
Research Article
Austin J Nutri Food Sci. 2021; 9(1): 1152.
Proximate Composition and Amino Acid Profile of the Edible Muscle of European Crayfish Astacus astacus L. Inhabiting the Orchomenos Region in Central Greece
Papachristou E1, Tyrpenou AE2, Kastritsi-Katharios I3 and Kotzamanis Y4*
1Department of Biology, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece
2Hellenic Agricultural Organization “DIMITRA” (former NAGREF), Veterinary Research Institute, Thessaloniki, Greece
3Department of Ichthyology and Aquatic Environment, University of Thessaly, Greece
4Hellenic Centre for Marine Research (HCMR), Institute of Marine Biology, Biotechnology and Aquaculture, Fish Nutrition Lab, 46.7 km Athens-Sounion Avenue Anavyssos, Attiki 19013, Greece
*Corresponding author: Kotzamanis Y, Hellenic Centre for Marine Research (HCMR), Institute of Marine Biology, Biotechnology and Aquaculture, Fish Nutrition Lab, 46.7 km Athens-Sounion Avenue Anavyssos, Attiki 19013, Greece
Received: April 09, 2021; Accepted: April 26, 2021; Published: May 03, 2021
Abstract
The aim of this study was to determine the proximate composition and amino acid profile of the edible muscle of European crayfish Astacus astacus L. Animals were collected from Orchomenos region in Central Greece and muscle tissue samples were collected for chemical analysis. Total crude protein and crude lipid content of muscle tissues were determined using the Kjeldahl method and Folch’s procedure, respectively. Amino acids profile was performed by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatographic (UPLC) determination of the acid hydrolysed muscle extract after derivatization with AccQ-Tag reagent (Waters, USA). The results showed that protein and lipid content of crayfish muscle tissue were 16.55 ± 0.4 g 100 g-1 and 0.52 ± 0.20 g 100 g-1, respectively. Also, the moisture and ash content were 80.93 ± 0.36 g 100 g-1 and 1.25 ± 0.14 g 100 g-1, respectively. Amino acids analysis of muscle tissue revealed that the highest values were those of glutamic acid (2.98 g 100 g-1) and arginine (2.19 g 100g-1) as well as those for aspartic acid (1.88 g 100 g-1), lysine (1.47 g 100 g-1) and leucine (1.33 g 100 g-1). The lowest values were found for histidine (0.35 ± 0.03 g 100 g-1) and methionine (0.47 ± 0.01 g 100 g-1). The results of this study showed that the crayfish of Orchomenos region can be considered as an important source of essential nutrients in the human diet due to its protein and essential amino acids content, which are relatively comparable to those of farmed sea bream (Sparus aurata L.), as well as to farmed and wild sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). However, the lipid content of Orchomenos crayfish was found to be insignificant and negligible. Overall, the protein quality of European crayfish can be considered as a main factor in selecting this species as a candidate species for European aquaculture diversification.
Keywords: Crayfish; Astacus astacus; Protein; Amino acids; Fat; Nutritional value
Introduction
The European crayfish Astacus astacus L. (Figure 1) is a species which is very common and popular in many European countries and specifically in Greece. Particularly, it is found in 28 European countries and outside Europe it can be found only in Morocco. European crayfish or Noble crayfish (Astacus astacus L.) is one of the few species of freshwater crustaceans that have been used for commercial purposes and as human food for a long time [1,2].

Figure 1: European crayfish Astacus astacus L.
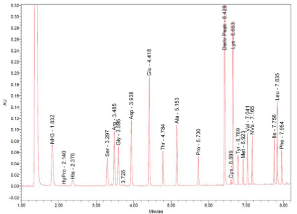
Figure 2: UPLC-UV chromatogram of amino acids of the muscle of European crayfish (Astacus astacus L). at 260nm.
