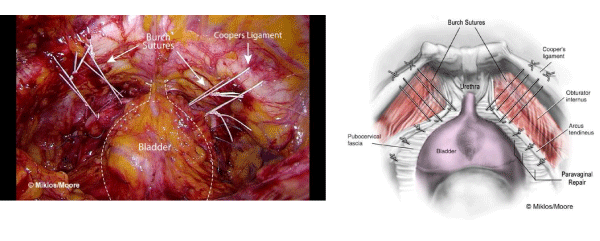
Clinical Image
Austin J Urol. 2014;1(2): 2.
Clinical Images of Laparoscopic Burch Colposuspension
Chinthakanan O, Miklos JR and Moore RD*
International Urogynecology Associates, USA
*Corresponding author: Moore RD, International Urogynecology Associates, Atlanta & Bevery Hills, 3400 Old Milton Pkwy, Building C, Suite 330 Alpharetta, GA 30005, USA
Received: May 27, 2014; Accepted: August 19, 2014; Published: August 22, 2014
Surgical treatment is the standard approach for women with stress urinary incontinence (SUI). There are hundreds of surgical techniques reported in the literatures. Burch colposuspension, first described in 1961 [1], is one of the gold standards of the treatment of SUI that has shown efficacy over long-term follow-up . Five year cure rates of 82%, 8-year rates of 90% and 10-year rates of 55–69% have all been reported [2]. Laparoscopic Burch colposuspension (Figure 1) was introduced in 1991 [3]. From a recent Cochrane review, cure rates between open and laparoscopic approach did not show significant differences for medium and long-term follow-up [4]. The advantages of laparoscopic approach were decreased blood loss, shortened hospitalization, and decreased postoperative pain and recovery time [5]. From the Colpopexy and Urinary Reduction Efforts (CARE) trial, prophylactic Burch colposuspension at the time of sacral colpopexy had protective effect for SUI in continent patients at 3 months and 2 year follow-up period [6,7]. However, prophylactic Burch colposuspension at the time of abdominal sacral colpopexy has not been uniform implemented into clinical practice since the publication of CARE trial [8]. According to the stress incontinence surgical treatment efficacy (SISTEr) trial, the autologous suburethral sling has higher cure rate at 2 years follow-up compared to Burch colposuspension, however, sling has higher rates of urinary tract infection, urge incontinence, voiding dysfunction, and the need for surgical revision to improve voiding [9]. A systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrated that suburethral sling has higher cure rate and higher risk of intra-operative complications compared to Burch colpopexy [10].
Figure 1 : Laparoscopic Burch Colposuspension.
Synthetic mesh slings, i.e. retropubic and transobturator, have become the new gold standard treatment of SUI secondary to their efficacy and ease of use. However, they also have been associated with complications such. urinary tract injury, voiding dysfunction, pain, dyspareunia, erosion, and surgical failure that required secondary surgical treatment [11]. Complications of mesh use in pelvic surgery in the US have led to highly publicized legal trials and this has resulted in many women avoiding treatment altogether as they feel there is no other option except synthetic mesh. To avoid these complications and their medicolegal implications, Burch colposuspension is undergoing a resurgence as a surgical of choice for both primary and secondary (after failed suburethral sling treatment) surgical management for female SUI. In one study, laparoscopic burch colposuspension after failed suburethral sling had 54% objective and 93% subjective cure rates with low complication rates [12].
