
Research Article
Austin J Urol. 2017; 4(1): 1053.
Sonochemical and Photochemical Degradation of Cresol Red by Potassium Monopersulfate (Oxone) in Aqueous Medium
Fassi S¹* and Petrier C²
¹Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Sciences, University of Constantine, Algeria
²Laboratoire de Rhéologie et Procédés, Domaine Universitaire, France
*Corresponding author: Fassi S, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Sciences, University of Constantine, Algeria
Received: December 26, 2016; Accepted: February 17, 2017; Published: February 23, 2017
Abstract
Potassium monopersulfate has been applied to oxidize the Cresol Red dye in aqueous solution by photochemical and sonochemical processes. The results showed that UV systems like Oxone+CR/UV and Oxone+CR/US were better than direct UV photolysis at .254 nm and sonolysis Moreover, the color removal occurred according to the following order: UV<US<Oxone/UV<Oxone/ US. The degradation rate was strongly dependent on the initial concentration of the Oxone. The effect of different parameters has been studied and the optimum operational conditions of these processes were set.
Keywords: Potassium monopersulfate; Degradation; Cresol red; Water; Environment
Introduction
The release of colored wastewaters from the textile industry is a current problem encountered by developed and under developed countries over the world. This release in natural environment, mainly in aqueous medium, is undesirable because of the potential transformation of these compounds to toxic and carcinogenic of species. Organic dyes represent one of the large groups of these effluents. However, several treatment processes are available for the removal of this type of pollutants
For instance, several decontamination methods, such as precipitation, biological treatment [1], coagulation [2], adsorption on various supports [3], membrane techniques, etc, are widely applied to treat aqueous effluents. The degradation by UV radiation and advanced oxidation processes [4-8] is an excellent alternative to treat Industrial effluents. Amongst the emerging technologies of removing aqueous contaminants, the application of potassium monopersulfate (Oxone) as oxidizing agent presents several advantages, besides, Oxone decomposition can be conducted in the presence of homogeneous catalysts [9], heterogeneous catalysts [10], UV radiation [11] or heat [12] leading to the formation of powerful sulfate and hydroxyl radicals
The goal of this study is to analyze the possibility of decolorization of Cresol Red by different advanced oxidation techniques (AOPs): photolysis (UV), sonolysis (US), Oxone/UV and Oxone/US. This research was carried out both in the presence and absence of UV under different operating conditions. Some kinetic approaches were also applied.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Cresol Red (CR) was purchased from Fluka chemical company and used without further purification. The potassium monopersulfat (Sigma-aldrich) solutions were prepared with ultra pure water from a MILIPORE unit. Figure 1 shows the structure of the dye.
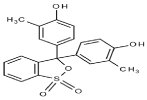
Figure 1: Structure of cresol red.
Photo reactor
Aqueous solutions were irradiated at 254nm in cylindrical reactor quartz (100 cm of length and 2 cm in diameter), located on one of the principal axis of the assembly and equipped with three symmetrical externals low-pressure mercury lamps (germicide lamp, Philips TUV 15W) emitting mainly at 254nm [13].
Ultrasonic irradiations were performed in a cylindrical waterjacketed glass cell equipped with a Teflon holder. The ultrasonic transducer was made from a piezo-electric disc fixed on a titanium plate with the piezo-electric element connected to a high-frequency power supply from Electric Service.
The reactor was hermetically sealed and connected to a gas burette to ensure a constant pressure (1atm). The temperature of the liquid was monitored using a thermocouple immersed in the reacting medium. The experiments were carried out with 300 mL of aqueous solution
Procedure and analysis
The irradiation experiments were carried out with 100 mL of a solution of CR at 6x105 M. The UV–vis absorption spectrum was recorded from 200 to 800nm using Unicam Helios “a” a UV–vis spectrophotometer at λmax = 436 nm. The residual concentrations of the substrate at different times were obtained at λmax = 436 nm from a calibration curve.
Toxicity of Dye
Chronic health effects
Long term exposure to respiratory imtants may result in disease of the airways involving difficult breathing and related systemic problems limited evidence suggests that repeated or long term occupational exposure may produce cumulative health effects involving organs or biochemical systems.
Long term exposure to high dust concentration may cause changes in lung function Triphenylmethane dyes (Cresol Red) are resistant to biodegradation because of their aromatic structure and many functional groups. Metabolic pathways of dyes transformations may be characteristics of each group of microorganisms. Sometimes biological processes are connected with formation of toxic intermediates. Environmental safety demands both pollutant removal and their detoxication. The valuation of decolourization effect should be related to ecotoxicity assessment. By now most of the decolourization projects were concentrated mainly on colour removal.
Results and Discussion
Direct photolysis of cresol red
The UV/Visible spectrum of the Cresol Red at natural pH (4.38) and in diluted medium (6 10-5M), showed two bands with variable intensities and located respectively at 436 nm and 268 nm (Figure 2).
