
Research Article
Austin J Nutr Metab. 2020; 7(4): 1087.
The Effects of Genetically Modified Feeds on Consumers’ Preferences in Buying Broiler Meat
Kerem Karasu and Ergin Öztürk*
Department of Animal Science, Ondokuz Mayis University, Institute of Science and Technology, Turkey
*Corresponding author: Ergin Öztürk, Department of Animal Science, Ondokuz Mayıs University, Faculty of Agriculture, 55139 - Samsun, Turkey
Received: June 02, 2020; Accepted: June 29, 2020; Published: July 06, 2020
Abstract
The possibility of Genetically Modified (GM) feeds to change animal products and their effects on human health have been frequently discussed in recent years. In this study, it was aimed to determine how the purchasing decisions of consumers change in case of feeding animals with GM feeds. For this purpose, data was collected by surveying 384 subjects from the central districts of Istanbul province by face-to-face interview with one-step random sampling method. Descriptive analysis and chi-square tests were used to analyze the data obtained from the survey. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 21.0 software. It was determined that the food consumed by the animals was GM feeds in the preferences of the consumers to purchase chicken meat, which negatively affected the consumers. 2.9% of consumers who participated in the survey stated that feeding animals with GM feeds will not affect their purchasing decisions at all, 22.4% will affect less, and 74.7% will affect too much. According to the results of the research, feed consumption with GM affects the purchasing decisions of male consumers more negatively than female consumers and older consumers than younger consumers and they reduce the amount of chicken meat they buy. In addition, as the number of people in the families of the respondent’s increases, the use of GM feed in animal feeding affects the purchase decision more. As the income status of consumers increases, the rate of affecting the purchase decision increases. Research results have shown that consumers of chicken meat have a deep suspicion that the use of GM feeds in animal feeding will negatively affect their health, and, if possible, they tend not to consume products obtained from animals fed GM feeds.
Keywords: Genetically Modified (GM) Feeds; Broiler Meat; Consumer Preference
Introduction
According to the UN, the world population will exceed 9.3 billion in 2050. Currently, one billion people are hungry and one child dies every 6 seconds. With the increase in the population, the food deficit increases, and the need for animal products and feed increases. With traditional breeding methods, the increase in yield does not reach the desired levels. On the other hand, the pressure of the production on the environment is gradually increasing and the cultivation areas are narrowing. In this case, it requires not only higher yields per unit area but also more economical production. These reasons made the application of new technologies in plant breeding inevitable. Therefore, modern agriculture techniques provide potential for sustainable nutrition of the growing population in the world.
Genetically Modified (GM) organism is produced by copying and transferring the genetic properties in an organism to another organism that does not have these properties. Plants obtained with this method are more resistant to drugs or pests, thereby reducing the use of chemical pesticides [1]. By interfering with genes, the characteristics of plants such as flavor, nutrition, and durability can be improved. This technology also makes it easier to respond to unwanted situations and events. The use of GM organisms, especially in the production of vaccines and drugs, is very important, and efforts to develop plants resistant to thirst are also ongoing. Today, it has become clear that GM products increase yield and reduce pesticide use. Due to the favorable growing conditions, GM organism production, particularly corn, soy, cotton, canola and safflower, mostly in North and South America, has increased rapidly and reached 185 million hectares worldwide in 2016 [2]. Nowadays, the scientifically evaluated direct hazardous effects of GM food and feed on fauna and flora are contradictory; Indeed, reviewing available data in the literature provides some evidence of GM human health and environmental risks. When it is evaluated in terms of food safety, GM organism products are uneasy even if they carry the risk of creating some unexpected effects for human health. However, controversy continues regarding gene flow and biodiversity risks, and no scientific conclusion has yet been reached. There may be risks to the environment and ecosystems, such as the development of weed herbicide resistance during GM cultivation. On the other hand, there are no case reports of allergic reactions or immunotoxic effects from GM feed consumption compared to non-GM feeds. The possibility of horizontal gene transfer of GM organism related DNA to different species is not different from other DNA and is unlikely to raise health concerns [3]. According to the results of many studies conducted in the past, the 1st generation revealed that there was no significant difference between the nutritional values of feeds prepared with GM and feeds without GM [4,1,5,6]. In addition, no recombinant DNA fragments were found in tissue or organ samples of animals fed with GM plants [3]. Also, Mesnage et al., show that the consumption of the widely cultivated GM maize varieties NK603 and MON810 even up to 33% of the total diet had no effect on the status of the faecal microbiota compared to non-GM near isogenic lines [7]. GM plants have become part of regular farming in many parts of the world for food and feed production. In addition to the food and feed sector, biodiesel or pharmaceutical use possibilities have also become widespread [8].
