
Clinical Image
Austin J Urol. 2021; 7(1): 1065.
Giant Testicular Cancer: Clinical Picture
Mohammed M*, Dieudonne ZOJ*, Jaafar M, Youness R, Soufiane E, Mustapha A, Soufiane M, Fadl TM, Jalal Eddine E-A, Jamal EM and Hassan FM
Urology Division, CHU Hassan 2, Fez, Morocco
*Corresponding author: Mzyiene Mohammed, Urology Division, CHU Hassan 2, Fez, Morocco
ZIBA Ouima Justin Dieudonne, Urology Division, CHU Hassan 2, Fez, Morocco
Received: April 09, 2021; Accepted: May 13, 2021; Published: May 20, 2021
Keywords
Orchiectomy; Testicular cancer; Germ cell tumours; Seminoma; Tumor marker
Clinical Image
Testicular tumour is the most malignant cancer in young males 15 to 34 years of age. Its accounts for 1% of all male cancer and 5% of urological malignancy [1]. The management of this type of cancer is radical inguinal orchiectomy which is the gold standard for the diagnosis and initial management of a suspected testicular cancer. Trans -scrotal orchiectomy is discouraged because scrotal violation is associated with higher rates of local recurrence and altered pathways of metastatic dissemination [2]. We report a young patient 23 years old. History: Chronic smoking, cannabis. Admitted for large bursa evolving for 14 months. The history of the disease dates back to 14 months by the gradual increase in the volume of the bursa with an alteration of the general status with a weight loss estimated at 10kgs. Clinical examination showed: right hemi-scrotum increased in volume with a hard consistency with a left testicle repressed in extreme lateral and some inflammatory lesions. Right testis was not palpable with a cord repulsed and glued to the inguinal orifice. The ultrasound of the scrotal content showed: large right testis hypervascularized with moderate anterior cloisonnae hydrocele, bilateral testicular microlithiasis. Tumor markers: Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) 229IU, beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (beta-hCG) 29.73mUI/ ml, Alpha-Foetoprotein (AFP) 400IU/ml. Patient benefited from a complete pre-operative assessment that did not object to any abnormality. Programmed for a right inguinal orchiectomy and reduction scrotoplasty (Figure 1).
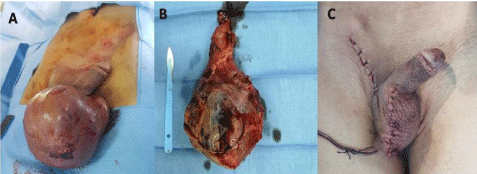
Figure 1: Illustrating of testicular cancer orchiectomy in pre and post-operative. A) Preoperative image of large right testicular mass. B) Peroperative image of the
giant testicular mass. C) Appearance of scrotum after scrotoplasty.
An elevation of the alphaoeto proteins as in our patient where the rate is 400 IU/ml may indicate unrecognized non seminomatous germ cell elements. Some studies reported that mild elevations in AFP, however, may be seen in some benign conditions [3].
References
- Cassell A, Jalloh M, Ndoye M, Yunusa B, Mbodji M, Diallo A, et al. Review of Testicular Tumor: Diagnostic Approach and Management Outcome in Africa. Res Rep Urol. 2020; 12: 35-42.
- Gilligan T, Lin DW, Aggarwal R, Chism D, Cost N, Derweesh IH, et al. Testicular Cancer, Version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw JNCCN. 2019; 17: 1529-1554.
- Ellimoottil C, Quek ML. Giant testicular seminoma. Urology. 2012; 80: e35-e36.