
Case Series
Austin J Clin Case Rep. 2024; 11(3): 1326.
Clinical Analysis and Literature Review of 18 Cases of Children Pulmonary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Guo YL1#; Qiu Y2#; Deng Y3; Gu YY4; Huang SK1; Qin X1; Zeng LJ1; Zhang X2; Sun LH1*
1Department of Pediatric Pulmonology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, China
2Department of Thoracics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, China
3Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, China
4Department of Pathology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, China
*Corresponding author: Sun LH Department of Pediatric Pulmonology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, No. 28, Qiaozhong Middle Road, Liwan District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province, China. Email: sunlihong9797@126.com
#These authors have been equally contributed to this article. Clinical Analysis and Literature Review of 18 Cases of Children Pulmonary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma.
Received: June 06, 2024 Accepted: July 02, 2024 Published: July 09, 2024
Abstract
Bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma in children is rare, the clinical manifestations are non-specific, and it is easy to be misdiagnosed as tuberculosis, pneumonia, right lung middle lobe syndrome, asthma and other diseases, delaying the time of treatment. This article reviews the medical history of 18 children with bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma treated by the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, summarizes their clinical features, treatment and prognosis, and concludes that pathological obstruction should be considered when children with recurrent respiratory symptoms do not respond to conventional treatment. Therefore, we recommend that any child with persistent, unexplained respiratory symptoms that do not resolve after 2 weeks of treatment undergo endoscopy as soon as possible, and once MEC is confirmed by biopsy, surgical treatment is recommended. The long-term prognosis after complete tumor resection is good, but there is still a risk of recurrence and metastasis, so long-term follow-up is recommended for the child.
Keywords: Children; Pediatric; Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma; Tumor
Abbreviations: MEC Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma; PMEC Pulmonary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Materials and Methods
Materials
The 18 pathologically diagnosed children treated by the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University from July 28, 2012 to July 25, 2023, which mean age was 11.10 years old (range 4-16years).
Method
The clinical symptoms of 18 children were collated, analyzed and summarized.
Results
Clinical Symptoms
The first symptom in the case was not specific, often with cough (12/18), fever (4/18), hemoptysis (3/18) as the main manifestations, among which one girl had no symptom and found lung nodules during physical examination (Table 1).
Number (%)
Gender (M/F)
7-Nov
Mean age (Year)
11.1
Symptom
Cough
12(66.7)
Fever
4(22.2)
Hemoptysis
3(16.7)
Gasp
3(16.7)
Chest pain
1(5.6)
Bellyache
1(5.6)
Asymptomatic
1(5.6)
Table 1: General Information and Clinical Manifestations.
Radiographic Findings
Among the imaging findings, the tumors were located in the left main bronchus in 4 cases, in the upper lobe of the left lung in 1 case, in the lower lobe of the left lung in 4 cases, in the right main bronchi in 2 cases, in the upper lobe of the right lung in 2 cases, in the middle lobe of the right lung in 2 cases, and in the lower lobe of the right lung in 3 cases. Among them, CT after enhancement showed uneven enhancement in 4 cases (Figure 1-3), 9 cases with distant pneumonia (Figure 4-5). 9 cases with distant occlusion and atelectasis, 4 cases with distant emphysema, 5 cases with distal bronchiectasis, and 2 cases with pleural effusion (Table 2).
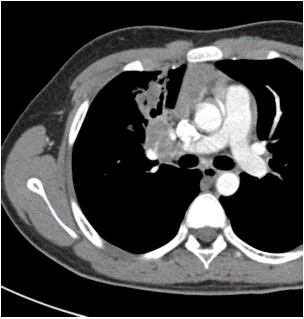
Figure 1: Chest enhanced image: Arterial phase.
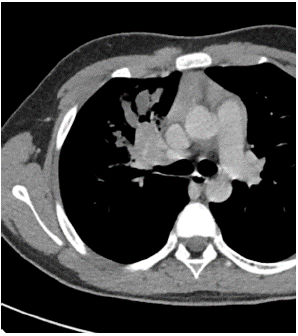
Figure 2: Chest enhanced image: Balance phase.
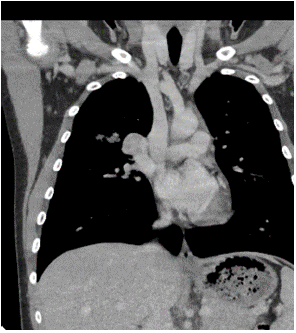
Figure 3: Image of multi-planar reconstruction.
