Abstract
Malignant Fungating wounds is caused by tumor growth, which give rise to skin damage, micro vascular rupture and tissue necrosis. The patient frequently suffers from pain, foul smell, functional impairment, bleeding as well as cataclysm due to necrosis and microbial contamination. It’s hard to cure for Malignant Fungating wounds, Despite the symptom management, and wound management strategies will improve quality of life and maintain personal dignity. Aromatherapy as an adjuvant treatment is used to relieve pain, remove odor and alleviate psychological distress on end-of-life care. The case is aim to analysis of a patient retrospective date using aromatherapy to deal with the symptoms of pain, bleeding and infection caused by Fungating Wounds. it was found that wound infection and pain were alleviated, psychological pain was relieved significantly and the patient’s malignant wound was surprisingly healed by aromatherapy, which met patient’s hope of the end of life.
Keywords: Fungating Wounds Aromatherapy a case
Background
Malignant Fungating Wounds (MFW) is a fungi which caused from growing Malignant tumors invade to tissue, skin, blood, lymph and destroy their integrity by tumor cell metastasis [1]. MFW is a chronic wound, which can be divided into fungating, ulcerating and necroticing type due to the different ways of tumor invasion into the skin (Figure 1). The prevalence of MFW in all types of tumors ranges from 10.0% to 14.5% [2-3], the incidence of metastatic wound is from 5% to 10%, which usually occurs in the last 6-12 months of life [4]. The most frequent area was the breast at 49.3% followed by the neck (20.9%), chest (17.6%), extremities (16.6%), genitalia (16.6%), head (13.5%) and other (1.7%) [5]. According to statistics of research, 70% of MFW in female patients is caused by breast cancer as well as 32% of MFW in male patients is caused by melanoma [4]. MFW is delayed with the rest of life once occurs, Although the incidence of MFW is not high. The symptom and the progression of the tumor itself not only affect the physical, psychological, social and spiritual health of the patient, but also may affect the patient's family and caregivers [6]. Therefore, the physical and mental burden and economic stress associated with MFW can lead to poor quality of life for patients and their family [7].
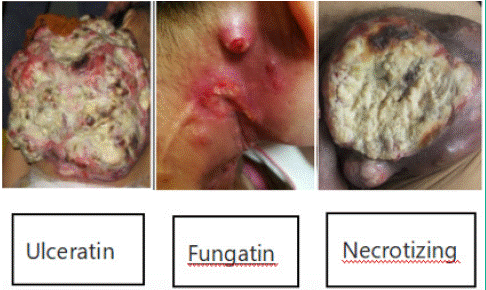
Figure 1: Type of Maligant Fungating Wounds.
The main intervention methods for MFW include local wound management or systemic diseases control at present. Systemic diseases are treated through interdisciplinary approaches such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, antibiotic and hormonal shocks. Local wound management will be the primary goals when the tumor is not curable or the treatment of tumor is not profitable. local wound management mainly include control pain, infection, bleeding, exudation and other complications by use of analgesia, homeostasis, antibiotic drugs or dressings. Some studies have shown that the analgesic effect of local opioids in ulcerative tumor wounds is still uncertain, local wound homeostasis with epinephrine can aggravate tissue necrosis and the most commonly used charcoal dressings and metronidazole deodorization are only 30% effective [5-6]. Therefore, the use of drugs and dressings for local symptom relief has different effects ,Which has a slim chance for home care . Wound management in hospital Long-term will definitely increase the economic burden of patients and society. Aromatherapy is mainly intervention used in cancer patients to relieve pain, remove odorant, reduce nausea of postoperative or post-chemotherapy, vomiting and anxiety symptoms currently. the clinical research of Aromatherapy is not mature in china. Because the research did not rise to the professional field on this aspect. Nowadays, The application of aromatherapy has been widely promoted because of its economic advantages and the characteristics of easy acceptance by patients.
The aim of the case report is to describe aromatherapy in a carcinoma patient with Malignant Fungating Wounds who focused on the control of wound symptoms, to improve the quality of life and to help the patient’s dream come true of malignant tumor wound healing finally.
