Abstract
Background: Significant number of IT professionals suffer from various health problems, including poor mental health and sleep quality, which affects their work efficacy and quality of life. Mind Sound Resonance Technique (MSRT) is a chanting based relaxation technique showed to be effective in improving the physical and mental health of individuals.
Aim: Present study is intended to evaluate the effect of MSRT on anxiety, mood profile, and sleep quality in IT professionals.
Methods: One hundred IT professionals (54 males) with age range 25-40 years (average 29 years.) received 45 minutes of MSRT intervention thrice a week for one month. Participants were excluded from the study if they had any kind of chronic disease, regular antipsychotic medication, auditory impairment, major depression, previous exposure to any kind of Yoga in past one year. The participants were assessed for state & trait anxiety, mood profile, and sleep quality at baseline and after one month using standard assessment measures. Data were analyzed in SPSS version 20 software.
Results: There was a significant improvement in state anxiety (23% decrease), trait anxiety (19% decrease), mood disturbance (84% decrease), and sleep quality (56% improvement) after one month of MSRT practice compared to baseline.
Conclusion: Present pilot study indicates the potential use of MSRT intervention in improving mental health and sleep quality in IT professionals. However, future studies should be conducted with a large sample size and robust research design.
Keywords: Chanting; MSRT; Sleep; Mood disturbance; IT professionals
Introduction
Sleep is a period of rest for the body and mind, during which volition and consciousness are in partial or complete abeyance and the bodily functions partially suspended. Sleep deprivation or poor sleep can have a negative influence on the body in the short term, and over a period, it can lead to chronic health problems and negatively impact on the quality of life, which can manifest in the form of various symptoms like mood swings, hallucinations, depression, Cold, Flu, and microsleep [1]. It can also lead to the impaired immune response, impaired cognitive functions and can affect our mental health, causing mood disorders like depression [2-4]. Poor sleep quality impairs emotional regulation, which can lead to disruptive mood dysregulation disorder [5] and can cause impairment in the performance during crisis management [6].
The most common workplace problem experienced by all professionals irrespective of their nature of work is job stress; however, this phenomenon is more common in situations that are deadline-driven. Software house is one such sector, which is affected profoundly by this challenge, and professionals serving these organizations are often observed to be under huge stress. Software professionals’ nature of the job is highly time-bound, client-oriented and technology-intensive, etc. Workplace stress is quite common and can be measured through different sources. Workload, time pressure, role ambiguity, role conflict, career progress, and communication are considered as major sources of pressure in the life of an Information System professional [7]. Stress has penetrated every profession, and the effect of stress has been prevalent in the IT profession as well. The threat is direct to the mental health, physical health, and overall well-being.
Mind Sound Resonance Technique (MSRT) is a chanting based relaxation technique that involves experiencing with closed eyes the internal vibrations and resonance developed while chanting the syllables A, U, M, Om, and Mahamrityunjaya mantra sounds [8]. It can be practiced in sitting as well as the supine position and has been found useful in reducing the state anxiety, pain, and tenderness in chronic neck pain patients [9]. MSRT intervention has also been found to have a potential role in reducing state anxiety and enhancing psychomotor performance in patients suffering from Generalized Anxiety Disorder [10].
Materials and Methods
Aims and objectives
Aim: The aim of this study was to assess the effect of chanting based relaxation technique MSRT (Mind sound resonance technique) on mental health and quality of sleep in IT professionals.
Objectives
• To study the effect of MSRT on anxiety levels and mood disturbances in IT professionals.
• To study the effect of MSRT on quality of sleep in IT professionals.
Source of subject
The source of sample population was IT Company located in Kochi, Kerala.
Sample
A sample of 100 IT professionals from various IT companies was included in the study.
Inclusion criteria
• IT professionals working in day-time.
• Minimum working experience of 6 months in any IT company.
• Willing to participate.
• Not suffering from any major neuro psychiatric illness.
• Not done Yoga in past one year.
Exclusion criteria
• Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) employees.
• Night-shift workers.
• Having job experience of <6 months.
• Not willing to participate
Informed consent
The consent form was filled by the respective subjects prior to the commencement of the study.
Design
Uncontrolled, Single group pre -post study.
