
Research Article
Austin J Nutr Metab. 2023; 10(1): 1126.
Identification, Synthesis and Characterization of the Two Process Impurities of Levonadifloxacin (WCK 771)
Bhavsar SB*, Pawar SP, Jadhav SB, Kayastha AK, Rane VP and Patel MV
Wockhardt Research Centre, D-4, MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad (MS), India
*Corresponding author: Satish Bhawsar Wockhardt Research Centre, D-4, MIDC, Chikalthana, Aurangabad (MS), India
Received: November 17, 2022; Accepted: January 17, 2023; Published: January 24, 2023
Abstract
Wockhardt pharmaceuticals have developed the novel antibacterial drug, levonadifloxacin (WCK 771); to treat the infections caused by resistant gm +ve bacteria, and subsequently launched into Indian market a year ago with the brand name EMROK. During the scale up of levonadifloxacin seven impurities were identified. Out of seven known process impurities, five impurities were synthesized earlier as reference standards and validated through High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). In order to compliment our earlier efforts, the current study describes the establishment of an efficient synthetic routes for remaining two process impurities i.e. impurity 5 and impurity 7 of levonadifloxacin. Here, the syntheses of remaining two impurities are demonstrated in details.
Keywords: Levonadifloxacin (WCK 771), Antibacterial, gm +ve, MRSA, EMROK
Introduction
Defining impurity profile is key element to ensure safe, efficacious and quality human drugs, so that the drug substance are in accordance with GDUFA II requirements [1]. ICH guidelines are well defined for impurities in new drug substance as Q3A (R2). In general impurities are the unwanted small chemical fragments which form during the process setup of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API). The formation of such surplus impurities can influence the efficacy and safety of the pharmaceutical products [2] hence identification and quantification of such impurities in drug substance is now receiving critical attention from regulatory authorities [3]. As per the regulatory requirement (ICH guidelines: International Council on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use) for the filing of investigational new drug applications (INDA) and New Drug Applications (NDA), it is essential to ensure identification impurities for the quality, purity and strength of the new drug product [4]., It is indispensable to understand all type of process impurities, like related substances, residual solvents, genotoxic impurities, elemental impurities and probable arising during drug product storage [5-7].
Identification of process impurities helps process scientist, to develop the process by minimizing the formation of unsought impurities so that assay of final product is improved. Purification of an API is the challenging stage in production and can be simplified by superseding the formation of impurities. For accurate quantification of impurities in drug substance and drug product, it is imperative to make available process impurities, during drug development. Identification of impurities and obtaining their reference standards are prime necessity for analytical method development and validation..
Recently Wockhardt pharmaceutical had launched levonadifloxacin (WCK 771, with chemical name S-(-)-9-fluoro- 6,7-dihydro-8-(4-hydroxypiperidin-1-yl)-5-methyl-1-oxo- 1H,5H-benzo[i,j]quinolizine-2-carboxylic acid L-(+) arginine salt tetrahydrate [8,9] into the Indian market by the brand name of EMROK as intravenous injection for Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections (ABSSI) including diabetic foot infections, Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) infections, and concurrent bacteremia. levonadifloxacin (WCK 771) is a novel broad-spectrum drug to treat methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)/vancomycinresistant staphylococcus aureus (VRSA)/VRE, formulated for intravenous administration [10,11].
Result and Discussion
The unambiguous identification of process impurities can increase process understanding, which in turn allows for better impurity control in the final API. Also, purification of final API is usually the most difficult step in its production and can be facilitated by suppressing the formation of impurities [12]. Well characterised impurities can help in quantification of final API purity. Reference standards of impurities are required for analytical method development, validation, and during batch release and stability studies of drug substance or product. In order to address these challenges recently we had published our research regarding various impurity syntheses which includes the synthesis of Impurity 1, Impurity 2, Impurity 3, Impurity 4, and Impurity 613 as depicted in scheme 1.
Main objective of current study is to develop an efficient, straightforward, route for the synthesis of the two vital, impurities (Impurity 5 and Impurity 7) of levonadifloxacin. During the process of API development of levonadifloxacin, impurities were observed in the bulk drug substance. The mass of the impurities was identified using Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LCMS) which helped us to predict the probable structures. Moreover, the structure of the impurity was confirmed after isolation and purification by chemical synthesis and confirmed through detailed spectroscopic analysis, followed by coinjection with final API using the original High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) method. The chemical structures of the above stated impurities of levonadifloxacin are shown in (Figure 2).