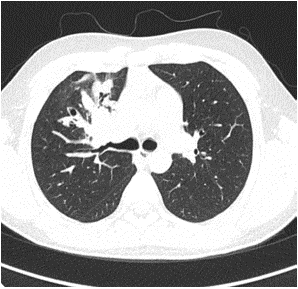
Figure 4: Chest image of one child showes distant pneumonia.
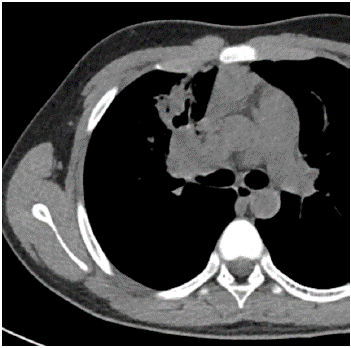
Figure 5: Chest image of one child showes distant pneumonia.
Location of the tumor
Number (%)
Left main bronchi
3(17.6)
Left upper lobe
1(5.9)
Left lower lobe
4(23.5)
Right main bronchi
2(11.8)
Right upper lobe
2(11.8)
Right middle lobe
2(11.8)
Right lower lobe
3(17.6)
Imaging Findings
Uneven enhancement
4(23.5)
Pneumonia
9(52.9)
Atelectasis
9(52.9)
Emphysema
3(17.6)
Bronchiectasis
5(29.4)
Pleural effusion
2(11.8)
Table 2: Tumor Location and Imaging Findings.
Diagnosis
All cases were diagnosed by pathological biopsy, 13 by bronchoscopic biopsy and 5 by surgical lung biopsy.
Pathological characteristics
In general, the grade of PMEC correlates with the degree of cells ‘cystic architecture, mitotic rate, perineural invasion, necrosis and degree of cytologic atypia. Low-grade tumors tend to be better circumscribed, more cystic, contain more mucous cells, show minimal cytologic atypia or mitoses and lack perineural invasion. On the other hand, higher-grade lesions are more infiltrative, more solid, have less mucous cells and more epidermoid cells, show more cytologic atypia, necrosis and perineural invasion. In our case series, there were 9 cases of low malignancy, 2 cases of moderate malignancy, 2 cases of high malignancy, and 5 cases were ungraded.
Treatment
14 cases were treated by surgery, 3 by tracheoscopic mass resection, and 1 by radiotherapy because of invasion of bulge (Table 3).
Pathology
Number (%)
Low grade
9(52.9)
Intermediate
2(11.8)
High grade
2(11.8)
Ungraded
4(23.5)
Treatment
Surgery
Sleeve resection
7(41.2)
Lobectomy
6(35.3)
Endoscopic excision
3(17.6)
Radiotherapy
1(5.9)
Metastasis
Yes
1(5.9)
No
16(94.1)
Table 3: Pathology, Treatment and Metastasis.
Metastasis
1 case of invasion of the visceral pleura, metastatic cancer in parabronchial lymph nodes; 1 case developed a second tumor (thyroid micropapillary carcinoma) 11 years later.
Prognosis
6 cases in this group were lost to follow-up, and the remaining 12 cases were followed up by telephone, except for 2 cases with decreased exercise tolerance compared with the same age, the remaining 10 cases were asymptomatic.
Discussion
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma was first proposed by Smetana and Liebow in 1952 [1], and is the most common malignancy of the salivary glands, occurring in children and young adults, but can be seen in people of all ages (3-78 years old) [2], and the smallest reported case to date is a 2-year-old boy in the United States [3]. Bronchial Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is rare, with an incidence of about 0.1-0.2% of primary lung cancer [4]. It has been reported that there is no gender preference for the onset of men and women in patients with MEC [5-7], the number of male children in our group of cases is about 1.6 times of female children, which is consistent with the study of Lily et al [8].