In Greece, freshwater crayfish are found in 20 out of 53 Prefectures and they form isolated populations in relatively pristine water bodies. Three Indigenous Crayfish Species (ICS) occur in Greek waters: Astacus astacus, Astacus leptodactylus and Austropotamobius torrentium, as well as one Non-Indigenous Crayfish Species (NICS) Pacifastacus leniusculus. Greece probably represents the most southern natural distribution limit for A. astacus and A. torrentium in the world [3].
It is very widespread in the north-western and central regions of Greece (Epirus, Sterea Ellada and Thessaly) and its distribution extends to the south in the region of Peloponnesus, to the north in the region of Central Macedonia and to the western part of the region of East Macedonia and Thrace [3,4]. According to the legislation crayfish is protected in Greece mainly by the Directive 92/43/EEC [5]. Also, Greek legislation forbids crayfish fishing from 15 February to 15 May and establishes a minimum size for fishing crayfish to 10cm total length [6] and only for 2kg of crayfish per fisherman per day.
Nevertheless, should be carefully controlled and managed in order to keep the fishing pressure as low as possible. Also, the new Water Framework Directive 2000/60/EC [7] requires the use of biota and especially macroinvertebrates in integrated freshwater quality assessment [8] as well as crayfish, which may be used as a powerful surface water quality indicator [9].
Proteins are present in almost all foods although they are often in very small amounts. Their principal nutritional value is that they are the exclusive source of essential amino acids, which are very important for all live organisms due to the fact that they cannot be synthesized within their body and therefore must be supplied in readymade form in their diet [10].
In recent years, food quality and its nutritional value is considered as a top issue for the consumers and the development of new sophisticated analytical instrumentation has enabled the precise detection and quantification of the amino acids with easy, rapid and reliable analytical methods. Among several analytical methods for amino acid determination the preferred method is High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with pre-column derivatization because amino acids in foods are generally determined as derivatives [11].
Ultimately, crayfish is considered a gourmet species of high commercial value as well as a nutritious and healthy food for the consumer. To the best of our knowledge, there are very limiting data on nutritional value of this species. Therefore, our research aimed to determine the basic chemical composition and the amino acid profile of the edible muscle of crayfish assessing its nutritional value and to compare it to those of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) and European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax), the most common and important farmed fish in the Mediterranean basin.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Test animals were collected from the area among the villages St. Andreas (B 38.47264°, A 22.95544°) and St. Spyridon (B 38.46327°, A 22.95754°) of the region of Orchomenos Viotia, Greece. Thirtyfive (35) male animals were collected in traps and by hand during the night (between May and July) and transferred directly to a trout farming establishment where they kept in steel cages submerged in a small tributary of Viotic Kifissos river, with continuous water running to a depth of about 1.0-1.5m and a water temperature of about 25°C. During the acclimatization period, they were fed on detritus, benthic animals and aquatic plants from the same region. Then, they were transported to the laboratory in special packaging with ice. The total length and weight of each animal was measured and muscle tissue samples were collected from their tail and stored immediately at -80°C pending analyses.
Standards and reagents
Kjeldahl catalysts (3.5 g K2SO4 + 0.4 g CuSO4× 5 H2O) were purchased from FOSS, Denmark. Sulphuric acid (95-97 %), sodium hydroxide (35%), hydrochloric acid (fuming, 37%), boric acid, chloroform, methanol, methylene blue and methyl red were from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Purified water was obtained from a MilliQ water purification system (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA).
The amino acid standard mixture (Amino acid Standard H, Waters, USA) was consisted of the following amino acids at 2.5 μMol/μL each in 0.1N HCl: aspartic acid, glutamic acid, serine, glycine, histidine, arginine, threonine, alanine, proline, tyrosine, valine, methionine, isoleucine, leucine, phenylalanine, cystine and lysine. Amino acids derivatization reagent was the AccQ•TagTM Ultra Reagent, 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) (Waters, USA). The mobile phase used was a combination of (A) AccQ-TagTM Ultra Eluent A1 and (B) AccQ-TagTM Ultra Eluent B (Waters, USA), and the 0.2μm regenerated cellulose filters paper were purchased from Whatman (Sigma-Aldrich).