Variables studied
• Anxiety using The State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) inventory
• Mood Disturbance using Profile of Mood States (POMS) questionnaire
• Sleep using Pittsburg sleep quality inventory
Intervention
The study group received the yoga relaxation therapy called Mind Sound Resonance Technique (MSRT) done in supine position three times a week for four weeks from August 25th, 2016 to September 29th, 2016.
Data Extraction and Data Analysis
Data extraction and analysis
The data was collected to assess the mood disturbance, anxiety, and quality of sleep through the appropriate questionnaires. A total of 100 IT professionals were divided into two batches, one in morning and other in the evening.
Intervention was given to both the batches at 7:30 morning as well as in the evening. The participants were requested to fill the 3 questionnaires on day 1 and after the completion of intervention period i.e. on day 30.
Normality of data was assessed using Shapiro-Wilk test and results were analyzed using Paired Sample t-test using SPSS 20.
Results
The sample size of 100 comprises of 46% females and 54% males with details given in (Table 1). The analysis of the results shows that there was a significant reduction in state and trait anxiety (p=0.000; 23% & 19% respectively) and total mood disturbance (p=0.000; 84%) shown in (Figure 1 and 2) respectively. A significant improvement in global sleep quality (p=0.000; 57%) was also found post intervention in IT professionals as shown in (Figure 3).
Gender
No. of Participants
Mean Age ± SD
Male
54
29.87±3.50
Female
46
28.52±3.328
Table 1: Demographic details of participants.
Measurement Tools
Pre-Mean ± Standard Deviation
Post-Mean ± Standard Deviation
%Change
p-Value
State Anxiety
35±7.55
26.91±5.61
23.11
0.000
Trait Anxiety
38.82±6.56
31.49±5.66
18.88
0.000
PQSI
2.87±2.82
1.25±1.57
56.44
0.000
POMS
25.87±31.08
4.04±16.89
84.38
0.000
Table 2: Pre and Post mean and standard deviation of various variables in the intervention group.
Measurement Tools
Pre-Mean ± Standard Deviation
Post-Mean ± Standard Deviation
%Change
p-Value
Subjective sleep quality
0.70±0.65
0.17±0.42
75.71
0.000
Sleep Latency
0.47±0.55
0.19±0.39
59.57
0.000
Step Disturbance
0.4±0.91
0.13±0.38
67.5
0.003
Use sleeping medication
0.16±0.42
0.07±0.25
56.25
0.002
Sleep Duration
0.53±0.62
0.3±0.48
43.39
0.000
Day time dysfunction
0.11±0.39
0.02±0.14
81.81
0.012
Habitual Sleep efficiency
0.58±0.76
0.36±0.71
37.9
0.002
Global PSQI score
2.95±2.8
1.24±1.54
57.9
0.000
The analysis of the results show that there was a significant reduction in state and trait anxiety (p=0.000) and total mood disturbance (p=0.000) and significant improvement in global sleep quality (p=0.000) post intervention in IT professionals.
Table 3: Mean and standard deviation of various domains of sleep as mentioned in Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index questionnaire.
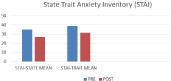
Figure 1: Graphical representation of the change in state and trait anxiety
due to intervention.
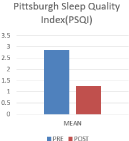
Figure 2: Graphical representation of the change in global sleep quality due
to intervention.
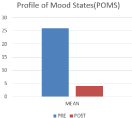
Figure 3: Graphical representation of change in mood disturbances due to
intervention.
Discussion
The study was aimed to assess the effect of chanting based relaxation technique, Mind Sound Resonance Technique (MSRT) on mood disturbances, anxiety levels and sleep quality of IT professionals. The analysis of the results shows that Mind Sound Resonance Technique improves the global sleep quality and reduces the total mood disturbance and anxiety levels in IT professionals significantly.
In the study done by Hemant Bhargav et al. in 2015 on 15 patients with generalized anxiety disorder, the mind sound resonance technique on was found to enhance the psychomotor performance and reduce the state anxiety immediately after the practice [11]. In another controlled study by P.S. Srinivas et al. in 2015 on 96 IT professionals, intervention of Cyclic Meditation for the period of 2 months reduced the job anxiety to 19.52 % and perceived stress by 34.4 % [12]. In our study, we found that 45 minutes of MSRT intervention 3 times a week for one month reduces the state anxiety by 23%, trait anxiety by 19%, improves the global sleep quality by 56% and reduces the total mood disturbance by 84%.