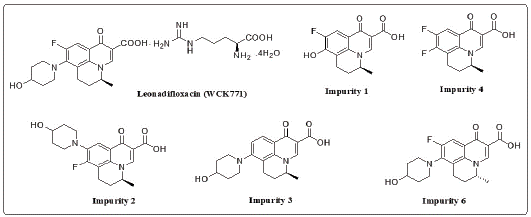
Figure 1:
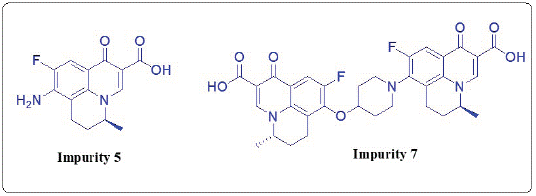
Figure 2:
Levonadifloxacin is an L-arginine tetrahydrate salt of S-nadifloxacin Impurity 4 and is synthesized from 5,6-difluoro-1,2,3,4- tetrahydro-2-methylquinoline through six steps. As a part of process research, efficient and cost effective routes for the synthesis and formulation of levonadifloxacin was already reported by Wockhardt [14]. During API development, associated impurities were primarily observed through HPLC and Mass spectroscopy. Then these predicted impurities were separately isolated and characterized by different analytical techniques like 1H NMR and 13C NMR analysis. Upon confirmation, separate synthetic routes were designed and established for the synthesis of these impurities. A schematic representation of the synthesis route of levonadifloxacin is given in Scheme 1.
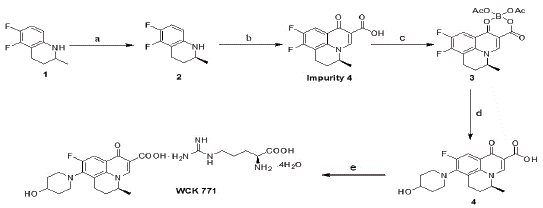
Scheme 1: Reagents: (a) dibenzoyl-L-tartaric acid (L-DBTA)/EtOAc,
NaOH/MeOH; (b) diethyl ethoxymethy-lenemalonate (EMME),
polyphosphoric acid (PPA), HCl/MeOH/H2O; (c) B(OH)3/CH3COOH/
(CH3CO)2O; (d) 4-hydroxy-piperidine/triethylamine (TEA)/dimethyl
sulfoxide (DMSO),NaOH/H2O/MeOH; (e) L-arginine/acetone/H2O.
A typical HPLC chromatogram of levonadifloxacin exhibits the peak with retention time 27.393 min. whereas the other recorded peaks were attributed to the target impurities under study and were marked as impurity 1 (retention time (RT): 13.350 min), impurity 2 (RT: 17.893 min), impurity 3 (RT: 20.493 min), impurity 4 (RT: 23.967 min), impurity 5 (RT: 10.913 min), impurity 6 (RT: 16.270 min) and impurity 7 (RT: 11.71 min). All impurities were analysed by chiral HPLC as shown in (Figure 3,4 and 5).
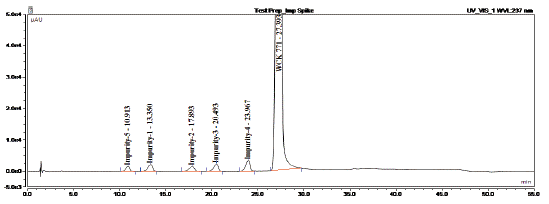
Figure 3: HPLC chromatogram of the Levonadifloxacin sample
spiked with five impurities.
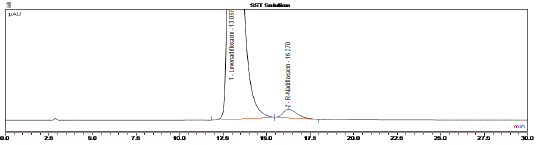
Figure 4: HPLC chromatogram of the Levonadifloxacin sample
spiked with R isomer impurity (Impurity 6).
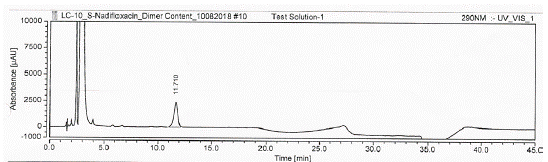
Figure 5: HPLC chromatogram of the Levonadifloxacin sample with
dimer impurity (Impurity 7).