Proximate composition analysis
Crayfish muscle tissue samples were homogenized and analyzed for moisture, crude protein and ash according to AOAC [12]. Moisture content was measured after drying the samples at 105°C for 24h, inorganic elements (ash) was determined after ignition at 500°C for 12h, crude protein (N×6.25) by Kjeldahl method using a FOSS analytical system and total lipids by the Folch’s procedure [13].
Amino acids determination
The amino acid composition of the crayfish muscles was analyzed according to the method of [14]. Briefly, muscle samples were acid hydrolysed (6 N, 110°C, 24 h) and derivatized by the AccQ•TagTM Ultra Reagent (Waters, USA), (6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) used as derivatization reagent) according to the amino acid analysis application solution (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA) [15]. DL-Norvaline (Sigma) 2.5 mM was used as an internal standard. UPLC was performed on an Acquity system (Waters Corporation) equipped with PDA detector and the detection wavelength was set at λ = 260 nm. The column used was a BEH C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm i.d., 1.7 μm) from Waters. The flow rate was 0.7 ml/min and the column temperature were kept at 55°C. Empower v.2.0 (Waters) software was used for the peak identification and integration using an Amino Acid Standard H (Waters) as an external standard. All analyses were performed in duplicate. In case that the values between replicates did not meet the standardized acceptance criteria based on the mean and standard deviation (<5%), new duplicate analyses were performed according to established procedures. Tryptophan was not quantified due to its susceptibility to acid hydrolysis, while cysteine reacts with cysteine forming a disulfide bridge to produce cystine. Moreover, during acid hydrolysis procedure asparagine is converted to aspartate (ionic form of aspartic acid) and glutamine to glutamate (ionic form of glutamic acid), so the reported values for these amino acids (Asx and Glx) represent the sum of both amino acids.
Results and Discussion
The mean (±SD) length and weight of sampled Orchomenos’s crayfish were found to be 10.56 ± 1.28 cm and 39.94 ± 12.99 g, respectively.
The analysis of the muscle tissues of the experimental animals showed an average moisture content of 80.93%, slightly higher than those of the farmed gilthead sea bream (68.6-76.6 %) and wild counterparts (75.4-79.9 %) which were mentioned previously [16]. The mean protein content was found to be 16.55 ± 0.04g per 100g muscle, which is slightly lower compared to those which were reported in the past for farmed and wild gilthead sea bream (18.1-22.9 % and 19.3-21.2, respectively) [16]. Crayfish muscle had a very low lipid content (0.65%), which is quite lower and much lower to those reported previously for the wild and farmed gilthead sea bream (0.85- 3.01 % and 2.5-11.0 %, respectively) [16]. The inorganic elements (ash) content of crayfish muscle was accounted for 1.25%, which is slight lower compared with those reported for farmed and wild gilthead sea bream (1.22-1.64 % and 1.31-1.47 %, respectively) [16]. Comparable, the corresponding values for muscle of farmed and wild European sea bass reported in literature for protein (18.6-23.4 % and 17.6-21.8 %, respectively), lipid content (3.90-9.20 % and 1.22-9.19 %, respectively), moisture (64.4-76.7 % and 69.5-77.9 %, respectively) and ash (1.23-1.89 and 1.05-1.5 %, respectively) were higher than those of crayfish muscle [16,17]. However, different factors such water temperature, feeding ratio, feed composition, fish size, etc., may affect the composition of edible muscle in those animals [16].