Case Report
A 44-year-old female was admitted to our hospital for left tongue with throat pain a week because of 14-years after Squamous cell carcinoma of the left tongue. the patient aggravated during eating and swallowing accompany with right neck rupture, intermittent bleeding, fluid discharge, odor after poor treatment of throat pain and discomfort 1 week. Admission examination: CRP: 83.34mg/L, WBC: 2.410^9/L, NEU: 90.0%, PLT: 352.010^9/L, Na+ 121.7mmol/L. she suffered from pain (NRS 7) on the throat and neck with about 8 hours a day, the pain would be worse during swallowing and eating as well as could lead to poor sleep and difficulty in eating. Physical examination: the patient suffered from oral ulceration with infection, hoarseness, neck see multiple scattered irregular malignant tumor skin rupture wound (6cm*3cm) with bleeding, a small amount of exudation, mild odor, redness, swelling, slightly higher skin temperature occasionally (Figure 2), which had already led to survival pain as well as lower quality of life.
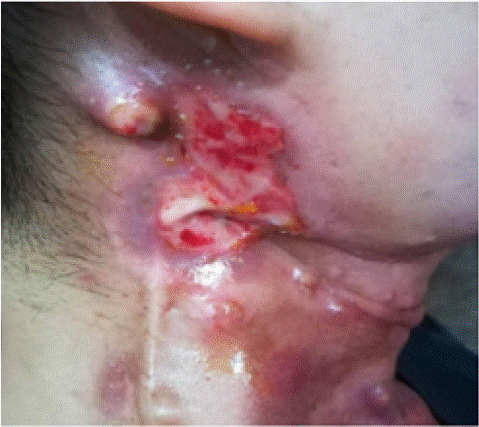
Figure 2: First assessment at admission.
Family Psychosocial Status
The patient is a PE teacher with bachelor degree, she’s family relationship is harmonious, who has a son 10 years old and husband as the main caregiver accompany with her everyday. Wound symptoms became seriously to affect the patient's spirit, sleep and mood; family economic became difficulties due to operations, multiple radiotherapy and chemotherapy being diagnosed with the disease. There is 6000-8000RMB a month before illness of her income and had medical insurance in Chengdu. She like to stay at home because of ashamed of appearance and odor of the wound. the patient's greatest wish was wound healing, Because she want to live as well as to love beauty.
Malignant Tumor Wound Nursing
Wound Treatment of Hospitalized Malignant Tumors
The patient was admitted to the palliative medicine department to care for malignant tumors on June 22,2020. using individual evaluation [6] of malignant tumor wound: right neck ulcer MFW 6*3cm, 1cm deep, light yellow purulent discharge with mild odor; with pain (NRS 7/10 points). morphine was given 5mg CIVI 24h analgesia, dexamethasone 10mg CIVI to relieve neck swelling and compression, amino acid 18AA-II nutritional support and immunity enhancement; sputum smear: + + + +, sputum culture: medium (50%) growth of hemolytic streptococcus. On 3 day after admission, the pain of wound relief (NRS 4/10), sleep improvement, Increased oral secretions with irritating cough, The morphine dose was increased to 7.5mg CIVI 24h and bubrotonine was added to 30mg CIVI 24h to reduce the oral gland secretion; Aromatic treatment to 50ml of 1.5% oil (sweet almond oil 30ml + gardenia oil 10ml + wheat germ oil 10ml + thyme essential oil 10 + 1 myrh 1 + frankincense 2 drops) gargle Q4h; flower water of rose gargle Q4h; 3% compound essential oil 30ml smear the wound (sweet almond 20ml + gardenia fruit 10ml + thyme 5 + blue gum 5 + permanent flower 1 + geranium 4 + 3 drops of frankincense); Washing the wound with flower water. the mass and the exudation of the wound was reduced after treatment, the pain was significantly relieved (3 / 10 points), no odor any time in the ward (Figure 3). Then she went home due to economic pressure and taking the oral morphine sulfate to 10 mg BID 8 days to control pain discharge.
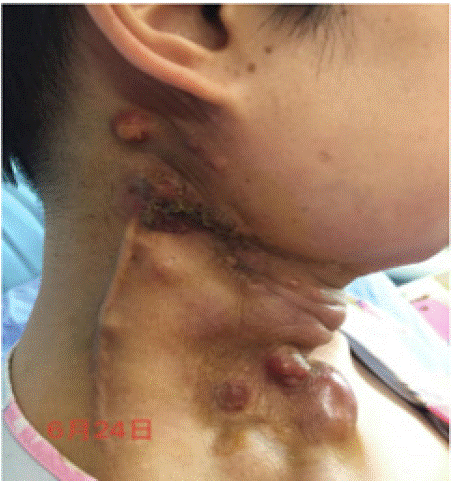
Figure 3: June 24, 2020 (Three days after admission).