Poultry meat and meat products are an indisputable food in the human nutrition due to its rich nutrient content. Today, broiler meat is the most important alternative to cover the animal protein deficit quickly and at low cost. The broiler industry is one of the fastest growing industries that can keep pace with the growing world population. For example, chicken meat production is 0.5 million tons in the 2000s in Turkey reached 2.5 million tons in 2019 and increased to 23 kg from 8.5 kg per capita [9]. Corn and soybean meal used as energy and protein source play an important role in this acceleration in broiler production. The fact that these two products are GM feeds causes the sector to be questioned about healthy food production among consumers. Consumer perceptions, attitudes and behaviors that do not rely on scientific data can seriously damage the industry over time [10-12].
In this study, it was aimed to determine the point of view of consumers by examining the use of Genetically Modified feeds that affect the decision process in purchasing chicken meat and which is met with concern. In addition, the content of animal feeds used in broiler meat production and the awareness of GM-based feed raw materials used in animal feed production were questioned, and what changes in product quality perceptions made by measuring consumers’ purchasing and general consumption trends were investigated.
Material and Methods
The data used in the study were collected in the central districts of Istanbul province in 2017 by interviewing 384 people face-toface with a single-stage random sampling method and formed the main data of the study. In collecting data; A questionnaire form was prepared to determine the demographic characteristics of consumers and general purchasing preferences and behaviors and the survey studies were carried out by the researcher himself. In the analysis of the data obtained from the survey, descriptive analysis and khi square (Χ²) tests were used. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 21.0 software. The effects were considered significant if P < 00.5.
Results
The family size for correspondents formed 50.3% family of 4 people, 16.9% family of 5 people, 12.5% family of 3 people, 11.7% family of 2 people, 7.6% ‘s consists of a family of 6 and 1% of 7 people. 40.4% of consumers monthly between 1.000 - 1.500 USD, 26.3% between 500 - 1.000 TL, 26% between 1.500 - 3.000 USD, 7.3% between 0 - 500 USD and 5% 2 of them stated that they earned more than 3.000 USD. In addition to this information, 66.9% of consumers are university graduates, 24% are secondary school and high school graduates, 8.3% are primary school graduates and 0.8% are literate. The responses of consumers to the question about how GMO feed use information will affect their purchasing decisions in the feeding of broiler chickens are shown in Figure 1, and the change in the effect of GM feed usage on purchasing behaviors is given in Table 1. While only 2.9% of consumers surveyed stated that using GM feed for feeding broiler chickens will not affect their purchasing decision, they stated that it would affect 22.4% little and 74.7% very much.
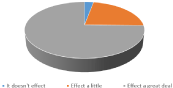
Figure 1: How does the use of GMO feed in the feeding of broiler chickens
affect your purchase decision? Answers to the question.
Gender (%)
Male
48.4
Education (%)
Illiterate
0.8
Female
51.6
Primary school
8.3
Age (%)
18-44
51.6
High school
24
45-59
34.1
University
66.9
60<
14.3
Number of family members (%)
2
11.7
Income (%)
0-1.500
7.3
3
12.5
1.500 - 3.000
26.3
4
50.3
3.000 - 5.000
40.4
5
16.9
5.000 - 10.000
26
6
7.6
10.000 ve üstü
5.2
7
1
Table 1: Demographic data of the research.
According to the research findings, there is no significant relationship between the educational status of consumers participating in the survey and their purchasing decisions. However, the knowledge that GM feed is used in broiler feed shows that consumers act slightly differently according to their gender (P <0.05). However, in fact, both sexes reported that the use of GM feeds in feeding would affect purchasing decisions at very close ratios (versus 74% to 76%). In our study, feeding information with GM affected the purchasing decisions of young consumers less than older consumers (Table 2). In other words, elderly consumers reduced the amount of chicken meat they bought if GM feeds were used in the diet. It has been determined that the level of education does not affect the willingness to purchase. As the number of family members increases, consumers’ GM feed information affects their decisions to purchase chicken meat more (P &0.05). Considering the income situation, low and high income groups have less response in terms of purchasing behavior, while middle income groups have more serious reactions. In other words, knowing that GM feed is used, they stated that they will reduce the consumption of chicken meat at a higher rate than the low and high income groups.