Amino acids are the basic constituents of proteins and for that reason a qualitative and quantitative determination of the amino acids profile of the hydrolyzed samples is used for the nutritional value estimation of human food and animal feed. Usually, for their determination typical derivatization reagents include 9fluorenylmethyl chloroformate (FMOC-Cl), Ortho-Phthalaldehyde (OPA), Phenyl Isothiocyanate (PITC), 1-fluoro2,4-dinitrobenzene, 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrophenyl-5-L-alanine amide, and dansyl chloride. These techniques have advantages and limitations and only the combined OPA/FMOC-Cl has been recommended to overcome several problems with UV detection of the resulting derivatives of both primary and secondary amino acids [18,19]. Also, these conditions require viscous and buffered mobile phases, which operate at high temperatures and have a relatively quite long time both for derivatization and chromatography like that of 17.5min to 22.5min [20] and in some cases exceeding the run time of 30min [11] due to the analytical column and the mobile phase used. In our study, the amino acids profile of the crayfish edible muscle tissue was measured, based on a previously published method [21] which was modified according to [14] using pre-column derivatization with 6-aminoquinolyl-Nhydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate and optimized chromatography conditions producing stable derivatives with high resolution and with a total chromatographic run time of 9.0 min.
The amino acid content determined in muscle tissue of crayfish in comparison to those of farmed gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) [16], farmed and wild European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) [14,32] is summarized in Table 3. The amino acid profile found in crayfish muscle revealed that the arginine and glutamic acid were higher in crayfish (2.19% and 2.98%, respectively) than in the other two species except glutamic acid in farmed sea bass (3.44%), while aspartic acid content was higher in crayfish (1.88%) comparing to farmed gilthead sea bream (1.55%), and lower to that found in farmed and wild European sea bass (2.41% and 1.99%, respectively). As regards lysine, which is an essential amino acid for humans and animals, it was found to be higher in crayfish (1.47%) compared to farmed sea bream (1.38%) and lower than farmed and wild European sea bass (2.13% and 1.76%, respectively). Methionine content in farmed sea bream muscle (1.40%) was much higher compared to the other species (0.44-0.69%). The same pattern was observed for histidine (0.62% in farmed sea bream versus 0.34-0.41 % for the other species). The amino acids contents of serine, glycine, threonine, alanine, proline, tyrosine, valine, isoleucine, leucine and phenylalanine were found to be more or less similar among the three species. However, the analytical method employed to determine the amino acid content in animal muscle should be taken into consideration The nutritional value of fish is directly affected by its chemical composition, which consequently is determined by many factors such as species, age, size [16,22], sex, spawning [16], environmental factors such as season [22,23], water temperature [16], salinity [24], changes in photoperiod [25], geographical origin [26-28] and feeding history especially concerning farmed fish (diet composition and feeding ratio) [29,30]. It is well known that amino acids are categorized for nutritional purposes into two groups, the Essential Amino Acids (EAA) and the Non-Essential Amino Acids (NEAA). EAA are those amino acids that cannot be synthesized within the animal body or at a rate sufficient to meet the physiological needs of the growing animal, and must therefore be supplied in a readymade form in the diet. NEAA are those amino acids that can be synthesized in the body from a suitable carbon source and amino groups from other amino acids or simple compounds such as diammonium citrate, and consequently it is not prerequisite to be supplied in a readymade form in the diet. Table 1 shows the identified EAA and NEAA as well as the EAA/ NEAA ratios in the edible muscles of crayfish (1.02), farmed gilthead sea bream (1.14) and farmed and wild European sea bass (0.97 and 1.00, respectively).
Amino acids g/100g tissue (w/w)
Astacus astacus
(wild)*Sparus aurata
(farmed)**Dicentrarchus labrax
(farmed)***Dicentrarchus labrax
(wild)****Essential amino acids
Arginine
2.19
1.54
1.41
0.76
Histidine
0.35
0.62
0.41
0.34
Isoleucine
0.7
0.87
0.99
0.84
Leucine
1.33
1.4
1.77
1.49
Lysine
1.47
1.38
2.13
1.76
Methionine
0.47
1.4
0.69
0.44
Phenylalanine
0.7
0.94
0.95
0.79
Threonine
0.7
0.82
1.02
0.88
Valine
0.71
0.92
1.08
1.17
Non-essential amino acids
Alanine
0.94
0.95
1.37
1.15
Asparagine +Aspartic acid
1.88
1.55
2.41
1.99
Cystine
nd
0.79
0.11
nd
Glutamine + Glutamic acid
2.98
2.24
3.44
1.83
Glycine
0.71
0.88
1.13
1.01
Proline
0.59
0.69
0.66
0.91
Serine
0.74
0.72
0.89
1.12
Tyrosine
0.61
0.84
0.79
0.47
EAA/NEAA
1.02
1.14
0.97
1
*Standard deviation of all the values measured for amino acids in crayfish was ranged from 0.01 to 0.09. **Based on reference [31].
