
Research Article
Austin J Vet Sci & Anim Husb. 2022; 9(5): 1108.
Assessment on the Awareness of Antimicrobial Drug Resistance on Human Health and Animal Health Professionals and Antimicrobial Profile of Staphylococcus aureus from Kality Clinic in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Bamlak Kassahun Ayelaw¹ and Shubisa Abera Leliso²*
¹Addis Ababa University College of Agriculture and Vterinary Medicine, Ethiopia
²Animal Health Institute (AHI), Ethiopia
*Corresponding author: Shubisa Abera, Animal Health Institute (AHI), Ethiopia
Received: October 03, 2022; Accepted: October 28, 2022; Published: November 04, 2022
Abstract
A cross-sectional study with purposive sampling was conducted from November 2021 to March 2022 to investigate the antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Staphylococcus aureus. A questionnaire survey was also undertaken to assess the awareness of human and animal health professionals from St.Paul Hospital and Addis Ababa University- Aklilu Lemma Pathobiology Institute / AAU-ALIPB/ on antimicrobial drug resistance. Out of the 40 participants 20 of them were physicians and the remaining 20 were veterinarians. Among the interviewed 20 veterinary professionals 80% of them were well aware of antimicrobial drug resistance and its impact on animal and public health. Parallel to that all veterinarians involved in this questionnaire survey or 100% of them had previous knowledge on one health approach and its role in solving the problem of anti-microbial drug resistance. Compared to the veterinarians, about 39.3% of physicians had poor awareness and knowledge on AMDR. Besides this only 40% of the physician know about one health approach and its role in fighting against AMDR. A statistically significant (P<0.05) relation was observed between the professionals and their knowledge. A total of Forty wounds, and nasal and vaginal swab samples from bovine, ovine, caprine and equine species were collected for Staphylococcus aureus isolation and antimicrobial susceptibility test. The samples collected from Kality veterinary clinic were examined using standard microbiological techniques including culture, colony characterization, primary and secondary biochemical tests as well as species-level identification of S.aureus done by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization (MALDI) Bio typer. Among the 40 samples, only 3 S.aureus is confirmed. Out of the tested 3 isolates, 100% of them were highly resistant to Penicillin G, and 100% of isolates were equally susceptible to all list of drugs used. Staphylococcus aureus completely develops resistance to penicillin G which mean this antibiotic doesn’t have any relevant importance in treating clinical cases that are caused by pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus species in both human and animal.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance; Kality; MALDI; Physician; Staphylococcus aureus; Veterinarian
Introduction
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) is a resistance that occurs when disease-causing agents like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites change over time and become no longer respond to drugs making the disease harder to manage and raising the chance of disease spread, severe illness, and death [1]. Due to drug resistance, antibiotics and other antimicrobial medicines become ineffective and infections become increasingly difficult or impossible to trea [2].
Genetic changes allow the AMR to occur naturally over time. Antimicrobial-resistant organisms are found in people, animals, food, plants, and the environment (in water, soil, and air) this connection truly explains how much collaborative work is important. They expand from person to person or between people and animals, including from food of animal origin [3]. The main Problems that are considered of antimicrobial resistance include the misuse and overuse of antimicrobials; lack of access to clean water, sanitation, and hygiene for both humans and animals; poor disease prevention and control system in healthcare facilities and farms, poor access to quality and affordable medicines, vaccines and diagnostics; lack of awareness and knowledge on antmicrobial drug resistance and lack of enforcement of legislation [4].
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) happens when diseasecausing microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. The word antibiotic resistance is under the umbrella of AMR, as it applies to bacteria that become resistant to antibiotics. Resistant microbes are more difficult to treat, requiring higher doses, or alternative medications that may prove more toxic [3]. These approaches may also be more expensive. Microbes resistant to multiple antimicrobials are called Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) [2].
Antimicrobial resistance is increasing globally due to increased prescription and utilization of antibiotic drugs in developing countries. Estimates are that 700,000 to several million deaths result per year and continue to pose a major public health threat worldwide According to World Health Organization (WHO) estimates, three hundred and fifty million deaths could be caused by AMR [5].
Antibiotics have been misused and/or overused in humans and animals, which has boost dramatically the problem of antimicrobial resistance. Physicians, Veterinarians, and Ecologists should have to well aware of the impact of AMR. Often antibiotics must be given for viral infections like cold and flu which do not require antibiotics at all [6]. Again, antibiotics are administered without any reason given to animals for growth promotion and/or prevention of diseases in healthy animals. Antibiotics are also used unreasonably in farms and for the preservation of farm products. Such misuses and/or overuses of antibiotics cause AMR [7].