Frequency
It does not affect
Effects a little
Effects a great deal
N
n
%a
%b
n
%a
%b
n
%a
%b
χ2
P
Gender
Male
186
0
0
0
45
11.7
24
141
36.7
76
10.909
0.004
Female
198
11
2.9
6
41
10.7
21
146
38
74
Age
18 - 44
198
8
2.1
4
34
8.9
17
156
40.6
79
28.115
<0.001
45 – 59
131
3
0.8
2
25
6.5
19
103
26.8
79
60>
55
0
0
0
27
7
49
28
7.3
51
Family size
45
2
48
0
0
0
6
1.6
13
39
10.2
87
24.242
0.002
3
193
0
0
0
11
2.9
23
37
9.6
77
4
65
11
2.9
6
48
12.5
25
134
34.9
69
5
33
0
0
0
8
2.1
12
57
14.8
88
6
0
0
0
13
3.4
39
20
5.2
61
Education Level
34
Primary
93
0
0
0
7
1.8
21
27
7
79
7.325
0.12
Under graduate
257
0
0
0
26
6.8
28
67
17.4
72
Post graduate
11
2.9
4
53
13.8
21
193
50.3
75
Income, USD
28
<500
101
0
0
0
8
2.1
29
20
5.2
71
20.985
0.002
500-1000
155
0
0
0
16
4.2
16
85
22.1
84
1001-1500
100
3
0.8
2
33
8.6
21
119
31
77
>1500
8
2.1
8
29
7.6
29
63
16.4
63
a:% of total respondents, b:% of related factors
Table 2: The effect of gender, age, number of family members, education and income status on the purchase decision of broiler meat produced by feeding with GM feeds.
Discussion
Discussions on the social, economic and political consequences regarding the safety of GM crop consumption in agriculture and food sectors continue increasingly. Some researchers report that laboratory animals fed diets containing GM product toxic problems [13,14], while others report that GM-containing feeds have no safety issues [15-17].
In our study, the rate of those who stated that the use of GM feeds in animal feeding would affect their purchasing desires was 22.4%, while the rate of those who reported that it would be very effective was 74.7%. Although consumers adopt biotechnological applications, it turns out that they are concerned about the products obtained from feeding with GM feeds and show negative attitudes. Yanpar et al., stated in their study that 10.1% of the surveyors stated that they
did not see any inconvenience in GM product consumption, 95.4% of them should be labeled with GM products and 86.2% of them would not buy a product with GM label [18]. Henderson reported that in the United States, consumers are willing to pay additional money to avoid chicken products fed with GM feed [19]. Thus, it has been stated that there are two different market segments and the industry producers should produce chicken products without GM with a regular labeling system.
Although it varies according to the person who makes shopping in the family, today, as the age increases, the demand for organic products increases [20]. Lusk reported that the chicken products with the label “GM does not contain crop” increased its market share by 17.9% and this label is one of the most important labels for consumers [21]. The vast majority of consumers imagine that hormones, antibiotics, GM feeds and some additives are used in animal nutrition and state that this situation is inconvenient for health [22,23]. In addition to this information, Şengül and Zeybek stated that older consumers are more concerned about whether chicken meat is healthy or not [23]. In our study, it was found that young and middle age group (18-59 years old) reduced the amount of chicken meat (79% vs. 51%) they bought when used GM feeds in broiler nutrition. The effect of educational status on purchasing behavior was not significant in our study. Although studies seemed to show some connection between level of education and a corresponding level of scientific understanding, level
of education has not been shown to reliably predict understanding of or attitude toward Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) [24]. In our study, the middle income group stated that if GM feed is used, it will reduce the consumption of chicken meat at a higher rate than the low and high income groups. Some researchers [25,26] reported that individuals do not prefer chicken products when they have sufficient income, prefer products that they think are more natural or organic products.
