
Case Report
Austin J Urol. 2021; 7(1): 1067.
Rupture of Dorsal Vein Mimicking Penile Fracture: a Case Series Report and Literature Review
Ba Z¹*, Ziba OJD²*, Khatraty CSB¹, Kanza R² and Overs C¹
¹Urology Division Centre Hospitalier Métropole Savoie, France
²Urology Division Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Hassan 2, Fez, Maroc
*Corresponding author: Zackaria Ba, Urology Division Centre Hospitalier Métropole Savoie, France
Ouima Justin Dieudonne Ziba, Urology Division Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Hassan 2, Fez, Maroc
Received: May 15, 2021; Accepted: June 07, 2021; Published: June 14, 2021
Abstract
Penile fracture is a rare and traumatic emergency in andrology. Immediate surgical repair is widely accepted as the therapy of choice in penile fracture. But some situations mimic penile fracture such as superficial dorsal vein rupture. There are few cases reported in the literature.
Aim: To present a case series of injuries of the penile dorsal vein that occurred during sexual intercourse.
Methods: A 48-year-old and 45-year-old patients both received in emergency for suspected penile fracture after one hour of vigorous sexual intercourse, the clinical examination and ultrasound were performed and the penile fracture was suspected. Surgical management in an emergency was indicated.
Results: Per-operative diagnosis was a dorsal vein injury. The surgical management which consisted of early exploration, evacuation of hematoma, and ligation of the bleeding vessel in this case was good with preserving erectile function after surgery, without abnormal curvature erection.
Conclusions: Vascular injuries of the penis can mimic perfectly penile fractures. The medical history and clinical examination can lead to prompted exploration for suspected penile fracture. The ultrasound exploration can be limited for detection of penile vascular injury and final surgical exploration offers final diagnosis and repairment of the trauma. Clinical evolution is favorable, without painful nocturnal erections or deviation of the penis or hypoesthesia of the glans.
Keywords: Dorsal vein; Penis; Fractures; Wounds and Injuries; Hematoma; Coitus; Sexual intercourse
Introduction
Penile fracture remains an andrology emergency, responsible for anxiety for the patient and urologic care is requested to repair the fracture. It is defined as a rupture of the corpus cavernosum caused by blunt trauma to an erect penis. Injuries to a flaccid penis or in the suspensor ligament of the penis are not included in this definition [1]. According to the literature review, the main predisposing factors are vigorous sexual intercourse or forceful manipulation of the erected penis. Others situations like vascular penile injuries are another cause of penile trauma which may mimic a penile fracture but without the tunic tear. They include rupture of the penile superficial dorsal vein, deep dorsal vein, dorsal artery, and non-specific dartos bleeding [2,3]. Dorsal vein injury is the most frequent entity and is clinically characterized by sudden onset hematoma and swelling of the penis [4].
Case 1
A 48-year-old patient with no specific history of pathology received in urological emergencies for brutal per coital, painless swelling of the penis without trauma. The clinical examination found: a voluminous oedematized penis in an uncircumcised patient with a hematoma beyond the dorsal face at the mid-point of the rod (Figure 1A). There was no associated uretrorrhagia. The ultrasound performed found an 8 cm hematoma with a fracture at the middle third of the length of the right cavernous body. An indication of emergency surgical exploration was given and the patient was warned of the risk of erectile dysfunction, hypoesthesia of the glans, and penile deviation. In the operating room, the patient was under general anesthesia in a supine position. A peripheral circumferential incision at 1cm beyond the corona was performed, then progressive release in contact with the cavernous bodies, respecting the vascularisation as well as the nerve strips laterally. Progressive dissection did not find any fracture. Cavernous bodies were visualized with the presence of a hematoma that fuses all along with them, but without fracture. Two erection tests were performed showing no fluid leakage. A U-stitches with PDS thread 3/0 was performed to close the two puncture points of the bilateral erection test. However, it was noticed that the superficial dorsal vein of the penis seems to be spontaneously disrupted (Figure 1B) and was hemorrhagic during the erection test. It was ligated with vicryl 3/0. Satisfactory control of hemostasis with bipolar clamp was added. Cutaneous mucosal closure was performed by separate points with rapid Monosyn, after having put bilateral blades to allow drainage, and installation of an 18Fr urinary catheter (to improve the urinary comfort of the patient).
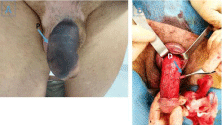
Figure 1: A) Pre operating aspect of penile mimicking penile (P) Localization
of the fracture seen in ultra-sonography corpus cavernosum. B) Intraoperative
photo: normality of two corpora cavernosa (D) Penile dorsal vein ligated.
In the urologic unit, urinary catheter and bilateral blades were removed on day 1, the patient was discharged to the hospital on day 2. He was reviewed in consultation for control at day 15, one month, and two months and there was a favorable clinical evolution with no hematoma. The patient reported painless nocturnal erections without deviation of the penis or hypoesthesia of the glans.
Case 2
A 45-year-old patient was admitted to a urological emergency for suspected trauma to corpora cavernosa for approximately 24 hours. At the clinical examination, we find a voluminous subcutaneous hematoma of the whole penis which is not painful with the absence of uretrorragia. An indication of exploration in the operating room was decided with an indication of the risk of erectile dysfunction, secondary deviation, and hypoesthesia of the glans as well as the risk of secondary necrosis of the foreskin if coronal incision without first elective.
