 45: 1631–1639.
- F J Sharom. ABC multidrug transporters: structure, function and role in chemoresistance. Pharmacogenomics. 2008; 9: 105–127.
- Javed Ahmad, Sohail Akhter, Nigel H Greig, Mohammad Amjad Kamal, Patrick Midoux. Engineered Nanoparticles Against MDR in Cancer: The State of the Art and its Prospective. CPD. 2016; 22: 4360–4373.
- Zhang C, Zhou X, Zhang H, Han X, Li B, Yang R, et al. Recent Progress of Novel Nanotechnology Challenging the Multidrug Resistance of Cancer. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2022; 13.
- L Milane, S Ganesh, S Shah, Z Duan, M Amiji. Multi-modal strategies for overcoming tumor drug resistance: Hypoxia, the Warburg effect, stem cells, and multifunctional nanotechnology. Journal of Controlled Release. 2011; 155: 237–247.
- Narottam Lamichhane, Thirupandiyur S Udayakumar, Warren D D’Souza, Charles B Simone, Srinivasa R Raghavan. Liposomes: Clinical Applications and Potential for Image-Guided Drug Delivery. Molecules. 2018; 23: 288.
- T M Allen, P R Cullis. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2013; 65: 36–48.
- R Chandrawati, F Caruso. Biomimetic Liposome- and Polymersome-Based Multicompartmentalized Assemblies. Langmuir. 2012; 28: 13798–13807.
- Abolfazl Akbarzadeh, Rogaie Rezaei-Sadabady, Soodebeh Davaran, Sang Woo Joo, Nosratollah Zarghami, et al. Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013; 8: 102.
- J Meng, F Guo, H Xu, W Liang, C Wang, et al. Combination Therapy using Coencapsulated Resveratrol and Paclitaxel in Liposomes for Drug Resistance Reversal in Breast Cancer Cells in vivo. Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 22390.
- Portnoy EG, Andriyanov AV, Han H, Eyal S, Barenholz Y. PEGylated Liposomes Remotely Loaded with the Combination of Doxorubicin, Quinine, and Indocyanine Green Enable Successful Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Tumors. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13: 2181.
- Francesca Rolle, Valeria Bincoletto, Elena Gazzano, Barbara Rolando, Giovanna Lollo, et al. Coencapsulation of disulfiram and doxorubicin in liposomes strongly reverses multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2020; 580: 119191.
- Yuqiong Xia, Mei Fang, Jingyu Dong, Chunzhong Xu, Zhen Liao, et al. pH sensitive liposomes delivering tariquidar and doxorubicin to overcome multidrug resistance of resistant ovarian cancer cells. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 2018; 170: 514–520.
- Q Shen, Y Shen, F Jin, Y Du, X Ying. Paclitaxel/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex-loaded liposomes for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Journal of Liposome Research. 2020; 30: 12–20.