***Based on reference [14].
****Based on reference [32].
Table 1: Amino acid composition of edible muscle in crayfish (Astacus astacus), farmed gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata), farmed and wild European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax).
Conclusion
In conclusion, the crayfish Astacus astacus L. of the region of Orchomenos, in Viotia, Greece is a freshwater species of great commercial value and a nutritious human food source mainly due to its protein content and amino acid profile. Undoubtedly, it can be considered as an important source of amino acids and relatively comparable to those of farmed gilthead sea bream as well as to farmed and wild European sea bass. Nevertheless, its lipid content was found to be insignificant and negligible. Crayfish is also a very important resident in the Orchomenos river areas and a solid freshwater quality indicator. The results of this study can also contribute to the development of a quality standard for the European crayfish in Greece and its protein quality can be considered as a main factor in selecting this species as a candidate species for European aquaculture diversification.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank Mr P. Dimou, owner of a trout farm in Orchomenos area, who supplied us with the test animals and with valuable remarks on the ethology of crayfish in its environment.
References
- Plancic J. Our crayfish, their lives and the importance of fishing use in our waters. Fishery of Yugoslavia. 1946; 1: 16-18.
- Rajkovic M, Simic V, Petrovic A. Length-weight gain of European crayfish Astacus astacus (L.) in the area of the upper course of the zeta river, Montenegro. Arch. Biol. Sci. Belgrade. 2006; 58: 233-238.
- Kastritsi-Kathariou I, Nikokirakis M, Armakas D, Kazanoglou A. Study on the crayfish Astacus astacus from the native population in Orchomenos Viotias. 2nd Report to the Greek Ministry of Agriculture. Athens University, School of Biology, Zoology Department, Athens. 1994b; 115.
- Kastritsi-Kathariou I, Skeparioti E. Study on indigenous population of freshwater crayfish Astacus astacus from Viotic River Kifissos. Athens University, Zoology Laboratory. 1990a; 85.
- Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora. Official Journal of the European Communities No L 206/7.
- Royal Decree 142/71-FEK 49A/71 about fishing of aquatic animals of lakes, rivers and their protection. The Government Gazette. 1972; 71.
- Directive 2000/60EC establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Communities L 327/1.
- Artemiadou V, Lazaridou M. Evaluation score and interpretation index for the ecological quality of running waters in central and northern Hellas. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 2005; 110: 1-40.
- Koutrakis E, Perdikaris C, Machino Y, Savvidis G, Margaria N. Distribution, recent mortalities and conservation measures of crayfish in Hellenic fresh waters. Bulletin Français de la pêche et de la pisciculture. 2007; 385: 25-44.
- Tacon AGJ. The nutrition and feeding of farmed fish and shrimp-a training manual 1. The essential nutrients. A report prepared for the FAO Trust Fund GCP/RLA/075/ITA Project Support to the Regional Aquaculture Activities for Latin America and the Caribbean. FAO of the United Nations. Brasillia, Brazil. 1987.
- Fabiani A, Versari A, Parpinello PG, Castellari M, Galassi S. High- Performance Liquid Chromatographic Analysis of Free Amino Acids in Fruit Juices Using Derivatization with 9-Fluorenylmethyl-Chloroformate. Journal of Chromatographic Science. 2002; 40: 14-18.
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International. (18th ed), AOAC. International. ArlingtonVirginia, USA. 2005.