Staphylococcus aureus is famous for its antimicrobial resistance nature. It is a responsible disease-causing agent in animals and humans such as cellulites, abbesses, and furuncles [8]. It common flora that is found in both humans and animals [9]. Understanding the antimicrobial drug resistance profile of this agent has an important role to indicate the importance of the multidisciplinary approach to the fighting crisis that is caused by antimicrobial drug resistance [10].
The objective of this research is
• To assess the awareness of physicians and veterinarians towards antimicrobial drug resistance.
• Isolation of Staphylococcus aureus from veterinary clinic determining its Antimicrobial drug resistance profile.
Matrial and Methods
Study area
The study is conducted from November 2021 to March 2022 in Kality veterinary clinic, St. Paul Millennium Hospital and Aklilu Lemma Pathobiology institute. Addis Ababa is the capital city of the federal democratic and republic of Ethiopia which is divided into eleven sub cities namely Addis Ketema, Akaky Kaliti, Arada, Bole, Gullele, Kirkos, Kolfe Keranio, Lideta, Nifas Silk-Lafto, Yeka and Koye feche. Addis Ababa is located near to the equator with latitude and longitude of between 8o 55’ and 9o 07’ north and 38o 40’ and 38o 50’ east respectively. It is a highland area with an altitude of 2000 to 3000 meters above sea level having average annual rainfall of 1800mm and the temperature of the area ranges from 14oC to 21oC. The overall average temperature is 17.5oC [11] (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Map of the study area.
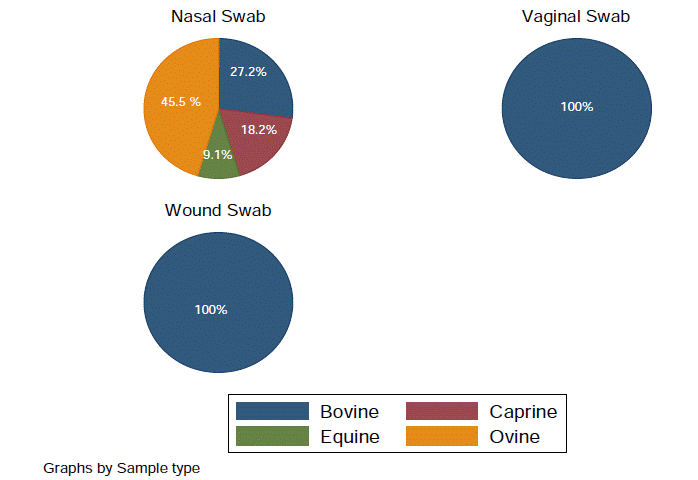
Figure 2: Total sample collection diagram species to sample type.
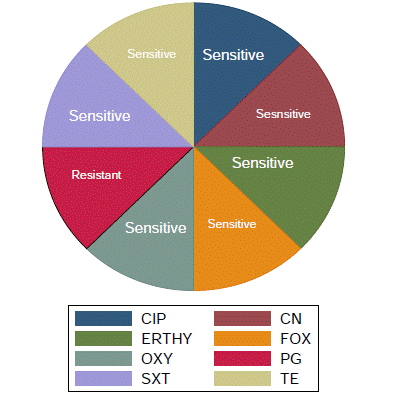
Figure 3: Pie chart representation of drug resistance test profile of
staphylococcus aureus.
Study population (Target population)
This study target human health professionals and animal health professionals in order to evaluate the awareness on antimicrobial drug resistance and their interest to work on common issues they are concerned. This study also target animals who arrive and presented to Kality veterinary clinic.
Study Design
A purposive study design guarded with experimental laboratory based study and a survey based study is designed to investigate the awareness of antimicrobial drug resistance in human health and veterinary health professionals and the antimicrobial drug resistance profile of staphylococcus aureus from Kality veterinary clinic respectively from (November 2021 to March 2022). The explanatory variables like age, sex and species of animal and management system are considered.
Sample size determination
The study sites (government hospital and veterinary clinic) were selected randomly by lottery system due to the ease and willingness to provide the information. The total sample size purposively adjusted during the questionnaire survey were 20 animal health professional, 20 human health professional who were actively working with drug prescription.