Primary bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma usually presents as an endobronchial tumor with polypoid growth, with no specific clinical manifestations, mostly bronchial irritation and obstruction symptoms (depending on the tumor site). Patients may have cough, hemoptysis, wheezing [9] and post-obstructive pneumonia, some children have no clinical symptoms (about 9%-28%) [10], but even some children will have carcinoid syndrome, Cushing syndrome and acromegaly and other manifestations [2], the disease is easy to be misdiagnosed as tuberculosis, pneumonia, right middle lobe syndrome, asthma and other diseases in clinical work [11]. According to the statistics of Lili et al [8], about 88.9% of children's MEC is misdiagnosed as tuberculosis and treated according to tuberculosis. As previously shown, the delay in diagnosis of tracheal MECs ranged from 3 months to 2 years [12-15], with the longest time from symptom onset to diagnosis in our group of cases being more than two years. Tsuchiya [16] and Dinopoulos [17] summarized the clinical manifestations of 84 children with MEC, concluded that cough, hemoptysis, fever and recurrent pneumonia were the most common manifestations. Looking back at our group of 18 cases, the first symptom of the children was cough as the most common, followed by hemoptysis and fever, which were consistent with the relevant literature reports, and one child even had no clinical symptoms, only found swollen lung nodules during body check, and then further biopsy confirmed bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
MEC is mainly manifested as a round-like or lobulated mass with a smooth inner edge of the bronchi and clear boundaries, and is often accompanied by obstructive atelectasis, obstructive pneumonia and other manifestations [18], and some children with smaller tumors do not even have clump-like masses on CT or chest radiograph, but only show pneumonia or atelectasis [19]. In general, tumors appear as isolated masses and do not have any specific segment or lobar predisposition [20]. The literature points out that tumors can be found in the trachea and each lobe, and segment bronchi [21], but more often occur in the main bronchi, middle and lobe bronchi. According to literature statistics, about 10% of tumors are confined to the trachea, about 15% are located in the main bronchi, about 75% are located in the lobes and segment bronchi [22], invasion of trachea and carina is rare [23], according to the data reviewed, less than 10 cases of tracheal MEC have been reported in the literature. Most of them are located about 2~4cm above the carina [12-15,24]. In our group of cases, there is no significant preference of the location of the masses (one case violated the tracheal carina), and distal pneumonia, atelectasis as well as pleural effusion may also occur. However, although the imaging of MEC is diverse and nonspecific, Li X, and Yi W believe that well-circumscribed oval or lobulated intraluminal or peripheral lung masses with significant heterogeneous contrast enhancement may suggest a diagnosis of mucoepidermoid carcinoma [25-27]. An analysis shows a centrally located or hilar mass with clear margins, regular shape, no necrosis, and moderately enhanced findings were associated with bronchial MEC [28]. However, in our cases, patients presenting with uneven enhancement are rare and may be limited by small sample sizes.
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma often covers the surface of normal mucosal epithelium, and there are usually no positive findings on bronchoscopic brushing or lavage, and in the case reported by Zhou X, et al, the patient did not find tumor cells on three smear examinations, but TCT (Thin-layer cytology test) showed a large number of atypical cells [29], so TCT may suggest the diagnosis of MEC, but its diagnosis still depends on tissue biopsy. The histologic findings of MEC typically show a mixture of squamous cells, mucin-producing cells, and intermediate cells, lacking keratinization and overlying epithelium (Figure 6-7). Though they are all composed of these cells, MEC has a different biological behavior clinically. According to histopathology, MEC can be divided into low, intermediate, and high grades, with the low grade (48% of 75 cases) being more common than the high grade (38.7% of 75 cases), and the intermediate grade (13.3% of 75 cases) being the least common [30]. Low-grade tumors are more common in children, with well-defined lesions, often presenting as endobronchial polypsoids. High-grade tumors are large, often invade adjacent lung parenchyma, and occur with lymphatic or hematogenous spread. All children in our group of cases underwent pathological biopsies, more than half of them showed low-grade malignancy, which with good differentiation was mostly only locally aggressive, while distant metastasis was rare. Metastases are mostly associated with tumor grade, with only 2% (in 45 patients) of low-grade MECs and 15% (in 13 cases) of high-grade MECs metastasizing to lymph nodes in a study by Yousem SA et al. [31]. In our cases, only one child had a tumor invading the visceral pleura and distant lymph node metastasis at the time of first diagnosis, and another child found a second tumor (micropapillary thyroid carcinoma) 11 years after the first time of the diagnosis of MEC, and then underwent total thyroidectomy, recovered well after surgery, and now survives asymptomatically.