Home Malignant Tumor Wound Aromatherapy
The malignant tumor wound home care was begun on July 1, 2020, the area of skin rupture increased and the purulent exudate increased. the patient hoped to continue aromatic therapy Because the wound therapy was effective in the hospital. Making the plan of Aromatherapy After the home visiting on July 5th.
Phase I: Anti-infection and odor removal (July 5- -July 11, 2020)
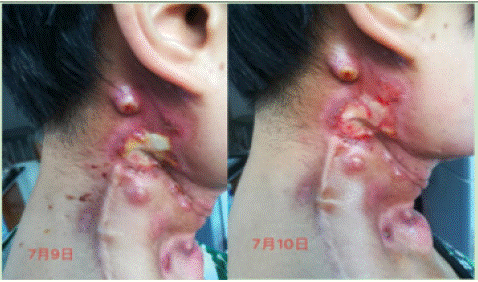
Figure 4: Phase 1.
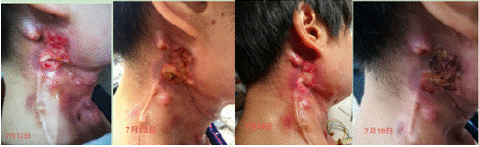
Figure 5: Phase 2.
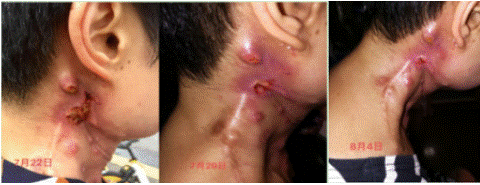
Figure 6: Phase 3.
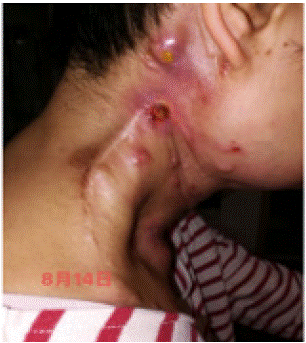
Figure 7: Phase 4.
Wound assessment: wound 5 * 4cm, redness around the wound, light yellow purulent discharge, mild odor, high skin temperature.
Aromatherapy plan: base oil (sweet almond + gardenia fruit oil) + essential oil (thymol thyme + blue gum yugali + frankincense + bourbon geranium + permanent flower)
Effection: Wound, exudation, odor Phase II: Anti-infection, skin repair (July 12-July 21, 2020) Aromatherapy plan: base oil (jojoba + seabuckthorn fruit) + essential oil (thymol thyme + clove + blue gum yugali + German chamomile + real lavender + maskincense + medicine)
Effection: wound surface and exudation reduced, temperature of skin normal, redness and swelling relieved.
Phase III: Anti-infection and skin repair (from 22 July-06 August 2020) Aromatherapy plan: base oil (gardenia fruit oil + marigold) + essential oil (thymol thyme + green gray thousand layer + German chamomile + real lavender + frankincense + no medicine).
Effection: The wound surface reduced further, skin temperature normal, no secretion Stage IV: Skin Repair (07 August- -15 August 2020)
Aromatherapy plan: base oil (gardenia oil + Caligula + seabuckthorn fruit) + essential oil (thymol thyme + blue gum ugali + German chamomile + real lavender + frankincense + medicine)
Effection: Wound healing.
Discussion
Key findings
This case report describes that aromatherapy effect to treat for infection of Malignant Fungating Wounds. Infection is one of the most common problems in MFW in palliative care., blood routine and sputum culture showed the presence of infection in this case, there can be caused suppurative inflammation of skin and subcutaneous tissue by 50% hemolytic streptococcus. normal saline and disinfect iodine to avoid aggravation of infection during hospitalization. long-term care will lead to antibiotic resistance Because MFW is chronic wounds. Oral rehabilitation solution will cause nausea and vomiting in some patients in Clinical, so it is difficult for patients to accept and compliance. In contrast, It is more acceptable to patients for the aroma of essential oils and plant oils. Aromatheraphy used to control infection and repair the mucosa by Oil Pulling, which is a safe and effective detoxification method from "Ayurveda" in India. It is easier to melt bacteria for the essential oil as well as to enhance the antibacterial efficacy of traditional oil extraction, because oil’s densityis are higher than water [8]. In the case, we were used to resist infection by the oil of thymol thyme, blue gum ugali, German chamomile to dissolve in sweet almond oil and gardenia oil. the infection effect was good through patient complaints and wound observation. Shapiro [9] found that thymol potently inhibited Cryptococcus neoformans and stimulated immune effects. analgesic, anti-inflammatory, especially against fungi by using of external, Cryptococcus neoformans. Penoel [10] found that 2% gum blue killed 70% of the surrounding S. aureus within a few hours. German chamomile is rich in mother chrysanthemum sky blue hydrocarbon and a-drug-free alcohol effectively resist Staphylococcus aureus, hemolytic streptococcus, Proteus, it used to treat infection of skin commonly [11]. Therefore, it was effective for anti-infection and anti-inflammatory by oil pulling with compound essential oil in the case.