The total required sample size required for testing of drug resistance profile for staphylococcus aureus from the Kality veterinary clinic is 40 which is selected purposively. This sample include any species of animal who arrived to the Kality clinic with wound and respiratory problem.
Questionnaire Survey
A semi structured questionnaire was designed to obtain a relevant information on the awareness of Antimicrobial drug resistance on both in human health professionals and animal health professionals. The questionnaire is prepared for the professionals to measure their knowledge attitude and practice. The questionnaire is designed and prepared in English language and distributed for Physician and Veterinarian to St.Paul Hospital and Addis Ababa University Pathobiology institute respectively.
Study methodology
The study started by taking of samples like wound swab, nasal swab and vaginal swab from Kality veterinary clinic (considering age, sex, and species). By careful evaluation of the animals that arrives to Kality Veterinary Clinic samples are collected from the animal and for further finding of Staphylococcus aureus from the samples they were aseptically collected and subjected to transporting media and presented to Animal Health Inistitute (AHI).
In parallel to the laboratory sample collection a questionnaire survey is conducted to St.Paul hospital and Addis Ababa University Aklilu lemma pathobiology institute.
Sample collection and transportation: Sampling was carried out daily for 6 consecutive days where a total of 40 samples were collected aseptically from patient animals that arrived to Kality veterinary clinic. The sample includes nasal swab, wound swab and vaginal swab. The collected samples presented to transporting media for purpose of further laboratory test in order to isolate Staphylococcus aureus from the sample.
For questionnaire survey again a total sample of 40 collected from Physician and Veterinarian from St. Paul hospital and Addis Ababa University pathobiology institute and other private veterinary clinic respectively.
Bacterial Isolation and Identification: Bacterial isolation and identification was conducted under the protocols of AHI. Since the primary and main step of any bacteriological isolation starts with preparation of media, the study started by preparing different selective, differential and indicator media that were needed for the research. Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) media, Maltose Purple Agar (MPA) media and also Nutrient agar media, blood agar media, and Muller-Hinton agar Media were prepared whenever they were needed to do colony characterization and to perform further biochemical, confirmatory and susceptibility tests. For confirmation of the isolates MALDI Biotyper is used which is the first work in history of Ethiopia in Identification of Staphylococcus aureus.
Culture on Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) broth, MSA, MPA and Nutrient Agar Medias: Brain heart infusion broth was prepared to enrich the samples in which a loop full of each sample was inoculated into 5ml of a brain heart infusion in a test tube and incubated aerobically at 370oC for 24h. After 24h of incubation the samples were ready for culture onto the first selective medium for Staphylococcus species, Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA). The organisms which grow in the brain heart infusion was sub-cultured onto Mannitol Salt Agar and incubated at 370oC for 24h. Staphylococcus aureus strains can rapidly ferment mannitol and produces colonies surrounded by yellow zones unlike other staphylococcal species. The colonies that grew on MSA were then sub-cultured on Maltose Purple Agar (MPA) Medium and again the colonies that grew on MPA were also subcultured purely by quadrant streaking on Nutrient Media to find single colonies for colony characterization with gram staining and to do biochemical tests like catalase, coagulase and motility tests and MBT tests for confirmation by species level identification of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. 5% sheep blood agar media was also used to sub-culture pure colonies and appreciate the typical beta (β) hemolysis characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus.
Biochemical tests: The following biochemical tests were performed including gram staining, Catalase test, Coagulase test and DNase test for the isolation of staphylococcus aureus pathogen.
Gram Staining: Gram staining was conducted to appreciate the gram positive Staphylococcus aureus colonies which stains purple and resembles the looks of clusters of grapes which were cocci shaped under microscope for positive samples [12].
Catalase Test: Catalase test was carried out where Staphylococcus aureus isolates had a catalase enzyme which could convert hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into water (H2O) and oxygen (O2). The presence of oxygen during the test was observed by immediate bubble formation upon the application of the suspected colony into a drop of 3% hydrogen per oxide on a glass slide and considered as catalase positive [12].
Motility test: Motility test is a test conducted to determine motility of a bacteria. A semi-solid agar used to examine a motile bacteria by observing a diffused color over the semi-solid agar. This media is basically a soft media in consistency for the sake of the motility of the bacteria.