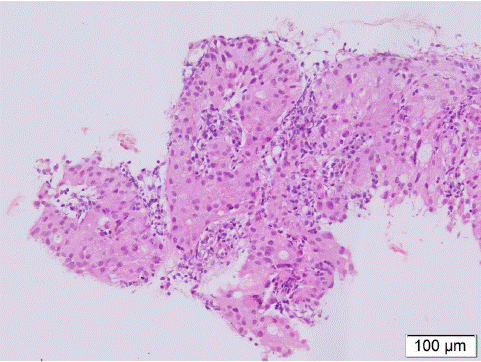
Figure 6: Picture shows squamous cells in MEC, lacking keratin pearls (H and E × 40).

Figure 7: The histologic findings of MEC typically show a mixture of squamous cells, mucin-producing cells, and intermediate cells. The nucleus of tumor cells are round or oval shapes, with mucus in the cytoplasm (H and E ×200).
The prognosis of bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma is related to whether the mass is completely resected and whether distant metastasis occurs, so the treatment is mainly surgical resection, which is the standard treatment for patients with bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma. In recent years, this procedure has often been performed using video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. In addition, bronchioplasty or sleeve lobectomy is performed to preserve lung function, and most lymph node dissection is performed at the same time to assess for metastases. Although endoscopic resection of tumor has little trauma, can quickly relieve mass obstruction and alleviating respiratory symptoms, and can maximize the preservation of normal lung tissue, due to the deception of MEC mass "small outside and large inside", it is often easy to misjudge the scope of its true invasion in bronchoscopy and make it impossible to completely remove the tumor. Therefore, endoscopic resection is not primary recommended [22]. Takayoshi Yamamoto et al. reported that two patients treated with endoscopic intervention had residual tumor in the bronchial wall. Therefore, in order to achieve complete resection, it is recommended that surgical resection should be considered even after resection of the endobronchial tumor [32]. MEC is not sensitive to chemoradiotherapy [33-36], radiotherapy has been shown to have little change in the long-term prognosis of MEC patients [37,38]. Due to the rarity of this disease, there are no evidence-based guidelines for radiotherapy in pediatric MEC, but one study showed that radiotherapy can significantly improve local control and survival in advanced and regional node-positive patients, especially those with positive margins after postoperative resection; Postoperative radiotherapy has a significant benefit on local control rates [39]. Chemotherapy has limited efficacy and has been used as palliative care, possibly due to increasing systemic toxicity and leading to poor clinical efficacy [40]. In addition, targeted therapies involving signaling pathways that characterize molecules are a new therapeutic pathway [41]. In some cases, patients with or without EGFR (Epidermal growth factor receptor) mutations have shown that treatment with TKI can benefit from treatment [42-45].
The overall prognosis of mucoepidermoid carcinoma is related to pathologic grade. Most of the children's MEC is low-grade tumor, the long-term prognosis is good, with the 10-year survival rate after lobectomy is 100% [46], but the prognosis of high-grade MEC is not optimistic with the 5-year overall survival rate is only 22.5% [36]. More than half of the cases in our group are low-grade tumors, and there was no recurrence in the follow-up cases, among which the longest postoperative asymptomatic survival time has been nearly 10 years.
Conclusion
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is defined by the World Health Organization as a malignant tumor consisting of mucus-secreting, squamous and intermediate cell types. Because the mass grows predominantly in the bronchi and presents clinically as a symptom of lower airway obstruction and is not specific, chest x-ray or chest CT may usually show atelectasis, consolidation, or large lung lesions, but if the tumor is small and does not obstruct the airway, chest imaging may be normal. High-grade tumor is rare in children, but it have a tendency to metastasize and have a poor prognosis, so early diagnosis and early treatment are required. The most common causes of lower airway obstruction in children include asthma, pneumonia, bronchiolitis, laryngotracheobronchitis, congenital malformations, foreign body aspiration and bronchial tumors, pathological obstruction should be considered when children with recurrent respiratory symptoms do not respond to conventional treatment. Thus, we recommend that any child with persistent, unexplained respiratory symptoms that do not resolve after 2 weeks of treatment undergo endoscopy as soon as possible. Once a biopsy confirms MEC, surgical treatment is primary recommended. The long-term prognosis after complete tumor resection is good, but there is still a risk of recurrence and metastasis of some patients, so long-term follow-up is recommended for the child.
Author Statements
Conflict of Interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during this study are available from the corresponding author (email: sunlihong9797@126.com) on reasonable request.