Surgical Technique
We routinely perform open laparoscopy technique at the inferior margin of the umbilicus using 10-mm port to introduce the laparoscope. Three additional ports are placed under direct vision. The abdomen is insufflated with CO2 to 15 mmHg intra-abdominal pressure. The superior edge of bladder is identified by retrograde filling the bladder. A peritoneal incision is made between the umbilical ligaments approximately 3cm superior to the bladder and the retropubic space entered. Anatomical landmarks including the pubic symphysis, bladder neck, obturator neurovascular bundle, Cooper’s ligament and the arcus tendineus fascia pelvis are identified. If the patient has a cystocele, we recommend laparoscopic paravaginal repair prior to performing the laparoscopic Burch. By performing this first, normal anatomic support of the anterior vaginal segment is recreated, decreasing risk of subsequent voiding obstruction due to overcorrection of the paraurethral Burch sutures. The laparoscopic Burch colposuspension is performed using nonabsorbable sutures. The surgeon’s non dominant hand is placed in the vagina and a finger is used to elevate the vagina around the bladder neck area. Blunt dissection is performed to identify the bladder neck and mid-urethra both sides. The first suture is placed 2 cm. laterals to the urethra at the level of the mid-urethra. The full thickness of the anterior vaginal wall except the epithelium is sutured with a figure of eight fashion. Then the needle passed through the ipsilateral Cooper’s ligament. The suture is tied down with a series of extracorporeal knots. The suture should bridge approximately 2-3 cm. to avoid overcorrection. Two sutures on each side is standard and an increased cure rate has been shown compared to one suture on each side [13]. The second suture is placed at the urethrovesical junction approximately 2 cm. lateral to the bladder edge adjacent to the first suture with similar fashion. The procedure is repeated on the opposite side. After completed, cystoscopy is routinely performed to rule out urinary tract injury. After cystoscopy, the anterior peritoneal defect is closed using absorbable suture with continuous fashion.
In conclusion, laparoscopic Burch colposuspension is and effective and safe option for SUI treatment. This procedure should be a new trend for recurrent SUI or patients who have sling complications.
References
- Burch JC. Urethrovaginal fixation to Cooper's ligament for correction of stress incontinence, cystocele, and prolapse. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1961; 81: 281-290.
- Norton P, Brubaker L. Urinary incontinence in women. Lancet. 2006; 367: 57-67.
- Vancaillie TG, Schuessler W. Laparoscopic bladderneck suspension. J Laparoendosc Surg. 1991; 1: 169-173.
- Lapitan MC, Cody JD. Open retropubic colposuspension for urinary incontinence in women. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2012; 6: CD002912.
- Miklos JR, Kohli N. Laparoscopic paravaginal repair plus burch colposuspension: review and descriptive technique. Urology. 2000; 56: 64-69.
- Brubaker L, Cundiff GW, Fine P, Nygaard I, Richter HE, Visco AG, et al. Abdominal sacrocolpopexy with Burch colposuspension to reduce urinary stress incontinence. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354: 1557-1566.
- Brubaker L, Nygaard I, Richter HE, Visco A, Weber AM, Cundiff GW, et al. Two-year outcomes after sacrocolpopexy with and without burch to prevent stress urinary incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 2008; 112: 49-55.
- Aungst MJ, Mamienski TD, Albright TS, Zahn CM, Fischer JR. Prophylactic Burch colposuspension at the time of abdominal sacrocolpopexy: a survey of current practice patterns. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2009; 20: 897-904.
- Albo ME, Richter HE, Brubaker L, Norton P, Kraus SR, Zimmern PE, et al. Burch colposuspension versus fascial sling to reduce urinary stress incontinence. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356: 2143-2155.
- Novara G, Artibani W, Barber MD, Chapple CR, Costantini E, Ficarra V. Updated systematic review and meta-analysis of the comparative data on colposuspensions, pubovaginal slings, and midurethral tapes in the surgical treatment of female stress urinary incontinence. Eur Urol. 2010; 58: 218-238.
- Daneshgari F, Kong W, Swartz M. Complications of mid urethral slings: important outcomes for future clinical trials. J Urol. 2008; 180: 1890-1897.
- Bakali E, Buckley BS, Hilton P, Tincello DG. Treatment of recurrent stress urinary incontinence after failed minimally invasive synthetic suburethral tape surgery in women. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2013; 2.
- Persson J, Wølner-Hanssen P. Laparoscopic Burch colposuspension for stress urinary incontinence: a randomized comparison of one or two sutures on each side of the urethra. Obstet Gynecol. 2000; 95: 151-155.