- Folch J, Leems M, Sloan Stanley GH. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. Journal Biological Chemistry. 1957; 226: 497-509.
- Kotzamanis Y, Kumar V, Tsironi T, Grigorakis K, Ilia V, Vatsos I, et al. Taurine supplementation in high-soy diets affects fillet quality of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture. 2020; 520: 734655.
- Waters. UPLC Amino acid analysis. The Science of What’s Possible. 720001946EN May 2009SC-AC. Printed in USA. 2009.
- Grigorakis K. Compositional and organoleptic quality of farmed and wild gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) and sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and factors affecting it: A review. Aquaculture. 2007; 272: 55-75.
- Erkan N, Ozkan O. Proximate composition and mineral contents in aqua cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax), sea bream (Sparus aurata) analyzed by ICP-MS. Food Chemistry. 2007; 102: 721-725.
- Sanchez-Machado DI, Lopez-Cervantes J, Lopez-Hernandez J, Paseiro- Losada P, Simal-Lozano J. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Analysis of Amino Acids in Edible Seaweeds after Derivatization with Phenyl Isothiocyanate. Chromatographia. 2003; 58: 159-163.
- Vilasoa-Martinez M, Lopez-Hernandez J, Asuncion Lage-Yusty M. Protein and amino acid contents in the crab, Chionoecetes opilio. Food Chemistry. 2007; 103: 1330-1336.
- Chen YB, Cheng Q, Rao B, Qin L. Improvement of a method for separation and determination of amino acids. Chinese Journal of Chromatography. 2001; 19: 560-563.
- Boogers I, Plugge W, Stockermans YQ, Duchateau AL. Ultra-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of amino acids in protein hydrolysates using an automated pre-column derivatization method. J Chromatography A. 2008; 1189: 406-409.
- Iverson SJ, Frost KJ, Lang SLC. Fat content and fatty acid composition of forage fish and invertebrates in Prince William Sound, Alaska: factors contributing to among and within species variability. Marine Ecology Progress Series. 2002; 241: 161-181.
- Grün IU, Shi H, Fernando LN, Clarke AD, Ellersiek MR, Beffa DA. Differentiation and identification of cultured and wild crappie (Pomoxix spp.) based on fatty acid composition. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und Technology. 1999; 32: 305-311.
- Roche H, Chaar K, Peres G. The effect of a decrease in salinity on the significant constituents of the tissue in the sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax Pisces). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology A. Comparative Physiology. 1989; 93: 785-789.
- Gines R, Afonso JM, Argüello A, Zamorano MJ, Lopez JL. The effects of lingday photoperiod on growth, body composition and skin colour in immature gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Aquaculture Research. 2004; 35: 1207-1212.
- Nettleton JA. Seafood Nutrition. Von Nostrand Reinhold, NY. 1985; 280.
- Ackman RG. Nutritional composition of fats in seafoods. Progress in Food and Nutrition Science. 1989; 12: 161-289.
- Saito H, Yamashiro R, Alasalvar C, Konno T. Influence of diet on fatty acida of three subtropical fish, subfamily Caesioninae (Caesio diagramma and C. tile) and family Siganidae (Siganus canaliculatus). Lipids. 1999; 34: 1073-1082.
- Huss HH. Quality and quality changes in fresh fish. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper. 1988; 348: 195.
- Nasopoulou C, Karantonis H C. Zabetakis I. Nutrition value of gilthead sea bream and sea bass. Dynamic Biochemistry, Process Biotechnology and Molecular Biology. 2011; 5: 32-40.
- Martínez-Llorens S, Vicente Moñino A, Vidal T, Javier Moya Salvador V, Pla Torres M, Miguel Jover Cerdá M. Soybean meal as a protein source in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) diets: effects on growth and nutrient utilization. Aquaculture research, 2007; 38: 82-90.
- Ozyurt G, Polat A. Amino acid and fatty acid composition of wild sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax): a seasonal differentiation. European Food Research and Technology. 2006; 222: 316-320.