Tube Coagulase Test: Tube coagulase test was also conducted which determines the production of coagulase enzyme by Staphylococcus aureus indicated by clumping of the isolates after heavy suspension of the bacterial colonies were inoculated into a test tube containing rabbit plasma of 0.5ml, mixed well and incubated at a temperature of 37˚C for at least 6h (sometimes incubation up to 24h is needed). The presence of the enzyme during the test differentiates Staphylococcus aureus from other Staphylococcal species like S. epidermidis and S. saprophyticus [12].
MALDI Biotyper: One of the most important aspect of microbiology is identification of microorganism to species level. In early time different traditional laboratory activity is implemented which are labor intensive and time taking like that of biochemical assay. Apart from that sequencing technology is developed recently which are very important in providing a precise information about the species and it is a very expensive technology now a times. The most advanced technology which is developed is identification of microorganisms on basis of their protein using a molecular based mass spectrophotometry identification method that enable faster and more effective with efficient analysis than conventional assay/ sequencing.
MALDI-TOF is a matrix assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrophotometry is the most advanced technology with high potential of differentiating microbes in small time. It is a technology which is characterized by easy procedure, rapid, robust and accurate result. Most importantly it is cost effective and efficient identification technology.
MBT now a times it is more preferable than whole genome sequence in microbe identification. MBT now a times taking the attention of scientific research because it results unique proteomic fingerprint of organism. Due to its potential to detect protein technically it is presented with high accuracy of identifying the given microbes from positive culture. The process of preparing the sample is involve in 4 bold major steps the first one is TFA-MALDI target plate cleaning procedure and the second one is eDT procedure for purpose of transfer colonies to the wheel the third one is EXT procedure for the ease of the MALDI to easily disperse the molecule when the leaser light is released in the vacuum and fourth one is direct transfer procedure.
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test: Disc Diffusion (Bauer- Kirby) Susceptibility Test
Antimicrobial Susceptibility test of the Staphylococcus aureus isolates was analyzed for 8 different antimicrobials namely Penicillin G (10 units), Tetracycline (30μg), Oxy-tetracycline (30μg) Ciprofloxacin (10μg), Cefoxitin (30μg), Sulphamethoxazole+Trimethoprim (25μg), Erythromycin (15μg) and Gentamicin (10μg) (Table1). The antimicrobials were selected based on their availability at the current market. The test was carried out by using the agar disc diffusion method, first 5ml of 0.85 saline water was dispensed in a test tube labeled for 3 isolates and the colonies from a nutrient media was then taken by a swab and put in the saline water and each suspension with the organism was mixed well and measured for a turbidity of 0.5 and cultured thoroughly on Muller- Hinton Agar (MHA) media of 4mm depth and 90mm diameter. After that the 8 different antimicrobial discs listed above were taken from their corresponding containers by disc diffuser and diffused in the respective MHA Media of the 3 isolates and incubated at 37oC for 18h. After incubating for 18h, measurement of the diameter of the clear Zones of Inhibition (ZOIs) around and including the antimicrobial discs of each isolate were conducted and interpreted to categorize as susceptible, intermediate and resistant according to the performance standards given by Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute [13].
Antibiotics
Disc code
Concentration
Susceptible
(mm)Intermediate
(mm)Resistance
(mm)Ciprofloxacin
CIP
5µg
≥ 21
16-20
≤15
Penicillin G
PG
30 µg
≥ 21
17-21
≤16
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim
SXT
5 µg
≥16
11-15
≤10
Cefoxitin
FOX
5µg
≥23
20-22
≤19
Oxytetracycline
OXY
30 µg
≥15
12-14
≤11
Gentamycin
CN
10 µg
≥15
13-14
≤12
Erythromycin
ERTHY
5 µg
≥15
13-15
≤12
Tetracycline
TE
30 µg
≥15
13-15
≤12
Table 1: Antibiotic disks used to test staphylococcus aureus and their respective concentration.
Data Analysis
Data obtained both from the survey and laboratory were entered to Microsoft excel sheet, coded and analyzed by using a computer software called STATA version 20. Descriptive statistics such as proportion or percentage were used to summarize the data and calculate status of Staphylococcus species at Kality clinic also the data which is found from questioner survey summarized in percentage. The prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus was calculated as number of samples examined multiplied by 100. Difference among between proportions of samples were determined by chi-square (X²) test. A P<0.05 was considered to be indicative of statistical significant difference.