References
- Anton-Pacheco J, Jimenez Ma, Rodriguez-Peralto Jl, Cuadros J, Berchi Fj. Bronchial Mucoepidermoid Tumor in A 3-Year-Old Child. Pediatr Surg Int. 1998; 13: 524-5.
- Ishikawa Y AEAM. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. Lyon, France: IARC Press. 2015: 99-100.
- Szymanski LJ, Molas-Torreblanca K, Bawab R, Kim E, Don D, Mascarenhas L, et al. Bronchial Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma with the Classic MAML2 Gene Rearrangement in a 2-year-old Boy. Pediatr Devel Pathol. 2018; 21: 480-5.
- Jiang MB, Li TN, Wu FY, et al. Clinical characters and diagnosis of CT imaging for bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Journal of Medical Imaging. 2012; 22: 1082-1086.
- Zhang BL, Chen KX. Clinical analysis of 12 cases of primary bronchial mucus epidermoid carcinoma. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology. 2003; 12: 61.
- Belgod SR, Reddy RHV, Kumar SP. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung: a rare entity. OXF MED CASE REP. 2015; 2015: 203-5.
- Li X, Guo Z, Liu J, Wei S, Ren D, Chen G, Xu S, Chen J. Clinicopathological characteristics and molecular analysis of primary pulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma: Case report and literature review. Thorac Cancer. 2018; 2: 316-23.
- Shui L, Li Q. Bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma 1 case and the literature review. Chinese Journal of Clinicians (electronic edition). 2013; 7: 10712-10716.
- Lin C, Chao Y, Wu K, Lin W. Primary mucoepidermoid carcinoma at the carina of trachea presenting with wheezing in an asthmatic child mimicking an attack of asthma. Medicine. 2016; 95: e5292.
- Stevic R MB. Tracheobronchial tumors. Thorac Dis. 2016; 11: 3401-13.
- Omesh T, Gupta R, Saqi A, Burack J, Khaja M. A rare case of endobronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung presenting as non-resolving pneumonia. Respir Med Case Rep. 2018; 25: 154-7.
- Noda S SSME. Tracheal mucoepidermoid carcinoma in a 7-year-old child. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998; 3: 928-9.
- Romão RLP, de Barros F, Maksoud Filho JG, Gonçalves MEP, Cardoso S, Tannuri ACA, et al. Malignant tumor of the trachea in children: diagnostic pitfalls and surgical management. J Pediatr Surg. 2009; 44: e1-4.
- Desai DP, Mahoney EM, Miller RP, Holinger LD. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the trachea in a child. Int J Pediatr Otorhi. 1998; 45: 259-63.
- Kim J, Park C, Kim K, Shim YM, Yang MK, Han J, et al. Surgical resection of mucoepidermoid carcinoma at the carina in a 9-year-old boy. J Pediatr Surg. 1998; 33: 1561-2.
- Tsuchiya H, Nagashima K, Ohashi S, Takase Y. Childhood bronchial mucoepidermoid tumors. J Pediatr Surg. 1997; 32: 106-9.
- Dinopoulos A LESI. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the bronchus. Pediatr Hemat Oncol. 2000; 5: 401-8.
- Li D, Zhou XH, Lv PX. The CT findings of pulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Journal of Medical Imaging. 2013; 23: 539-541.
- Lin MF, Yang ZY, Zhang HY. Clinical analysis of 96 cases of bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Journal Of Practical Oncology. 2006; 20: 129-130.
- Kalhor N MC. Pulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma: diagnosis and treatment. Expert Rev Resp Med. 2018; 3: 249-55.
- Wang HY, Ma Y, Jiang HY. Radiographic and CT findings of bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma (report of one case with literatures review). Journal Of Medical Imaging. 2003; 752-754.
- Vogelberg C, Mohr B, Fitze G, Friedrich K, Hahn G, Roesner D, et al. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma as an unusual cause for recurrent respiratory infections in a child. Journal of pediatric hematology/oncology. 2005; 27: 162-5.
- Jaramillo S, Rojas Y, Slater BJ, Baker ML, Hicks MJ, Muscal JA, et al. Childhood and adolescent tracheobronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC): a case-series and review of the literature. Pediatr Surg Int. 2016; 32: 417-24.
- Papiashvilli M, Ater D, Mandelberg A, Sasson L. Primary mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the trachea in a child. Interact Cardiov Th. 2012; 15: 311-2.