Aromatherapy is also Effective for Pain Relief
The patient felt pain in the throat and neck mass (NRS 7 / 10 points, 8 hours per day) affected sleep a week, Pain led to become difficulties for patient's eating. It was mainly morphine civi analgesia in hospital, then adjusted to morphine sulfate oral solution 10MgBID after discharge. Because of the pain caused by touching the wound when changing the dressing and applying the medicine, Frankincense essential oil was applied to assist the analgesia by the way of aromatherapy to reduce the pain of the wound. It has been reported that terpenes and other chemical groups found in essential oils have potential clinical applications as analgesics. All are low molecular weight compounds, usually with high lipid solubility. They can penetrate the blood-brain barrier and act in the central nervous system. Frank incense essential oil containing a-ene suppresses the pro-inflammatory enzyme 5-lipoxygenase acts similar to aspirin and suppresses acetate-induced pain [12]. Therefore, the application of aromatic essential oil in this case has good analgesic effect, and the pain score of the patient during the period of home is 2/10-4/10. The patient said "it is hard to believe that after the pain is relieved, it is easy to eat and the appetite has become better".
Aromatherapy Can Relieve the Psychological Pain of Patients
The patient always felt depressed, anxious, shame due to the odor, pain and appearance of the fungating wound. Patients stay at home all day and undesirable somebady to see their wounds as refuse to visit of relatives and friends. she said “it is very painful to live”. The team care from medical staff, family members and social workers formed a nursing team to establish a trusted relationship with patients, care for patients, encourage family members to accompany them and try to meet the patients’ reasonable needs, but it is still difficult to appease patient’s inner pain. Numerous studies have shown that aromatherapy is an effective intervention for psychological distress. Dunwoody et al [13] used focus group interviews with 22 patients and the perceived benefits of aromatherapy include a sense of social support, increased hope, improved quality of life, a general reduction in anxiety and tension, improved sleep patterns and a reduction in aches and pains. A meta-analysis in China [14] concluded that there were statistically different anxiety scores between the consistent baseline aromatherapy group and the conventional therapy group. Therefore, this case applied aromatic therapy to deal with the tumor wound problems concerned by the patients achieved good results, the relief of wound symptoms greatly improved the mood of the patients, after the symptoms relieved patients becomeing optimistic, worried that they could not care for the wound after returning home, after home aromatic therapy, patients no longer anxious about wound treatment; visit more willing to actively express their ideas, wound healing patients feel comfortable, and regain confidence in life.
Aromatherapy can inhibit wound bleeding
There are several cases of aromatherapy used for hemostasis, and it has been reported that the tincture component of yarrow essential oil is a hemostatic agent. Yarrow was used to help wounded soldiers stop the bleeding during the Trojan War. In addition, yarrow essential oil also contains azure hydrocarbon, dihydrochamazulene hydrocarbon and other components with anti-allergy, anti-inflammation and anti-histamine effects, can relieve itching and inflammation symptoms, and promote wound and rough skin tissue regeneration. Therefore, in this case, yarrow hydrolate applied to wash the wound to clean and stop bleeding during home nursing. Because the hydrolate was weakly acidic, it was refreshing and comfortable to use, and there was no bleeding in the wound after washing.
Aromatherapy Reduces the Bruden of Medical Expenditure
Treating MFW with aromatherapy reduces medical expenses and financial stress for patients. The patient underwent 10 surgeries, multiple chemoradiotherapy and iodine-125 particle implantation, which cost nearly 1 million yuan, resulting in huge economic pressure. The main reason for admission to the palliative care department was that the wound symptoms could not be treated at home. The total cost of analgesia and symptomatic and supportive treatment for 9 days was about 15000 yuan. The total cost of aromatherapy until wound healing was 1200 yuan. Home aromatherapy is significantly less cost-effective than inpatient MFW. An Australian study comparing the cost of conventional and aromatic essential oil dressings for treating fungal infected MFW: Silver sulfonadiazine cream 500g $52.27, metronidazole gel 500g $314.50, base cream and essential oils 500g $18.08, and finally the total cost of conventional dressing treatment of fungal infection wound $54.40, the total cost of aromatherapy dressing treatment $0.40 [15]. It can be seen that home aromatherapy treatment MFW greatly reduces the cost of manpower and material resources, and reduces the waste of medical resources and medical expenditure.