Result
The present study cover two research program. The first one is questionnaire survey which target professionals like physician and veterinarian from St. Paul hospital and Addis Ababa University Aklilu lemma Pathobiology institute respectively. In this study 40 professionals are selected 20 physician (50%) and 20 veterinarian (50%) from both institute. The second one is examining the drug sensitivity profile Staphylococcus aureus on samples which are collected from Kality veterinary clinic. In this study is 22 samples from nasal, 17 sample from wound and 1 from vagina is collected.
Questionnaire survey result
A semi structured questionnaire survey was designed on a total of 40 professionals which consists 50% physician and 50% veterinarian. In this questionnaire survey out of the 20 physician 75% are male and 25% are female and 65% of the physician are well aware about the difference between antimicrobial drug resistance and antibiotic resistance the remaining 35% of the physician consider both terms are the same in parallel to this only 40 % of physician know about one health approach the remaining 60% did not know about this concept.
Relatively on this survey result veterinarian have good knowledge and awareness about AMR. Among the 20 veterinarians 95% of the respondent was male and the remaining 5% are female and 90% of the veterinarian well know about the difference between antimicrobial drug resistance and 100% the veterinarian well know about the one health concept and its importance.
In this study period many variable are significantly related with the professional status. From the total study groups 67.5% are first degree holder and 27.5% are second degree holders and only 5% are third degree holders. The result of this study basically reflects that veterinarians are relatively have a good knowledge and awareness about antimicrobial drug resistance than physicians (Table 2).
Variables
Profession
X2
P-value
Physician
Veterinarian
(MD)
(DVM)
Education status
MD/DVM
12
15
2.42
0.2
MSc/MPH
6
5
PhD
2
0
Sex
Male
15
19
3.1
0.07
Female
5
1
Source of knowledge
Education
10
13
8.1
0.01
Internet
0
4
Research
10
3
AMDR is major public health threat
Yes
20
19
1.02
0.03
No
0
1
Difference between antibiotic drug resistance and antimicrobial drug resistance
Yes
12
13
0.106
0.744
No
8
7
Causes of AMDR
Misuse of drug
7
9
12.8
0.005
Over use of drug
3
0
Hospital setting
0
7
All
10
4
Impact of AMR
Increase the risk of illness for prolonged period
4
0
4.44
0.035
Epidemics are prolonged
0
0
All
16
20
Knowledge about one health
Yes
8
20
17.14
0
No
12
0
Does one health approach is very important to fight AMR
Yes
8
20
17.14
0
No
12
0
Recent drug resistance profile of staphylococcus aureus
Yes
7
17
10.14
0.001
No
13
3
Problem of AMR solved in the future
Yes
14
15
0.125
0.723
No
6
5
Table 2: Summary of the status, knowledge and attitude of veterinarians.
Knowledge and attitude about antimicrobial drug resistance in the veterinarian side: Among the interviewed 20 veterinary professionals 80% of the professionals are well aware about antimicrobial drug resistance and its impact on animal health and the public health. Parallel to that all veterinarians who are involved in this questionnaire survey 100% of them know about one health approach and the importance of its role in solving the problem about anti-microbial drug resistance.
Knowledge and attitude about antimicrobial drug resistance in the physician side: On the physician side the awareness and knowledge on antimicrobial drug resistance is relatively poor comparing to veterinarians. Around 60.7% of physician well aware about antibiotic drug resistance and the remaining 39.3% have a poor awareness and knowledge on AMDR. Beside this the more than 60% of physician don’t know about one health approach and its role in solving the problem of AMDR. Only 40% of the physician know about one health approach and its role in fighting against AMDR.
Bacterial isolation and identification result
According to this study, all the 40 samples which are collected from bovine, caprine, ovine and equine were subjected to transport media and then inoculated to MSA and MPA for isolation of staphylococcus aureus (Table 3).
Sample type
Growth on MSA
Growth on MPA
BHIA
Gram stain
Catalase test
Coagulase test
Motility test
Blood agar test
Nasal Swab (22)
11
9
9
3
3
3
3
3
Wound swab (17)
4
4
4
4
4
4
2
2
Vaginal swab (1)
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Table 3: Number of samples that showed growth on MSA and MPA and that were positive for catalase, coagulase tests and motility test.
MALDI-Biotyper test Identification: A total of 5 susceptible isolates were introduced to MALDI-Biotyper machine and among the 5 isolates 3 (7.5%) of the isolated samples are confirmed as Staphylococcus aureus. These isolates were analyzed for 8 different antimicrobials to assesses their antibiotic profiles and categorize them as susceptible, intermediate or resistant (Table 4).