- Li X, Yi W, Zeng Q. CT features and differential diagnosis of primary pulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma and pulmonary adenoid cystic carcinoma. J Thorac Dis. 2018; 10: 6501-8.
- Li X, Zhang W, Wu X, Sun C, Chen M, Zeng Q. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung: common findings and unusual appearances on CT. Clin Imag. 2012; 36: 8-13.
- Ishizumi T, Tateishi U, Watanabe S, Matsuno Y. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung: High-resolution CT and histopathologic findings in five cases. Lung Cancer. 2008; 60: 125-31.
- Ban X SXHH. Predictive CT features for the diagnosis of primary pulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma: comparison with squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. Cancer Imaging. 2021; 1: 2.
- Zhou X, Zhang M, Yan X, Zhong Y, Li S, Liu J, et al. Challenges in diagnosis of pulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma. MEDICINE. 2019; 98: e17684.
- Sana Mehmood Qureshi OSJS. Research Article Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma: A Clinico-Pathological Review of 75 Cases. International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012; 2: 5-9.
- Yousem SA HL. Mucoepidermoid Tumors of the Lung. Cancer-Am Cancer Soc. 1987; 6: 1346-52.
- Yamamoto T, Nakajima T, Suzuki H, Tagawa T, Iwata T, Mizobuchi T, et al. Surgical treatment of mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung: 20 years’ experience. Asian Cardiovascular and Thoracic Annals. 2016; 24: 257-61.
- Kaplan MJ JMCR. Chemotherapy for salivary gland cancer. OTOLARYNG HEAD NECK. 1986; 2: 165-70.
- Pires FR DAOD. Prognostic factors in head and neck mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004; 2: 174-80.
- Grisanti S, Amoroso V, Buglione M, Rosati A, Gatta R, Pizzocaro C, et al. Cetuximab in the treatment of metastatic mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands: a case report and review of literature. Journal of medical case reports. 2008; 2: 320.
- Guzzo M, Andreola S, Sirizzotti G, Cantu G. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands: clinicopathologic review of 108 patients treated at the National Cancer Institute of Milan. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002; 9: 688-95.
- Chen AM GPGJ. Local-regional recurrence after surgery without postoperative irradiation for carcinomas of the major salivary glands: implications for adjuvant therapy. 2007; 4: 982-7.
- Neill ID. t(11;19) translocation and CRTC1-MAML2 fusion oncogene in mucoepidermoid carcinoma. ORAL ONCOL. 2009; 45: 2-9.
- Olsen MP, Mitchell AO, Miles EF. Postoperative radiation therapy for parotid mucoepidermoid carcinoma. CASE REP ONCOL MED. 2014; 2014: 345128.
- Ferrell JK, Mace JC, Clayburgh D. Contemporary treatment patterns and outcomes of salivary gland carcinoma: a National Cancer Database review. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-L. 2019; 276: 1135-46.
- Wagner VP, Martins MD, Martins MAT, Almeida LO, Warner KA, Nör JE, et al. Targeting histone deacetylase and NFκB signaling as a novel therapy for Mucoepidermoid Carcinomas. SCI REP-UK. 2018; 8.
- Neill ID. Gefitinib as targeted therapy for mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung: Possible significance of CRTC1–MAML2 oncogene. Lung Cancer. 2009; 64: 129-30.
- Rossi G, Sartori G, Cavazza A, Tamberi S. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung, response to EGFR inhibitors, EGFR and K-RAS mutations, and differential diagnosis. Lung Cancer. 2009; 63: 159-60.
- Han S, Kim H, Jeon YK, Oh D, Lee S, Kim D, et al. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of lung: Potential target of EGFR-directed treatment. Lung Cancer. 2008; 61: 30-4.
- Macarenco RS, Uphoff TS, Gilmer HF, Jenkins RB, Thibodeau SN, Lewis JE, et al. Salivary gland-type lung carcinomas: an EGFR immunohistochemical, molecular genetic, and mutational analysis study. Modern Pathol. 2008; 21: 1168-75.
- Jieli Z, Yunzhi Z, Nan Z, Heng Z, Hongwu W, Jiankun L, et al. Different effects of bronchoscopic interventions on children and adults with tracheobronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Tumori J. 2022 2022; 108: 134-40.