Improve Patients' Quality of Life
In order to determine the role of essential oil in wound care, we searched English literature CINAHL and Medline, Cochrane, Embase and other databases since 1980 from aromatherapy, essential oils, wound care. Few clinical randomized controlled studies of essential oils to treat MFW, due to the large number of studies on essential oils were published in French. However, to review of the extensive literature of case and cohort studies has found that aromatherapy is most effective in helping patients and families cope with infection at the end of life. Studies have also shown that the use of aromatherapy to address wound pain improves the quality of life of patients in palliative care [16]. Studies have shown that 2.5% lavender and tea tree oil compound oil was used to directly dilute and applied to the wound QD and no smell was detected after 2 days [11]. In the case, essential oils such as blue gum yugali, thymol thyme and German chamomile were used to treat infection, to reduce odor and to relieve anxiety and sleep disorders; Myrrh oil used to improve exudation and promote skin wound repair; Aromatherapy was mainly used to support patients' wishes for home care. The patient began to have confidence in getting along with others after the wound had no odor. Aromatherapy procedures increase skin contact between the family and the patient, the patient feel that her family can face and would like to deal with the wound with her. After about 1 week of aromatherapy, the odor disappeared; Patients' appetite increased after pain control, good sleep, greatly improving the quality of life.
Conclusions
In this case,the nurse applied aromatherapy methods to care the patent with MFW at home. Practiced the concept of hospice care for patient and their families with all-round care for body, psychology, spirit and society. Respect patient needs and realize MFW in home care; Improved patient’ comfort and quality of life; MFW healing after four stages of aromatherapy reduces medical costs and helps patients achieve their greatest wishes.
Author Statements
Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of the case report and accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
References
- Wan D, Zhu J, Zhou Z. Stoma therapy and rehabolitation theory and practice. Bei Jing The medicine science and technology press of China. 2006: 282.
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm KF. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: A retrospective study of 4020 patients. Journal of the American Academy of ermatololy. 1993; 29: 228-236.
- Maida V, Corbo M, Dolzhykov M, Ennis M, Irani S, Trozzolo L. Wounds in advanced illness: A prevalence and incidence study based on a prospective case series. Int Wound J. 2008; 5: 305-314.
- Dorothy B, Doughty MN. Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nurses Society Core Curriculum: Wound Management. Holland: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2015.
- Patricia Grocotta, Georgina Gethinb, Sebastian Probstc. Malignant wound management in advanced illness new insights.Current Opinion in Supportive and Palliative Care. 2013; 7: 101–105.
- Gethin G, Grocott P, Probst S, Clark E. Current practice in the management of wound odour:An international survey. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2014; 51: 865-874.
- Merz T, Klein C, Uebach B, Kern M, Ostgathe C, Bukki J, et al. Fungating Wounds – Multidimensional Challenge in Palliative Care. Breast Care. 2011; 6: 21–24.
- Vagish Kumar L Shanbhag. Oil pulling for maintaining oral hygiene-A review. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine. 2017; 7: 106-109.
- Shapiro S, Meier A, Guggenheim B. The antimicrobial activity of essential oils and essential oil components towards oral bacteria. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1994; 9: 202-208.
- Eucalyptus smithi essential oil and its use in aromatic medicine. 2: 154-159.
- Hong Ci Ya. Clinical Aromatherapy 2nd Edition (M). Elsevier Taiwan Co., LTD. 2011.
- Damião Pergentino de Sousa. Analgesic-like Activity of Essential Oils Constituents. Molecules. 2011; 16: 2233-2252.
- Dunwoody L, Smyth A, Davidson R. Cancer patient’s experiences and evaluations of aromatherapy massage in palliative care. International Journal of palliative Nursing. 2002; 8: 497-504.
- Peng W, Liu Y, Liu P, et al. Effects of aromatherapy on symptom control in cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Chongqing Medical Journal. 2017; 46: 358-359.
- Mercier D, Knevitt A. Using topical aromatherapy for the management of fungating wounds in a palliative care unit. Journal of Wound Care. 2005; 14: 497-501.
- Probst S, Arber A, Faithful S. Malignant fungating wounds – the meaning of living in an unbounded body. European Journal of Oncology Nursing. 2013; 17: 38-45.