Variables
Number of tested
Positive sample
X2
P-value
Sex
Male
38
3
0.17
0.67
Female
2
0
Species
Bovine
24
0
12.6
0.006
Equine
2
0
Ovine
10
1
Caprine
4
2
Sample type
Nasal swab
22
2
2.6
0.256
Wound swab
17
1
Vaginal swab
1
0
Table 4: Association of risk factors with staphylococcus aureus.
Association of potential risk factors with the presence staphylococcus aureus is indicated on the above (Table 2). As a result, no statistically significant difference of Staphylococcus aureus was observed between both sexes of the species and sample type (P>0.05). Additionally the species were found significantly associated with staphylococcus aureus positivity.
Prevalence of staphylococcus aureus: The overall prevalence of staphylococcus aureus in 4 types of animal from Kality veterinary clinic is 7.5% (3/40). The specific prevalence was 0%(0/40), 0%(0/40), 2.5%(1/40) and 5%(2/40) from bovine, equine, ovine and caprine respectively.
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Test
A total of 3 isolates were subjected to the 8 antibiotic discs for AMDR test. The AMDR test results showed that S. aureus is 100% susceptible to only one antimicrobial agents and showed different percentage of sensitivity to seven antimicrobial discs.
As shown in table, all the 3 isolates of Staphylococcus aureus were found to be highly susceptible to seven antimicrobials namely Ciprofloxacin (100%), Gentamycin (100%), Sulphamethoxazole+Trimethoprim (100%), Erythromycin (100%), Cefoxitin (100%), Oxytetracycline (100%) and Tetracycline (100%). However the three isolates were also found to be highly resistant to Penicillin G (100%).
Risk analysis
In this study the occurrence of a risk factors like lack of knowledge on one health approach and the government healthcare policy leads to variation in the knowledge and attitude of antimicrobial drug resistance in physician and veterinarian. A significant difference was observed between human health professional and animal health professional on their knowledge in antimicrobial drug resistance. Parallel to that, prevalence of the Staphylococcus aureus from Kality clinic also revealed significant differences in each species (P< 0.001) however, no significant relationship was observed between the prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and sample type and sex (P= 0.17) and (P=0.25) respectively.
Discussion
This research study is a two phase research program. In the first phase it involves on the awareness and knowledge of antimicrobial drug resistance on human health professional and animal health professional and the second phase of this research program involves in isolation identification and drug sensitivity test of staphylococcus aureus.
Through this research study the physician shows a strong knowledge gap on the awareness and knowledge of antimicrobial drug resistance. In this research finding 40 % of the physician did not know about the difference between antimicrobial drug resistance and antibiotic drug resistance. The result of this statement strongly agree with [14]. Such kinds of knowledge gap often occur due to educational curriculum of the country and health regard policy. Parallel to that most of the physician almost around 60 % of the interviewed professionals do not know about the one health concept which only 40 % of the participant know about one health approach with poor information this finding is closely related to (Minen et al., 2010). Beside to this in this research study only 50 % of physician know well about the exact cause of antimicrobial drug resistance the remaining 50% only have a partial knowledge on the etiology of AMDR. This finding is almost consistent with [15].
On the veterinarian side relatively there is a good knowledge and awareness about antimicrobial drug resistance. Around 65% of veterinarians well aware about antimicrobial drug resistance this result fit with the finding of [16]. On the other hand in this study veterinarian are well aware about one health approach. In this study the participant veterinarian 100% of them have a sufficient knowledge and awareness about one health approach. This finding is in agreement with [17]. On top this in this research veterinarians do have a sufficient knowledge on the impact of antimicrobial drug resistance. In this finding the veterinarians do have a better knowledge and awareness on the impact of antimicrobial drug resistance and is in agreement with the finding of [18].
In the present day the problem of antimicrobial drug resistance is a headache problem for our world. It requires strong collaboration and effective work to reduce the impact of the AMR. In this research study a strong knowledge gap is observed between human health care professionals and animal health care professionals. This result indicate that to combat the risk of AMR there should be a strong common and collaborative work is required between physician and veterinarian.