Synthesis of Impurity 5: 8-Amino-9-Fluoro-5-Methyl-6, 7-Dihydro-1-oxo-1H, 5H-Benzo[i,j]- Quinolizine-2-Carboxylic Acid
The synthesis of impurity 5 was carried out through two step easy and convenient synthetic protocol. Initially intermediate 3 was reacted with aq. ammonia and dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) at 1200C for 2h to get the corresponding intermediate 5, which subsequently reacted with aq. NaOH in presence of DMSO and methanol at 200C to get the required impurity 5. The schematic representation for the synthesis of impurity 5 is shown in scheme 2. The application of methodology from organic synthesis, regarding the use of aqueous ammonia for the replacement of fluorine in one step; proving an efficient reaction condition, done very first time on such system. Earlier the same transformation was carried out in two steps involving the substitution of benzyl amine in first step followed by deprotection of benzyl group. Upon completion of the second step, the mixture was treated with activated charcoal (3 Eqv W/W) maintained stirring for 30 min. The reaction solution was filtered through celite bed, was washed with water (2 volumes). In filtrate, added conc. hydrochloric acid drop wise to adjust pH 5.0 to 5.5, solid precipitate was separated and washed with water (4 volumes). The above residue was dried on high vacuum, to provide title (impurity 5) as pale yellow solid in 75 % yield. Mol. Formula: C14H13FN2O3; Mol. Weight: 276.27; ESMS: (M+H): 277.1: HPLC purity: 96.06% 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): d (ppm) 1.33 (d, 3H), 2.09-2.16 (m, 2H), 2.62-2.64 (m, 1H), 2.76-2.77 (m, 1H), 4.83-4.86 (m, 1H), 6.46 (s, 2H), 7.73-7.76 (d, 1H), 8.82 (s, 1H), 15.83 (s, 1H); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6): d (ppm) 17.06, 19.40, 24.44, 56.50, 105.82, 107.21, 108.77, 114.57, 134.09, 140.33, 146.27, 150.46, 166.62, 176.14.
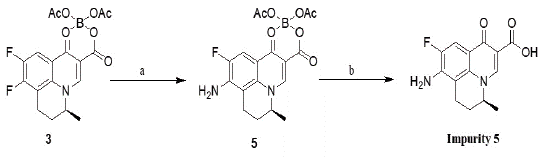
Scheme 2: Reagents: (a) Aq. Ammonia, DMSO, 120 0C, 2h: (b)
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), NaOH/H2O/MeOH, 35 0C, 2h.
Scheme 3: Reagents: (a) Sodium Hydride (50%), THF, Reflux, 4h:
(b) Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), DCM, -5 to 0 0C, 2h: (c) N, N-Diisopropylethylamine
(DIPEA), compound 11, Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO),
110 0C, 10h.
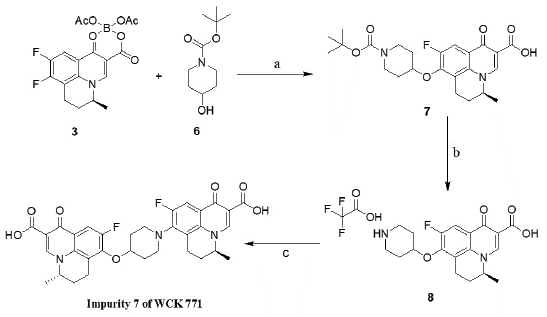
Synthesis of Impurity 7: S-(-) 9-Fluoro-8-[4-[8’-[S-(-) 9’-Fluoro-5’-Methyl-6’,7’-Dihydro-1’-Oxo1’H,5’H-Benzo[i,j]- Quinolizine-2’-Carboxylic Acid]] Oxy-Piperidin-1-yl)-5-Methyl- 6,7-Dihydro-1-Oxo-1H,5H-Benzo [i,j]-Quinolizine-2-Carboxylic Acid
Initially, impurity 7 was unidentified in chiral HPLC analysis, due to same retention time of levonadifloxacin and impurity 7; while the impurity was exhibiting the mass of dimer in Mass spectroscopy analysis. This had prompted us for the designing and synthesis of the impurity 7; later which has been prepared separately in three steps and validated through high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
4-Hydroxy piperidine was reacted with intermediate 3 in presence of THF and sodium hydride to get the corresponding intermediate 7 which then reacted with trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in presence of dichloromethane (DCM) to get the desired intermediate 8. The above amine salt 8, was then reacted to intermediate 3 in presence of DMSO and DIPEA to get the crude impurity 7.
For the purification of crude impurity 7, it was dissolved in 5 volume of DMSO. The resulting suspension was gradually heated to 1000C and maintained for 1h. Hot reaction mixture was filtered, cake washed by ethyl acetate (15 ml), dried on high vacuum to provide brown colour solid impurity 7 in 3.0 gm (50% yields). Mol. Formula: C33H31F2N3O7; Mol. Weight: 619.63; ESMS: (M+H): 620.4; HPLC purity: 92.06%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): d (ppm) 1.52 (2d, 7H), 1.80-2.40 (m, 8H), 2.80-3.60 (m, 8H), 4.56 (bs, 2H), 8.05-8.14 (2xd, 2H), 8.72 (2xs, 2H), 14.92 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): d (ppm) 17.11, 18.69, 19.96, 20.04, 25.46, 25.75, 32.43, 40.11, 48.44, 49.30, 49.83, 57.84, 57.94, 77.20, 107.19, 107.40, 110.44, 110.67, 110.96, 111.18, 123.74, 126.09, 133.57, 133.67, 146.56, 146.69, 147.17, 156.93, 159.44, 159.69,167.64, 167.70, 177.30.
Conclusion
A short and efficient synthesis of two process impurities of the novel anti-MRSA drug levonadifloxacin (WCK 771) has been established. Among these, the synthesis of impurity 5 involves two step efficient protocols comprising the use of aqueous ammonia for the nucleophilic substitution of activated aromatic fluorine substituent. Moreover, the separate synthesis of impurity 7 which is unidentified earlier through existing methods of chiral HPLC, had been resolved and validated through different analytical methods. The synthesis of both impurities provided an access to the reference standards for analytical method development, batch release, and for qualification through toxicity studies.
Supporting Information
Materials and methods, experimental details and characterization data, including 1NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MS data, micro analysis and isolated yields of intermediates and final compounds were incorporated in separate file of supporting information. This material can be found via the “Supplementary Content” section of this article’s webpage.
References
- Keitel S. Impurity Profiles in Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. EU/Swissmedic GMP Workshop Beijing University; Sep. 2006.
- Josephs JL, Sanders M, Shipkova P. Detection and Characterization of Pharmaceutical Metabolites, Degradants and Impurities by the Application of MS / MS Software Algorithms; Technical Program Feb 25, 2007.
- Pilaniya K, Chandrawanshi HK, Pilaniya U, Manchandani P, Jain P, Singh N. Recent trends in the impurity profile of pharmaceuticals. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2010; 1: 302–310.
- Snodin D. ICH Guideline M7 on Mutagenic Impurities in Pharmaceuticals. 2017; 5-9.
- (a) ICH Guidelines, Q3A (R), Impurities in New Drug Substances, The Quality Guidelines for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Related to Impurities According to the International Conference of Harmonization, 2002. (b) ICH Guidelines, Q3B (R) Impurities in New Drug Products, The Quality Guidelines for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Related to Impurities According to the International Conference of Harmonization, 2002. (c) International Conferences on Harmonizations, Impurities Guidelines for Residual Solvents. Q3(c), Federal Register, 1997.
- ICH guideline Q3 (R2) Impurities in new drug substances, International Conference on Harmonization, IFPMA, Geneva. 2006.
- ICH guideline Q6A Specifications: Test procedures and acceptance criteria for new drug substances and new drug products: Chemical substances, International Conference on Harmonization, IFPMA, Geneva. 1999.
- Bhagwat S, Nandanwar M, Kansagara A, Patel A, Takalkar S, Chavan R, et al. Levonadifloxacin, a novel broad-spectrum anti- MRSA benzoquinolizine quinolone agent: review of current evidence. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2019; 13: 4351-4365.
- Bhavsar S, Kale R, Deshpande P, Yeole R, Bhagwat S, Patel M, Design and synthesis of an oral prodrug alalevonadifloxacin for the treatment of MRSA infection. Bioorg and Med Chem Lett. 2021; 54: 128432.
- Yeole R, Jadhav A, Patil K, Rane V, Kubal M, Singh S, et al. Validated chiral high performance liquid chromatography method for a novel anti methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus fluoroquinolone WCK 771. J Chromatogr A. 2006; 1108: 38-42.
- Saxena D, Kaul G, Dasgupta A, Chopra S. Levonadifloxacin arginine salt to treat acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection due to S. aureus including MRSA. Drugs Today 2020; 56: 583-598.
- Snodin, D. ICH Guideline M7 on Mutagenic Impurities in Pharmaceuticals. 2017; 5-9.
- Kilbile J, Tamboli Y, Rafeeq M, Yadav R, Rane V, Bhamare V, et al. Efficient Synthesis of Potential Impurities in Levonadifloxacin (WCK 771). ACS Omega 2021; 6: 29993-30002.
- (a) Kulkarni D, Shinde P, Siddiqui M. Efficient Process for Synthesis of An Intermediate of Nadifloxacin. Indian Patent Application MU1015/20072009. (b) Kulkarni D, Khan N, Siddiqui, M. Economic Process for Synthesis of An Intermediate of Nadifloxacin. Indian Patent Application MU1010/ 20072009. (c) Gangakhedkar K, Deshmukh R, Rallapalli S, Deshmukh V. 8,9-Disubstituted- 5-Methyl-1-Oxo-6,7-Dihydro- 1H,5H-Pyrido[3,2,1-IJ]Quinoline- 2-Carboxylic Acid and Salts Thereof. Indian Patent Application MU1781/20082010. 20142015.