It is a remarkable result that the perceptions, attitudes and behaviors of consumers towards chicken meat produced with GMO feeds vary and differ according to their demographic characteristics. Although the rate of responses of consumers with different demographic structure to GM products in our study varies, it is clear that all consumers, as the main axis, are unscientific about GM feeds and their effects on broiler meat. Whereas, the results presented in the vast majority of experiments did not indicate any negative effects of GM materials, it can be concluded that commercialised transgenic crops can be safely fed to target food-producing animals without affecting metabolic indices or the quality of such products as meat, milk and eggs [1]. Consumer information about how GM is obtained and what effects it has on animal products when GM products are used in animal nutrition is either too inadequate or full of scientific facts and even false information [27-30,24]. The vast majority of consumers receive information on GM food products from the media, internet and other news sources. These resources may be less reliable than scientific knowledge, where consumers rely more on delivering the facts. Consumers worldwide are displaying limited understanding, misconceptions, and even unfamiliarity with GM food products [24]. Also, these researchers proposed to distinguish between GMOs ‘scientific understanding’ which includes self-reporting and deeper information about scientific principles. Interestingly, consumer attitude may be affected by the potential for improved nutritional qualities in bioengineered foods. In a study, only 8.7% of Turkish students approve genetic modification for improved nutritional content, compared with 68.2% who oppose modification for nutritional purposes and 22% who remain undecided [30]. McComas et al., showed that those who are more knowledgeable about gene transfer see GMO products less negative than those who have less knowledge [31]. Participants in their study read the explanations on how GMOs can be used to protect plants from the spread of plant diseases, which suggests that those who know more about GMOs have more confidence in their power and can justify their use.
The false perception that chicken meat is unsafe, due to the very rapid spread of communication technologies, can spread quickly in the society. Chicken meat, which is mostly referred by nonspecialists, is referred to as unhealthy, risky and hormonal food, and this information pollution created in the society causes serious damage to the poultry sector [10-12]. Since the broiler meat is strategic in meeting the protein needs of the increasing population cheaply [12], the decrease in consumption decreases the balanced nutrition opportunities of the general pıblic. Food products demand of consumers, who are at the center of production and marketing strategies and are end users; product quality perceptions cover a complex decision process, which can vary depending on the internal and external qualities of the products. İnci et al., reported that the main factors negatively affecting the poultry meat consumption in Turkey are drugs or feed additives [32]. Comsumer perception on chicken meat which include GM product, even include antibiotics or growth hormones in Turkey and in the United States (Alabama) threats sustainable production in these countries [26].
Some findings in the literature suggest that consumers’ knowledge of GMO foods is typically quite limited, and that avoiding GM foods is mainly due to subjective rather than objective knowledge [22,33,1,34] asked four basic questions to test the knowledge of German consumers about GM foods. None of the 397 surveyed person answered all questions correctly, and 36% did not answer any of them correctly. Results of a U.S. study with a broader set of questions suggest that peoples’ beliefs have no solid scientific groundings, and 30–50% of the respondents had little or no knowledge about genetics [35]. In a meta-analysis, [36] found that public perceptions of benefits associated with GM food consumption had increased over time. Recent results from several countries also indicate substantial positive willingness to pay premiums to avoid GM foods. In a sample of U.S. students, 75% of the participants were on average willing to pay a 13% premium for non-GM items in restaurants [37]. In a study including Belgium, France, the Netherlands, Spain, and the United Kingdom, participants were willing to pay 4 to 13 times more to avoid GM rice [15]. In line with the results in [35,34] McFadden and Lusk and Wuepper, Wree, and Ardali, Ardebili and Rickertsen find that respondents were not very knowledgeable about GM-related issues, and around 56% of our sample thought GM technology was applied in Norwegian agriculture [22]. Consumer attitude towards plant based GM foods, GM-fed animals, and GM animals have compared in some studies [4,5] and the lowest aversion was towards a GMfed animal and the highest against a GM animal. Also, consumers become less averse when genetic modification is not directly applied to the final product that he/she consumes. Therefore, GM-fed animal products might be more accepted in the market than GM plant and animal products for human consumption.