All the variables assessed in the study i.e. sleep disturbance, mood disorders and anxiety are interrelated. All these affect each other individually [13]. A person having greater mood disturbance and higher anxiety levels tends to have poor mental health and poor sleep quality [14]. Therefore reducing the mood disturbance and anxiety levels improve the mental health of an individual, which in turn can improve the sleep quality of a person also.
Mind Sound Resonance Technique is a meditation technique that helps to induce relaxation in the body as well as mind. Meditation and relaxation practices help to bring sympatho-vagal balance and cause the parasympathetic dominance thereby reducing the stress, anxiety and improving the sleep quality of an individual.
The present study is the first study to see the effect of the Mind Sound Resonance Technique (MSRT) in IT professionals. The study included a good number of participants; however, the studies with a control group are required to validate the results of this study.
Conclusion
The present single group pre-post study shows that Mind Sound Resonance Technique (MSRT) helps to reduce the mood disturbance and anxiety levels in the IT-professionals and improves their sleep quality.
References
- Horne JA. A review of the biological effects of total sleep deprivation in man. Biol Psychol. 1978; 7: 55-102.
- Smith TJ, Wilson M, Karl JP, Orr J, Smith CD, Cooper AD, et al. Impact of sleep restriction on local immune response and skin barrier restoration with and without “multinutrient” nutrition intervention. J Appl Physiol. 2017; 124: 190-200.
- Wadhwa M, Kumari P, Chauhan G, Roy K, Alam S, Kishore K, et al. Sleep deprivation induces spatial memory impairment by altered hippocampus neuroinflammatory responses and glial cells activation in rats. J Neuroimmunol. 2017; 312: 38-48.
- Giuntella O, Han W, Mazzonna F. Circadian Rhythms, Sleep, and Cognitive Skills: Evidence from an Unsleeping Giant. Demography. 2017; 54: 1715- 1742.
- Waxmonsky JG, Mayes SD, Calhoun SL, Fernandez-Mendoza J, Waschbusch D, Bendixsen BH, et al. The association between Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder symptoms and sleep problems in children with and without ADHD. Sleep Med. 2017; 37: 180-186.
- Arzalier-Daret S, Buléon C, Bocca ML, Denise P, Gérard JL, Hanouz JL. Effect of sleep deprivation after a night shift duty on simulated crisis management by residents in anaesthesia. A randomised crossover study. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2018; 37: 161-166.
- Rashidi Z, Jalbani AA. Job stress among software professionals in Pakistan: A Factor analytic study. J Independent Stud Res. 2009; 7: 1-2.
- Saoji A, Mohanty S, Vinchurkar SA. Effect of a single session of a yogic meditation technique on cognitive performance in medical students: A randomized crossover trial. J Relig Health. 2017; 56: 141-148.
- Yogitha B, Nagarathna R, John E, Nagendra HR. Complimentary effect of yogic sound resonance relaxation technique in patients with common neck pain. Int J Yoga. 2010; 3: 18.
- Dhansoia V, Bhargav H, Metri K. Immediate effect of mind sound resonance technique on state anxiety and cognitive functions in patients suffering from generalized anxiety disorder: A self-controlled pilot study. Int J Yoga. 2015; 8: 70.
- Dhansoia V, Bhargav H, Metri K. Immediate effect of mind sound resonance technique on state anxiety and cognitive functions in patients suffering from generalized anxiety disorder: A self-controlled pilot study. Int J Yoga. 2015; 8: 70.
- Srinivas PS, Kumari S, Akhilesh KB, Nagenra HR. Is job anxiety and perceived stress modifiable in Indian IT professionals? An experimental study using yoga-based intervention. Journal of Health Research and Reviews. 2015; 2: 81.
- McCrae CS, McNamara JP, Rowe MA, Dzierzewski JM, Dirk J, Marsiske M,et al. Sleep and affect in older adults: using multilevel modeling to examine daily associations. J Sleep Res. 2008; 17: 42-53.
- Breslau N, Roth T, Rosenthal L. Sleep disturbance and psychiatric disorders: a longitudinal epidemiological study of young adults. BIOL PSYCHIAT. 1996; 39: 411-418.