In the operating room, the patient under general anesthesia, installed in a supine position. Conduct a first urethral catheter, then coronal degloving incision of the balano-preputial furrow to then deglove the penis respecting Buck’s fascia. We immediately find the dorsal vein of the penis which at half-height is thrombosed and severed (Figure 1B). The exploration of the two corpora cavernosa to the root of the shaft is strictly normal. The hematoma is next to the section of the dorsal vein of the penis. The defect is closed by lock sutures, using delayed absorption 3/0 PDS. Then remission of degloving with cutaneous closure to the mucous membranes of the incision by separate stitches. Removal of the urinary catheter at the end of the operation.
Discussion
In the literature, some authors suggest that circumcision could be one of the risk factors for dorsal vein rupture due to stretching of the penile skin during intercourse [5,6]. In this present case, the patient was not circumcised. We suggested that maybe sex position, quality, and intensity of per-coital friction could give a physiopathologic explanation. Most patients with penile fracture report hearing a “snap” sound, followed sometimes by pain, penile detumescence, and then swelling penis with hematoma and deformity [7,8]. Our patient did not hear a “snap” and there was no associated with uretrorrhagia but he noted brutal, painless per-coital swelling without trauma. Some patients notice concurrent urethral bleeding, a difficulty for voiding, and haematuria [9]. In this case, the physical examination of the penis was mimicking a fracture and the ultrasound performed found an 8 cm hematoma with paradoxically a fracture at the middle third of the length of the right cavernous body. Ultrasound is known to have a limited role and low sensitivity in the diagnosis of superficial penile dorsal vein rupture [5]. The management of the superficial penile dorsal vein rupture can either be conservative or surgical. Conservative management includes the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, plus compressive bandage [10]. When a penile fracture is suspected, it is recommended to perform early surgical exploration to decrease the rate of penile deviation, or erectile dysfunction. Surgical exploration is commonly decided when a clinical diagnosis of penile fracture is suspected, based on appropriate history and physical signs [11]. Here we performed surgical management in an emergency. A delayed surgery is more difficult because of the increase of the hematoma and oedematous infiltration of the tissue. The use of drainage is not recommended, because increases the risk of infection. A circumcision can be discussed with the patient, because of the high risk of secondary necrosis of the foreskin of the glans. An elective incision can be performed for distal fracture, when it is clinically palpable, which was not the case in this patient. The prognosis after surgery is excellent, long-term success depends on careful patient selection [7]. Conservative management can be an option if the patient does not agree to surgery, however, the clinical outcomes are less favorable. Muentener et al. reported a favorable outcome in 10 of 17 (59%) patients who were managed conservatively, and in 11 of the 12 (92%) patients who were treated with immediate surgery [12].
Conclusion
Vascular injuries of the penis can mimic perfectly penile fractures. The medical history and clinical examination can lead to prompted exploration for suspected penile fracture. The ultrasound exploration can be limited for detection of penile vascular injury and surgical exploration offers final diagnosis and repairment of trauma. This procedure consists of early exploration, evacuation of hematoma, and ligation of the bleeding vessel which leads to favorable results and may preserve the erectile function of the patient.
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Dr. Overs Camille for her assistance and guidance in this paper.
Author Contributions
The authors contributed equally to preparing the manuscript.
Attestation of Clinical Consent
Patient consent has been obtained and filed for the publication of this case report.
References
- Eke N. Fracture of the penis. Br J Surg. 2002; 89: 555–565.
- Herrero Polo E, Megías Garrigós J, Puertas Ruiz M, Torrús Tendero P, Sánchez Marcos M. [Penile hematoma caused by deep dorsal vein rupture during intercourse]. Arch Esp Urol. 2000; 53: 473–475.
- Koifman L, Barros R, Júnior RAS, Cavalcanti AG, Favorito LA. Penile fracture: diagnosis, treatment and outcomes of 150 patients. Urology. 2010; 76: 1488–1492.
- Kurkar A, Elderwy AA, Orabi H. False fracture of the penis: Different pathology but similar clinical presentation and management. Urol Ann. 2014; 6: 23–26.
- Eken A, Acil M, Arpaci T. Isolated rupture of the superficial vein of the penis. Can Urol Assoc J J Assoc Urol Can. 2014; 8: E371-373.
- Baran C, Topsakal M, Kavukcu E, Karadeniz T. Superficial dorsal vein rupture imitating penile fracture. Korean J Urol. 2011; 52: 293–294.
- Bar-Yosef Y, Greenstein A, Beri A, Lidawi G, Matzkin H, Chen J. Dorsal Vein Injuries Observed During Penile Exploration for Suspected Penile Fracture. J Sex Med. 2007; 4: 1142–1146.
- Baran C, Topsakal M, Kavukcu E, Karadeniz T. Superficial Dorsal Vein Rupture Imitating Penile Fracture. Korean J Urol. 2011; 52: 293-294.
- El-Assmy A, El-Tholoth HS, Abou-El-Ghar ME, Mohsen T, Ibrahiem EHI. False Penile Fracture: Value of Different Diagnostic Approaches and Longterm Outcome of Conservative and Surgical Management. Urology. 2010; 75: 1353–1356.
- Puñal Pereira A, Pérez Fentes D, Toucedo Caamaño V, Blanco Parra M, Villasenín Parrado L, Cortegoso González M. Rupture of the superficial vein of penis: therapeutic options. Arch Esp Urol. 2010; 63: 871–873.
- Schultheiss D, Truss MC, Becker AJ, Stief CG, Jonas U. [Dorsal ligation of the penile vein--prognostic factors and long-term outcome]. Urol Ausg A. 1997; 36: 351–355.
- Muentener M, Suter S, Hauri D, Sulser T. Long-term experience with surgical and conservative treatment of penile fracture. J Urol. 2004; 172: 576–579.