On the other hand in the second phase of this research program the antimicrobial drug resistance profile of staphylococcus aureus is examined. In this study finding staphylococcus aureus is become 100 % resistant for penicillin G antibiotic. This finding completely agree with the research conducted in [19]. Although in this research staphylococcus aureus become susceptible for seven antimicrobials namely Ciprofloxacin (100%), Gentamycin (100%), Sulphamethoxazole+Trimethoprim (100%), Erythromycin (100%), Cefoxitin (100%), Oxytetracycline (100%) and Tetracycline (100%). Basically this finding more closely related to in this research finding staphylococcus aureus species have a big opportunity to develop a resistance for recent antibiotic drugs because of over use and misuse of drugs (Table 5).
Drug lists
Antiobiotics code
Concetration
Susceptible
Intermediate
Resistant
Ciprofloxacin
CIP
5μg
3(100%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
Gentamycine
CN
10 μg
3(100%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
Erythromycin
ERTHY
5 μg
3(100%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
Cefoxitin
FOX
5μg
3(100%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
Oxytetracycline
OXY
30 μg
3(100%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
Penicillin G
PG
30 μg
0(0%)
0(0%)
3(100%)
Sulphamethoxazole trimethoprim
SXT
5 μg
3(100%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
Tetracycline
TE
30 μg
3(100%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
Table 5: Antimicrobial drug resistance susceptibility test result of staphylococcus aureus from the isolated sample.
In Kality veterinary clinic where staphylococcus aureus is collected for this research, there is over use of antibiotics like Oxytetracycline, Tetracycline and Gentamycin and this increase significantly the capacity of the bacteria to be resistant for such kind of drugs. Meanwhile this bacteria develop a resistance for drugs like that of gentamycin, cefoxitin, and oxacillin in research finding of [20].
This Finding from this research show that staphylococcus aureus species have a significant correlation with species. 75% of the staphylococcus aureus species is isolated from goat and the remaining 25% is isolated from sheep. This finding agree with the research conducted in university of Zurich, Zurich-Switzerland [21]. Results from this research indicates that pathogenic staphylococcus aureus can be isolated from nasal discharge which can be harmful for the animal. 75% staphylococcus aureus is isolated from the nasal swab of goats which can indicate that the presence this pathogenic bacteria in the body system can be an opportunity for the animal to be exposed for staphylococcal disease.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Antimicrobial drug resistance is one of the biggest headache problem for our universe. Now a times pathogenic bacteria is developing a resistance for many antibiotic drugs which can cause a serious problem for the health of animal human and environment. Staphylococcus aureus is one of the pathogenic bacteria which causes a clinical cases like abscesses, furuncles and cellulitis. This bacteria can be found as normal flora in the body of animal and human. In this research finding it is noted also that this bacteria is found in nasal fluid of the animal. Once this bacteria entered to body system it can collapse the physiology by releasing its toxin. This bacteria is a very important bacteria in the dairy sector too. In this research finding this bacteria is not isolated from bovine. Staphylococcus aureus completely develop a resistance for penicillin G which mean this antibiotic don’t have any relevant importance in treating clinical cases that are caused by pathogenic staphylococcus aureus species in both human and animal and it is true that if the knowledge and the attitude of physician and veterinarian if it is not changed with one health perspective then it became very difficult to fight AMR crisis in the health sector. There is a strong knowledge gap in physician and veterinarian in the issue of antimicrobial drug resistance. This serious gap can be a good and great opportunity for pathogenic bacteria to develop a resistance for antimicrobial.
• Therefore, relying on the conclusion given above the following recommendations are forwardedIt is very important to develop a well-designed and well organized educational curriculum which allows the physician and veterinarian to know their common background and need of their collaboration
• Strong one-health approach based health policy is needed to fight the risk of antimicrobial drug resistance
• It is very important to reduce the contact of animals especially with ovine and caprine to touch their nasal fluid in bare hand
• Training should be given for physicians and veterinarian to build a common background and knowledge about antimicrobial drug resistance
Acknowledgement
First and foremost, I would like to praise my Heavenly Father and the almighty, GOD, who has given me the strength to complete my thesis work with victory through his son the Lord Jesus Christ.
Secondly I would like to express my deepest and sincere gratitude to my advisor, Prof. Gezahegn Mamo for his guidance, comments, and devotion of time in rectifying the manuscript and I would like to express my deepest gratitude for Dr. Tesfaye Rufael General Director of Animal Health Institute and Hika Waktole Dean of Addis Ababa University college of Veterinary medicine for their contribution and support to do my thesis in my interest area.
