Clinical Image
Austin J Emergency & Crit Care Med. 2019; 5(1): 1065.
Talus Bone Fracture and Medial Ankle Dislocation and Type-3 Salter Harris Fracture in Knee Joint
Heidari SF*
Seyed Farshad Heidari MD, Department of Emergency Medicine, Emam Khomeini Hospital, Medical Faculty, Ilam University of Medical Sciences, Ilam, Iran
*Corresponding author: Seyed Farshad Heidari, Department of Emergency Medicine, Emam Khomeini Hospital, Medical Faculty, Ilam University of Medical Sciences, Ilam, Iran
Received: May 03, 2019; Accepted: May 13, 2019; Published: May 20, 2019
Clinical Image
Case 1: Talus bone fracture and medial ankle dislocation
A 43-year-old man presented to the emergency department by two people because of right ankle trauma. The mechanism of trauma was right ankle sprain following to fall from footstool with the right foot. Past medical history and drug history were negative. The vital sign was stable. On physical examination, the patient had swelling of the right ankle and right forefoot inversion. The neurovascular examination was normal. In the AP view of radiography, talus bone fracture, the displacement of the distal part and forefoot towards medial and medial dislocation of the right ankle joint were seen (Figure 1A). In the lateral view of the right ankle, increased joint space was observed between the talus and tibia bones (Figure 1B). After the initial proceedings in the emergency department, the patient was transferred to the operating room and repair of fracture and dislocation of the right ankle was performed. There is the possibility of talus bone necrosis following these injuries.
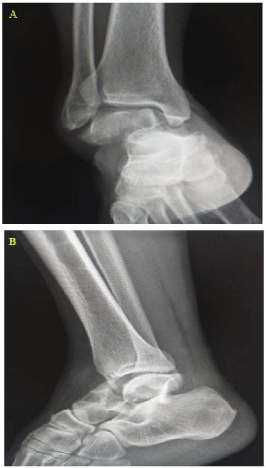
Figure 1: Radiographic view of the right ankle. AP view (A) and lateral view
(B).
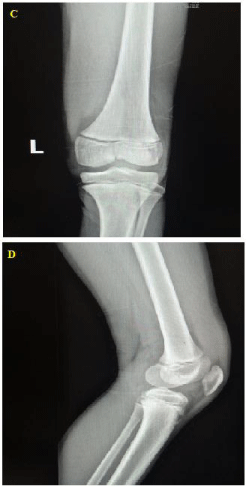
Case 2: Type-3 Salter-Harris fracture in knee joint
A 13-year-old boy presented to the emergency department by EMS because of left knee trauma. The mechanism of trauma was falling three people on the left knee of the patient after a quarrel. The patient's left knee was in extension position and the patient was not able to flex the left knee. Past medical history and drug history were negative. The vital sign was stable. On physical examination, the patient had swelling and tenderness of the left knee. The neurovascular examination was normal. In the AP view of radiography, type-3 Salter-Harris fracture in the medial aspect of distal of femural bone and increased tibio-femural articular space without dislocation were seen (Figure 2C). The lateral view of the left knee was normal (Figure 2D). After the initial management was taken in the emergency department, the patient was transferred to the operating room and repair of fracture of the left knee was performed.