Lusk and Briggeman’s results showed that the most important food attributes for consumers were food safety, price and taste [38]. Consumer responses to food safety risks are affected by their demographic characteristics, such as gender, age, income, and education [39,40]. Concerns about unnaturalness of GM foods could change quite rapidly given increased familiarity with these products and information about the similarities between GM techniques and conventional breeding. Ardebili and Rickertsen [22]’s results suggest that the acceptance of GM foods is associated with attitudes towards naturalness, trust in public authorities, knowledge, and personality traits. A distinction must also be made between GMO familiarity and scientific understanding, because those who are more familiar with it tend to be more resistant to bioengineering, whereas those with higher scientific knowledge scores tend to have less negative attitudes toward GMOs. This brings to question the relation between scientific literacy, sources of information, and overall consumer knowledge and perception of GM foods. It is important to provide producers, consumers, regulatory agencies, governments, policy makers, researchers with accurate and sufficient up-to-date information so that they can investigate potential risks in detail [24,6]. Furthermore, given the importance of trust in public authorities, more liberal regulations on the use of GM technologies in agriculture and sales of GM foods could also increase the acceptance [41-43]. Information and changes in regulations, which are based on solid scientific evidence and emphasize that there is nothing inherently more unnatural about GM foods than conventional products, are likely to increase the acceptance of GM foods over time.
Conclusion and Suggestions
The results of the research indicated that the vast majority of consumers do not prefer to buy meat that is fed with GM feed, and this affects their buying decisions. Understanding the effects of GM products on environment, animal and human health and ecosystem depends on increasing the level of awareness of the society. It is very important to act with scientific data so that the perceptions, attitudes and behaviors of consumers can be conscious and directed correctly. Accurate and adequate up-to-date information should be provided to manufacturers, consumers, regulatory agencies, governments, policy makers, researchers so that GM products can investigate potential risks in detail.
Acknowledgement
We thank Ondokuz Mayıs University (PYO.ZRT.1904.17.005) for providing financial support to our research project.
References
- Swiatkiewicz S, Swiatkiewicz M, Arczewska-Wlosek A, Jozefiak D. Genetically modified feeds and their effect on the metabolic parameters of food-producing animals: A review of recent studies. Animal Feed Science and Technology. 2014; 198: 1-19.
- Kleter G, McFarland S, Bach A, Bernabucci U, Bikker P, Busani L. Surveying selected European feed and livestock production chains for features enabling the case-specific post-market monitoring of livestock for intake and potential health impacts of animal feeds derived from genetically modified crops. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2018; 117: 66-78.
- De Santis B, Stockhofe N, Wal JM, Weesendorp E, Lalles JP, van Dijk J, et al. Case studies on Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs): Potential risk scenarios and associated health indicators. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2018; 117: 36-65.
- Chern WS, Rickertsen K, Tsuboi N, Fu TT. Consumer acceptance and willingness to pay for genetically modified vegetable oil and salmon: A multiplecountry assessment. AgBioForum. 2002; 5: 105-112.
- Rickertsen K, Gustavsen GW, Nayga RM. Consumer willingness to pay for genetically modified vegetable oil and salmon in the United States and Norway. AgBio Forum, 2017; 20: 1-11.
- Tsatsakis AM, Nawaz MA, Tutelyan VA, Golokhvast KS, Kalantzi OI, Chung DH. Impact on environment, ecosystem, diversity and health from culturing and using GMOs as feed and food. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2017; 107: 108-121.
- Mesnage R, Le Roy CI, Biserni M, Salles B, Antoniou MN. Relationship between faecal microbiota and plasma metabolome in rats fed NK603 and MON810 GM maize from the GMO90+ study. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2019; 131: 110547.
- Alderborn A, Sundström J, Soeria-Atmadja D, Sandberg M, Andersson HC, Hammerling U. Genetically modified plants for non-food or non-feed purposes: Straightforward screening for their appearance in food and feed. Food and chemical toxicology. 2010; 48: 453-464.
- TÜİK. Türkiye İstatistik Kurumu. 2019.
- Dokuzlu S, Barış O Secer C, Güldaş M. Türkiye’de tavuk eti tüketim alışkanlıkları ve marka tercihleri. Uludağ Üniversitesi Ziraat Fakültesi Dergisi. 2013; 27: 2, 83-92.
- Topçu Y, Uzundumlu SA, Baran D. Tüketicilerin tavuk eti tüketimi ile ilgili tutum ve davranışlarını etkileyen faktörlerin analizi. Türk Tarım-Gıda Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi. 2015; 3: 5, 242-247.