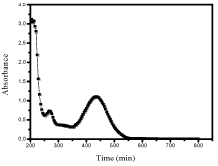
Figure 2: UV–vis spectrum of CR, [dye]o = 6 10-5M.
Organic pollutants can be dissociated by direct UV excitation (λ<250 nm). However, it is necessary to satisfy two conditions: pollutants must have a strong absorption for the excitation light and a sufficient quantum yield. The excitation compound from the initial photo excitation reaction (I) reacts with oxygen dissolved in water before its transformation into by products (reactions 2 and 3).
R + hv → R* (1)
R* + O2 → R+• + O2•- (2)
R+•→ produits (3)
Direct UV photolysis experiments were carried out in a static tubular reactor in diluted medium. The photo degradation was followed by recording UV/Visible spectra at different irradiation time. The results obtained showed that this compound undergoes very slow photolysis for the purposed concentration 2 10-5M (32,1 %), 6 10-5M (12.2%), 8 10-5M (8.1%). This could be attributed on one part to the size of the molecules present in the solution, preventing the exposure of certain of them to light, and on the other part to the absence of OH• radicals which are generated by H2O2. Therefore, the efficiency was not significant (Figure 3).
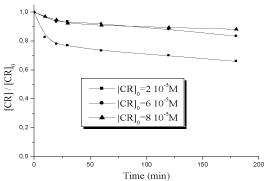
Figure 3: Decolourization of CR by direct UV photolysis, λirr =254 nm.
Sonolysis of cresol red
The application of a 300 kHz ultrasonic wave to the aerated CR solution (6 10-5M) induced the reduction of the initial concentration (Figure 4). CR concentration decreased with time following an apparent first order kinetic. Besides the degradation process, the ultrasonic treatment caused to the concurrent formation of hydrogen peroxide according to the following reactions.
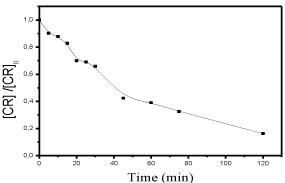
Figure 4: Sonolysis of Cresol Red, [Dye]o = 6 10-5M, T=20°C, Ultrasound=
300 kHz /Power=20W.
OS: Organic substance
H2O → H▪ + °OH (4)
O2 → 2O (5)
H + O2 → HOO▪ (6)
O + H2O → 2▪ OH (7)
▪ OH + OS → HOOS▪ (8)
2▪ OH → HOOH (9)
2HOO▪ → HOOH + O2 (10)
Oxidation of cresol red by potassium monopersulfat (Oxone)
Sensitivity of CR to the Oxone in absence of light: In this work, we considered the highest concentration of the Oxone (10-1 M). No reaction was observed during 180 minutes, The UV/Visible spectrum resulted from the addition of both products spectra (CR/Oxone) (Figure 5).
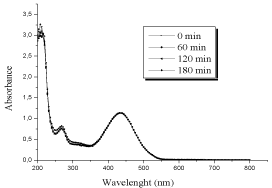
Figure 5: Sensibility of CR to the Oxone (10-1M) in absence of light [dye]o =
6 10-5M.
Photoxydation of Cresol Red by potassium monopersulfat (Oxone): Effect of UV (254nm) radiation: Direct UV photolysis of CR is not very effective. For this reason, we combined UV (254nm) and Oxone at different concentrations to enhance the removal efficiency of the CR.
The results obtained from the solutions of the CR (6 10-5M) and oxone (10-1M, 10-2M, 10-3M and 10-4M) in ultra pure water showed that (Figure 6a).
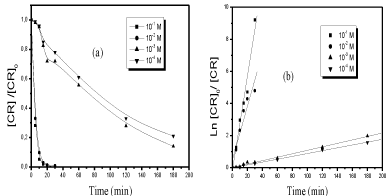
Figure 6: Decolourization of the dye [dye]o = 6 10-5M by Oxone/UV254 nm process. (a): presence of oxone at various concentration at 254 nm radiation, (b): Kinetics
of CR decolourization (linear transform Ln (C\0/Ct) vs. t) in UV254nm/Oxone process.
- The presence of Oxone increased the rate of photo degradation of CR.
- The efficiency of this oxidation process (Oxone / UV) increased with increasing dose of Oxone.
This enhancement of the disappearance of CR observed in the presence of oxone (10-1 M to 10-4M) can be described by an apparent first-order kinetics law 1 (Figure 6b). The values of the rate of degradation are summarized in (Table 1).
[Oxone] M
rate %
(30 min)
t50%(min)
R2
Apparent rate constants (min-1)
10-1
99.8
3.5
0.98628
0.29349
10-2
99.7
3.9
0.96206
0.16705
10-3
28.7
71.1
0.9968
0.0108
10-4
22.5
83.9
0.99829
0.00891
Table 1: Values of parameters characterizing the oxone/UV process at 254 nm.