I am also pleased to thank my father Kassahun Ayalew and my mother Alemenesh Tesegaye for their unlimited contribution and support to me and the entire Kassahun’s family for their love, support, and help. Dr. Rediet Wolde Assitant Professor of Veterinary Pathology at Jimma University was helping me in all staff of my paper work and for her constant encouragement and support in all my activity. Dr. Berhanu Abera PhD Student at Addis Ababa University, Dr. Shubisa Abera a staff at Animal Health Institute, I would like to thank them for their incredible support and for the true inspiration and courage they have given to me in the process of preparing this research and through every aspect I was struggling in.
Finally I owe my deepest gratitude for United People Global (UPG) Leadership school (Switzerland, Geneva) for their moral support, help and mentor in designing and preparation of my paper I really benefited a lot from them.
References
- Wise R, Hart T, Cars O, Streulens M, Helmuth R, et al. Antimicrobial resistance. BMJ. 1998; 317: 609-610.
- McEwen SA, Collignon PJ. Antimicrobial Resistance: a One Health Perspective. Microbiol Spectr. 2018; 6.
- Abushaheen MA, Muzaheed null Fatani AJ, Alosaimi M, Mansy W, George M, et al. Antimicrobial resistance, mechanisms and its clinical significance. Dis Mon. 2020; 66: 100971.
- Ferri M, Ranucci E, Romagnoli P, Giaccone V. Antimicrobial resistance: A global emerging threat to public health systems. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017; 57: 2857-2876.
- Brinkac L, Voorhies A, Gomez A, Nelson KE. The Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance on the Human Microbiome. Microb Ecol. 2017; 74: 1001-1008.
- Bright-Ponte SJ, Walters BK, Tate H, Durso LM, Whichard JM, et al. One Health and antimicrobial resistance, a United States perspective. Rev Sci Tech. 2019; 38: 173-184.
- Collignon PJ, McEwen SA. One health-its importance in helping to better control antimicrobial resistance. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2019; 4: 22.
- Al-Masaudi SB, Day MJ, Russell AD. Antimicrobial resistance and gene transfer in Staphylococcus aureus. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991; 70: 279-290.
- Abdi RD, Gillespie BE, Vaughn J, Merrill C, Headrick SI, Ensermu DB, et al. Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Dairy Cows and Genetic Diversity of Resistant Isolates. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2018; 15: 449-458.
- Boss R, Overesch G, Baumgartner A, Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli, Enterococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus from Raw Fish and Seafood Imported into Switzerland. J Food Prot. 2016; 79: 1240-1246.
- Kabite G, Suryabhagavan KV, Argaw M, Sulaiman H, n.d. GIS-Based Solid Waste Landfill Site Selection in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia 15.
- Quinn PJ, Carter ME Markey B, Carter GR. Clinical Veterinary Microbiology. Wolf/Mosby, London, 1994.
- CLSI: Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. 30th ed. CLSI supplement M100. Wayne, PA: Clinical and laboratory standards institute. 2020.
- Abbo L, Sinkowitz-Cochran R, Smith L, Ariza-Heredia E, Gómez-Marín O, et al. Faculty and resident physicians’ attitudes, perceptions, and knowledge about antimicrobial use and resistance. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2011; 32: 714-718.
- Guerra CM, Pereira CAP, Neto ARN, Cardo DM, Correa L. Physicians’ perceptions, beliefs, attitudes, and knowledge concerning antimicrobial resistance in a Brazilian teaching hospital. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology. 2007; 28: 1411-1414.
- Adekanye UO, Ekiri AB, Galipó E, Muhammad AB, Mateus A, et al. Knowledge, attitudes and practices of veterinarians towards antimicrobial resistance and stewardship in Nigeria. Antibiotics. 2020; 9: 453.
- Monath TP, Kahn LH, Kaplan B. One health perspective. ILAR journal. 2010; 51: 193-198.
- Wangmo K, Dorji Thinley Pokhrel N, Dorji Tshering Dorji J, Tenzin T. Knowledge, attitude, and practice on antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance among the veterinarians and paraveterinarians in Bhutan. PLoS One. 2021; 16: e0251327.
- Chambers HF, Deleo FR. Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009; 7: 629-641.
- Guo Y, Song G, Sun M, Wang J, Wang Y, Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020; 10: 107.
- Minen MT, Duquaine D, Marx MA. Weiss D. A survey of knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs of medical students concerning antimicrobial use and resistance. Microbial Drug Resistance. 2010; 4: 285-289.: