
Research Article
Austin J Nutr Metab. 2015; 2(5): 1032.
Effect of Cherry Juice on Angiogenesis Determined By Chorioallantoic Membrane (Cam) Assay
Atta UR Rehman*
Margalla College of Pharmacy, Margalla Institute of Health Sciences, Pakistan
*Corresponding author: Atta UR Rehman, Margalla College of Pharmacy, Margalla Institute of Health Sciences, Pakistan
Received: July 04, 2015; Accepted: August 10, 2015; Published: August 12, 2015
Abstract
The study was conducted with the objective to determine the effect of cherry juice on angiogenesis by Chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) Assay. Fifty fertilized fresh eggs were taken, incubated and on 6th day cherry juice of 0, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75 and 1.0 concentration was applied. The image of angiogenesis on CAM was recorded on 7th day. The surface roughness was also measured to quantify angiogenesis. The result of the study revealed that cherry had anti angiogenic characteristics. The application of cherry juice resulted in marked reduction in vessel development. As concentration of cherry juice increased, the vascular development decreased accordingly in concentration dependent manner. This aspect was further verified by observations recorded for surface roughness. The parameters of surface roughness viz surface height, dispersion, surface roughness, surface skewness, and developed surface area ratio and core fluid retention were affected by application of cherry juice. As the concentration of cherry juice increased, the surface roughness of all parameters decreased. This may be inferred from the study that cherry had angiogenic properties. The inclusion of cherry in diet may curtail or at least retard tumor growth, diabetes and other diseases. The cherry may be included in the dietary plan to prevent diseases to considerable degree.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cherry; Chorio-allantoic Membrane assay; Antiangiogenesis
Introduction
Angiogenesis is a physiological process in which new blood vessels are formed from the existing blood vessels. Angiogenesis is a complex enzymatic process. Angiogenesis is of immense significance in human health, as it is a vital process for development, wound repair and is also involved in reproduction activity. Angiogenesis is sustained in the body because a balance exists between growth regulators and inhibition factors in the body. Whenever, this natural balance is disturbed. The degree of angiogenesis may vary subsequently and the abnormal blood vessel growth results in number of diseases such as skin disease, diabetes, arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and a number of other diseases. The growth of solid tumor is usually limited, however is boosted up by angiogenesis. The blood for tumor growth is derived from adjacent tissues with propagation of new blood vessels [1,2].
The angiogenesis is to be reserved by use of anti angiogenic substances that restrict the growth and development of tumor. These substances are derived from chemical compounds and are also isolated as angiogenesis inhibitors from dietary items. Among the anti angiogenesis compounds, non steroidal anti- inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are widely used for arthritis, cardiovascular disease and also for colon cancer prevention. The NSAID had been demonstrated to inhibit angiogenesis by alteration of regulators, induction of vascular endothelial growth factor, inhibition of cell migration and modification of blood platelets and inflammatory cells. The angiogenesis inhibitors isolated from functional food included a number of fruits and vegetables such as strawberry, cherry, pomegranate and bitter melon, egg plants are rich source of anthocyanin, that act as a natural antioxidants. The anthocyanin containing fruits and vegetables and their constituents optimally regulate mechanistic pathway to promote human health and prevent diseases outlined above. Compared to chemical angiogenesis inhibitors compounds, the angiogenesis inhibitors isolated from functional food are quite effective, safe, reversible easily accessible, digested optimally with no side affect and above all are cost effective as well [3].
The scientist had employed number of methods to ascertain angiogenesis, most commonly used are cell proliferation and chromatic assay, Miniature Ring Supported (MRS) assay, rate aortic ring models, matrigel plug assay, tube formation angiogenesis assay and chicken chorioallantoic membrane assay (CAM) and a variety of other assays/ models. The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane is extra embryonic membrane formed on fourth day of incubation by fusion of chorion and allantois. The CAM act as a gas exchange surface and its function is attributed to dense capillary network. The capillary proliferation continues till day eleventh and vascular system attains its final arrangement on day 18th. The CAM model is extensively used to determine the morphofunctional aspect of angiogenesis process in vivo in order to study the mechanism and efficacy of proangiogenic and anti angiogenic synthetic and natural compounds. The CAM assay was a preferred model to ascertain tumor angiogenesis and metastatis strawberry, a member of rosaceae family, is rich in anthocyanin and had been tested in angiogenesis investigation using CAM assay and anti angiogenic property of edible berry are well documented [4]. However, similar research in respect of cherry, another member of Rosaceae is lacking and call for investigations in this regard. The hypothesis to be tested is cherry juice may- or may- not affect angiogenesis was conducted with the objectives.
- To investigate the effect of cherry juice on angiogenesis using CAM assay.
- To assess the effect of various concentration of cherry juice on angiogenesis.
- To sort out antiangiogenic properties of cherry.
Roy et al. studied the anti angiogenesis properties of edible berries. In cancer treatment anti angiogenesis approach is focal point in investigation of tumor biology. Vascular Endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays a critical role for vascularization of tumor. The vasculature in adult skin is quiescent. The skin is susceptible to initiation of angiogenesis during inflammatory skin disease such as cancer. They tested the effect of multiple berry extract on inducible VEGF expression. Six berries extracts viz. wild blue berries, bilberry, cranberry, elderberry, raspberry; seed and strawberry and grape seed proanthocyanidin (GSPE) were studied. The antioxidant value of strawberry and GSPE were higher than cranberry, elderberry or raspberry seed extract. Matrigel assay using human dermal micro vascular endothelial cell depicted that edible berries impair angiogenesis [5].
Bagchi et al. investigated the antiangiogenic, antioxidants and ant carcinogenic properties of rick berry extract. Edible berry anthocyanin had a broad spectrum of therapeutic and anticareinogenic characteristics. Berries are rich source of anthocyanin and act as natural antioxidants. Anthocyanin repair and protect integrity of genomic DNA. They studied extract of wild blue berry, elderberry, cranberry, bilberry, strawberry and raspberry for antioxidant efficacy, cellular uptake, and cytotoxic potential and antiangiogenic properties. They tested various combinations of edible berries and evolved optiberry1H141 that had high Oxygen Radical Absorbing capacity (ORAC). Moreover, optiberry impaired angiogenesis, reduced formation of hemangioma and decreased tumor growth more than 50%. Antiangiogenic determination at present is priority area in vascular tumor biology [6].
Ejaz et al. quantified the angiogenesis by image probing system (IPS). The Chorioallantoic membrane assay is commonly used in angiogenesis studies. They demonstrated that by application of IPS technique, diameter, vascular length, area and 3D roughness. The graph of normal and angiogenesis calls were prepared and compared for tumor assessment and treatment thereafter [7].
Tufon and satiroglu employed chick Chorioallantoic membrane model to study tumor angiogenesis, invasion and development of antiangiogenic agent. Angiogenesis, formation of new blood vessel is pre-requisite for tumor propagation and metastasis. They concluded that CAM model described quite well the tumor angiogenesis, invasion and development of Ontigngiogeneses agent [4].
Stone et al. described the berry anthocyanin as novel Oxidants in human health and disease prevention. They demonstrated that edible berries were potential source of natural anthocyanin antioxidants that perform a variety of biomedical functions, in advanced age various degenerative diseases, decrease tumor growth, improve brain function and protect genomic DNA integrity. They elaborated that optiberry; a contained extract of various berries had a potential cytotoxicity against Helicobacter pylori that was responsible for gastrointestinal disorder like duodenal ulcer and gastric cancer. They concluded that berry anthocyanin trigger genetic signaling in promoting human health and disease prevention [8].
Some scientists investigated the inhibition of angiogenesis by bill berry extract in chick Chorioallantoic member. Bill berry is used as folk medicine in some countries. They observed that bill berry reduced angiogenesis and inhibition was function of concentration of bill berry extract. This bill berry significantly decreased vessel proliferation and hence decreased angiogenesis and as such was useful for treatment of angiogenesis dependent human diseases [9].
Material and Methods
The cherry as test plant was used in present investigations. These are two types of cherries, sweet cherry and sour cherry. The sweet cherries belong to species Prunus avium while sour cherry is prunus cerosus. Cherry belong to family rosaceae of plant kingdom. Sweet cherry is tall tree with fruits of different shapes, globular depressed and heart shaped; color may be red and yellow. Cherry is propaged by grafting or budding. The tree may bear fruits for decades. The cross pollination may result in better yield than otherwise. Sweet cherry are taken as fruits while sour cherry are used for cooking purposes or preparation of jams, the strawberry, a member of Rosaceae family contain anthocyanin and are known for antioxidant characteristics and regulate carcinogenic enzymes to prevent cancer and tumor angiogenesis and number of other diseases [10,11]. The cherry another member of Rosaceae family call for such investigations and that is target of present study. In this regard fifty fertilized fresh eggs were taken and sprayed with 70% ethanol to reduce contamination. The eggs were air dried and incubated at 60% humidity, temperature 37C for five days. Figure 1 shows macroscopic evaluation of chicken chorio-allantoic membrane at day 6 of incubation.
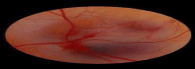
Figure 1: Macroscopic evaluation of chicken chorio-allantoic membrane at
day 6 of Incubation.
The fresh yellow cherry was squeezed to obtain juice using stainless steel squeezer. The juice was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm and supernatant was stored in freezer, on day fifth the incubated eggs were windowed by removing shell the window size was 2 cm diameter. Then 5ml of albumin was aspirated to allow the embryo to develop for quantification. The windows were sealed with Para film and incubated at 37°C for another day. The cherry concentration of 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 1.0% were prepared and adjusted to PH 7.0. The dilutions were filtered. The windows were opened and 200ml of each dilution was applied. The windows were sealed gain and kept for another one day. On 7th day the image was acquired by using high resolution camera as per image probing system of Ejaz et al. The image of angiogenesis on CAM was recorded in x and y dimensions at camera shutter speed of 1/2000.
All images were converted into gray scale and contrast was developed in black and white. All images were scanned in software. The length and diameter of blood vessel was measured. The surface roughness’s were measured to quantify angiogenesis on surface of CAM vascular area. The blood vessels on micrometer/nanometer scale were quantified to determine effect of cherry juice on angiogenesis. The data was subjected to statistical analysis. ANOVA was performed and statistical significance was tested at 5% level. The inferences were drawn in accordance with standard biostatic analysis.
Results and Discussions
The cherry juice has considerably affected the macroscopic vascular transformations in chicken Chorioallantoic membrane as depicted in Figure 1. In control treatment blood vessels were profusely distributed and cover the whole CAM area. The blood vessels in this treatment were differentiated into primary, secondary, and tertiary branches. The application of 0.25, 0.50, 0.75 and 1.0% cherry concentration resulted in marked reduction in vessel development and as cherry concentration increased, the vascular development decreased and maximum reduction was observed at highest cherry concentration of 1.0%. The secondary and tertiary vascular development decreased substantially in cherry juice concentration of 0.75 and 1.0%. These results evidently indicate that cherry juice had antiangiogenesis characteristics that indicate it has the ability to reduce the unwanted growth of blood vessels. Antiangiogenesis increased as the concentration of cherry juice increased. The results of present study are synonymous to Bagchi etal. (2004) they demonstrated that anticareinogenic and antiangiogenic properties of berry extract, that was a mix obtained from wild blue berry , strawberry, and other berries. The berries are rich in anthocyanin that acts as antioxidants and prevent a no of diseases.
The data pertaining to effect of cherry juice on surface height, surface roughness and dispersion is presented in table. This is evident from the data in Table 1, that maximum surface height of 248.3 nm was recorded in control treatment. The surface height was affected by application of cherry juice. The surface height decreased as the concentration of cherry juice increased and minimum surface height of 232-7nm was observed in case of 1.0% cherry juice treatment that was statistically similar to 0.75% cherry juice treatment. These two highest cherry juice treatments were statistically significant to all other treatment. The cherry juice treatment of 0.25 and 0.5% were statistically similar to each other, but different to other three treatments. The data of surface roughness in Table 1 revealed that maximum surface roughness of 107.5nm was recorded in control treatment. The surface roughness decreased as concentration of cherry juice increased and minimum was 64-6nm in case of 1.0% cherry juice treatment. The 1.0 percent treatment was statistically similar to 0.75% cherry juice treatment. However these two treatments were significantly different in comparison to all other treatments. The difference between the maximum and minimum surface roughness was 67 percent. The data pertaining to dispersion, which is root mean square of surface, is also presented in Table 1. The dispersion was also maximum in case of control treatment and it decreased in sequential order of 0.25 to 1.0% cherry juice concentration. The dispersion in case of control and 0.25% cherry juice treatments was statistically similar and different in comparison to other treatments. The surface height, surface roughness and dispersion were statistically different and revealed that dispersion was more affected by application of cherry juice than surface height and less affected than surface roughness and was intermediate between these two surface parameters. The results of present investigations are testimony to Bachi et al.
S.No.
Cherry Juice Concentration
(Present)
Surface Height Nanometers (nm)
Surface Roughness (nm)
Dispersion (nm)
1
0
248.3±1.8a
107.5±2.6a
132.1±2.2a
2
0.25
245.2±1.4ab
100.2±1.3b
126.3±0.91a
3
0.50
241.6±2.3b
85.9±2.1c
112.6±2.3b
4
0.75
236.7±1.6c
73.2±1.7b
102.7±2.8c
5
1.00
232.7±1.6c
64.6±2.7
92.8+3.2d
Average
240.8nm A
86.3c
113.3B
Table 1: Effect of cherry juice on surface height, surface roughness and dispersion.
The effect of cherry juice on surface skewness, developed area ratio and core fluid retention is presented in Table 2. The surface skewness is a measure of surface deviation from the mean surface plane. This parameter is used to describe shape of topography height distribution. The symmetric shape of surface height distribution indicates that skewness is zero. The surface skewness value obtained in present study for control treatment was 1.81. The surface skewness value decreased with application of cherry juice in sequential pattern, higher the cherry juice concentration, lesser the value of surface skewness. The lowest surface skewness value of 1.28 was recorded at highest cherry juice concentration of one percent. The surface skewness in case of 0.50% and 0.75% cherry juice treatment was statistically non significant, while significant in respect of control 0.25% and 1.0% treatments. The developed surface area ratio is increment of interfacial area of surface in relation to surface area. The data of developed surface area ratio in Table 2 indicate, the developed surface area ratio was 2.13 in control treatment that was significantly highest in comparison to other treatments that were subjected to application of cherry juice. The developed surface area ratio decreased with each increment of cherry juice and minimum of 1.25 was observed in 1.0% cherry juice treatment. The 1.0% treatment was no significant to 0.75% cherry juice treatment that in turn was no significant to 0.50% treatment. The remaining two treatments viz. control and 0.25% was significantly different compared to other treatments.
S.No.
Cherry Juice Concentration
(Present)
Surface Skewness
Developed Surface Ares Ratio
and Core Fluid Retention
1
0.0
1.81±0.14a
2.13±0.03a
1.34±0.06a
2
0.25
1.67±0.02b
1.78±0.02b
1.13±0.05b
3
0.50
1.42±0.03c
1.54±0.01c
0.98±0.03c
4
0.75
1.37±0.08c
1.36±0.04cd
0.87±0.02cd
5
1.00
1.28±0.07d
1.25±0.03d
0.79±0.03d
Average
1.5 AB
1.61 A
1.29 B
Table 2: Effect of cherry juice on surface skewness, developed surface area ratio and core fluid retention parameter.
The core fluid retention is ratio of void volume of unit sample area at core zone in comparison to root mean square deviation. A high value of this parameter indicate good fluid retention was 1-34 in control treatment and it was highest and statistically significant compared to other treatments that were applied cherry juice the minimum core fluid retention of 0.79 was obtained at 1.0% cherry juice treatment. The treatment 0 and 0.25% cherry juices were significant to each other and also statistically different in comparison to other treatment. The treatment 0.50 and 0.75% was also similar to 1.0% treatment in statistical notion. The core fluid retention was statistically non significant to surface skewness and that in turn was no significant to developed surface area ratio. These results revealed that various surface roughness parameters are interrelated and one may be function of another parameter and reverse statement may be valid in this regard as well.
The surface roughness parameters narrated in the preceding paragraphs elucidate that cherry has antiangiogenic properties that were function of concentration of cherry juice. These results are testimony to Bagchi et al. pertaining to berry extract in respect of antiangiogenesis characteristics.
The present study invariably demonstrates that cherry has antiangiogenic properties and may serve as natural antioxidants, antiangiogenic and anticareinogenic fruit/ vegetable. As ingredient of diet cherry may curtail or at least retard tumor growth, diabetes and other diseases. This is recommended that cherry may be included in dietary plan as regular phenomenon. This may be visualized that it was a pioneer study and lot is still to be investigated. This is recommended that cherry as component of diet plan may be tested for tumor growth and diabetes in the first instance and may be extended to other diseases later on the anthocyanin aspect of cherry also call for a comprehensive study and may be addressed accordingly in future research.
References
- Deng Q, Hu B, Cao S, Song HN, Chen JL, Zhou Q. Improving the efficacy of therapeutic angiogenesis by UTMD-mediated Ang-1 gene delivery to the infarcted myocardium. Int J Mol Med. 2015; 36: 335-344.
- Zhao Y, Adjei AA. Targeting Angiogenesis in Cancer Therapy: Moving Beyond Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Oncologist. 2015; 20: 660-673.
- Bimonte S, Barbieri A, Rea D, Palma G, Luciano A, Cuomo A, et al. Morphine Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis and Increases Breast Cancer Progression. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015: 161508.
- Tufan AC, Satiroglu-Tufan NL. The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane as a model system for the study of tumor angiogenesis, invasion and development of anti-angiogenic agents. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2005; 5: 249-266.
- Roy S, Khanna S, Alessio HM, Vider J, Bagchi D, Bagchi M, et al. Antiangiogenic property of edible berries. Free Radic Res. 2002; 36: 1023-1031.
- Bagchi D, Sen CK, Bagchi M, Atalay M. Anti-angiogenic, antioxidant, and anti-carcinogenic properties of a novel anthocyanin-rich berry extract formula. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2004; 69: 75-80, 1 p preceding 75.
- Ejaz S, Seok KB, Woong LC. A novel image probing system for precise quantification of angiogenesis. Tumori. 2004; 90: 611-617.
- Zafra-Stone S, Yasmin T, Bagchi M, Chatterjee A, Vinson JA, Bagchi D. Berry anthocyanins as novel antioxidants in human health and disease prevention. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2007; 51: 675-683.
- Tulio AZ Jr, Chang C, Edirisinghe I, et al. Berry fruits modulated endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis via phosphoinositide-3 kinase/protein kinase B pathway in vitro in endothelial cells. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. 2012; 60: 5803-5812.
- Martin KR, Wooden A. Tart cherry juice induces differential dose-dependent effects on apoptosis, but not cellular proliferation, in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Med Food. 2012; 15: 945-954.
- Traustadóttir T, Davies SS, Stock AA, Su Y, Heward CB, Roberts LJ 2nd, et al. Tart cherry juice decreases oxidative stress in healthy older men and women. J Nutr. 2009; 139: 1896-1900.