Effect of ultrasound: Figure 7a shows the results obtained with different concentrations of the Oxone. As observed, the process is significantly enhanced if compared to sonolysis alone.
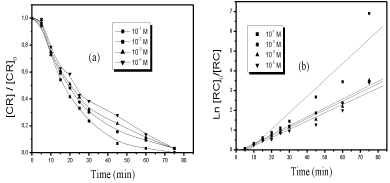
Figure 7: Decolourization of the dye [dye]o = 6 10-5M by Oxone/US process. (a): presence of Oxone at various concentration at F=300KHz and W=20W, (b):
Kinetics of CR decolourization (linear transform Ln (C\0/Ct) vs. t) in US/Oxone process.
Moreover, the bleaching process of CR by Oxone/US is described correctly by an apparent kinetics law of order 1 (Figure 7b). In addition, the measure of the half time for each curve (t1/2) allowed us to compare the performance of this process: t1/2 (10-1 M) < t1/2 (10-2 M) < t1/2 (10-3 M) < t1/2 (10-4M) (a short half time means a fast rate of decolourization).The calculated rate and t50% are recapitulated in (Table 2).
[Oxone] M
rate %
(120 min)
t50%(min)
R2
Apparent rate constants (min-1)
10-1
99.9
16.2
0.95586
0.08312
10-2
96.6
18.8
0.99549
0.04516
10-3
96.3
20.2
0.98417
0.04411
10-4
96.1
22.8
0.97267
0.04168
Table 2: Values of parameters characterizing the US /Oxone process.
Conclusion
In this study, photochemical and sonochemical methods; direct UV photolysis, Oxone/UV, sonolysis and Oxone/US were investigated for the color degradation of the CR. Each removal was then examinated in the basis of the obtained results.
In direct photolysis, the results obtained indicate that CR undergoes a very low decolourization. A real improvement of the efficiency has been reached by using the systems: sonolysis, Oxone/ UV and Oxone/US, the optimal concentration of oxone was 10-1 M.
The application of potassium monopersulfate combined with photochemical and sonochemical methods might an interesting treatment of wastewater and an advantageous application in industry.
References
- Kurbus TY, Stokar M, Marechal L. The study of the effects of the variables on H2O2/UV decoloration of vinylsulphone dye. Dyes Pigm. 2002; 54: 67-78.
- J Garci a Montan OX, Dome Nech JA, Garci a Hortal F, Torrades J Peral. The testing of several biological and chemical coupled treatments for Cibacron Red FN-R azo dye removal. J Hazard Mater. 2008; 154: 484-490.
- Ahmed MN, Ram RN. Removal of basic dye from wastewater using silica as adsorbent. Environ Pollut. 1992; 77: 79-86.
- Milano JC, Loste-Berdot P, Vernet JL. Photooxidation of malachite green in aqueous medium in the presence of hydrogen peroxide: Kinetic and mechanism. J Environ Technol. 1995; 16: 329-341.
- Silva GD, Leds Faria C. Photochemical and photo catalytic degradation of an azo dye in aqueous solution by UV irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem. 2009; 155: 133-143.
- Galindo C, Kalt A. UV–H2O2 oxidation of monoazo dyes in aqueous media: A kinetic study. Dyes Pigm. 1998; 40: 27-35.
- Arslan I, Balciodlu I, Tuhkanen T, Bahnemann D. H2O2/ UV-C and Fe2+/H2O2/ UV C versus TiO2/UV–a treatment for reactive dye waste water. J Environ Eng. 2000; 126: 903-911.
- Galindo C, Jacques P, Kalt A. Photo degradation of the aminoazobenzene acid orange 52 by three advanced oxidation processes: UV/H2O2, UV/ TiO2 and VIS/TiO2: Comparative mechanistic and kinetic investigations. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem. 2000; 130: 35-47.
- Wang Z, Yuan R, Guo Y, Xu L, Liu J. Effects of chloride ions on bleaching of azo dyes by Co2+/Oxone regent: kinetic analysis. J Hazard Mat. 2011; 190: 1083-1087.
- Zhang W, Tay HL, Lim SS, Wang Y, Zhong Z, Xu R. Supported cobalt oxide on MgO: highly efficient catalysts for degradation of organic dyes in dilute solutions. App Catal B Environ. 2010; 95: 93-99.
- Rivas FJ, Gimeno O, Borralho T, Carbajo M. UV-C photolysis of endocrine disruptors. The influence of inorganic peroxides. J Hazard Mat. 2010; 174: 393-397.
- Rivas FJ, García de la Calle R, García Araya JF, Gimeno O. Promoted wet air oxidation of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons. J Hazard Mat. 2008; 153: 792-798.
- Djebbar K, Aliouche S, Chenini H, Sehili T. Decolourization process of an azoi¨que dye (Congo red) by photochemical methods in homogeneous medium. Desalination. 2009; 247: 412-422.