- Öztürk E. Yumurta ve Piliç Eti Kalitesi Güncel Bakım ve Besleme Uygulamalarından Etkilenir mi?. Tavukçuluk Araştırma Dergisi. 2016; 13: 2, 5-11.
- Dona A, Arvanitoyannis IS. Health risks of genetically modified foods. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2009; 49: 164-175.
- Krimsky S. An illusory consensus behind GMO health assessment. Sci Technol Hum. 2015; 40: 883-914.
- Delaney B, Goodman RE, Ladics GS. Food and feed safety of genetically engineered food crops. Toxicol. Sci. 2018; 162: 361-371.
- Nicolia A, Manzo A, Veronesi F, Rosellini D. An overview of the last 10 years of genetically engineered crop safety research. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2014; 34: 77-88.
- Ricroch AE. Assessment of GE food safety using ‘-omics’ techniques and long-term animal feeding studies. N Biotech. 2013; 30: 349-354.
- Yanpar H, Müftüoğlu S ve Saka M. Ankarada yaşayan üniversite öğrencilerinin genetiği değiştirilmiş organizmalar ile ilgili bakış açısının değerlendirilmesi. Adnan Menderes Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Fakültesi Dergisi. 2010; 2: 12- 20.
- Henderson C. Consumer Preferences for GM Food Labeling: A market segments analysis. Agricultural economics and agribusiness undergraduate honors theses. 2018; 9.
- Ustaahmetoğlu E, Toklu Tİ. Organik gıda satın alma niyetinde tutum, sağlık bilinci ve gıda güvenliğinin etkisi üzerine bir araştırma. Ekonomik ve Sosyal Araştırmalar Dergisi. 2015; 11: 1.197-211.
- Lusk LJ. Consumer Beliefs, Knowledge, and Willingness-to-Pay for Sustainability-Related Poultry Production Practices Broiler Survey Report. 2018.
- Ardebili AT, Rickertsen K. Personality traits, knowledge, and consumer acceptance of genetically modified plant and animal products. Food Quality and Preference. 2020; 80: 103825.
- Şengül T, Zeybek S. Diyarbakır il merkezinde yaşayan tüketicilerin tavuk eti algıları ve bu algıları etkileyen faktörler üzerinde bir araştırma. Türk Tarım ve Doğa Bilimleri Dergisi. 2020; 2, 433-440.
- Wunderlich S, Gatto KA. Consumer perception of genetically modified organisms and sources of information. Advances in Nutrition. 2015; 6: 842- 851.
- Demir AP, Aydın E. Hormon ve Antibiyotik kullanımına ilişkin olumsuz haberlerin tüketicilerin tavuk eti tüketim alışkanlıklarına etkisi (Kars ili örneği). Mehmet Akif Ersoy Veteriner Fakültesi Dergisi. 2018; 3: 1, 55-63.
- Yang R. The impact of hormone use perception on consumer meat preference. Southern Agricultural Economics Association Annual Meeting. 2017; 4: 1-22.
- Aleksejeva I. Latvian consumers’ knowledge about genetically modified organisms. Management of Organizations: Systematic Research. 2014; 71: 7-16.
- Hallman WK, Cuite CL, Morin XK. Working Paper 2013-1: Public perceptions of labeling genetically modified foods. New Brunswick (NJ): Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey, School of Environmental and Biological Sciences; 2013.
- Jurkiewicz A, Zagórski J, Bujak F, Lachowski S, Florek-Luszczki M. Emotional attitudes of young people completing secondary schools towards genetic modification of organisms and Genetically Modified Foods (GMF). Ann Agric Environ Med. 2014; 21: 205-211.
- Turker T, Kocak N, Aydin I, Istanbullouglu H, Yildiran N, Turk YZ, et al. Determination of knowledge, attitude, behavior about genetically modified organisms in nursing school students. Gulhane Tip Derg. 2013; 55: 297-304.
- McComas KA, Besley JC, Steinhardt J. Factor’s influencing U.S. consumer support for genetic modification to prevent crop disease. Appetite. 2014; 78: 8-14.
- İnci H, Karakaya E Şengül T. Söğüt B. Bingöl ilinde kanatlı eti tüketiminin yapısı. Türk Tarım ve Doğa Bilimleri Dergisi. 2014; 1: 17-24.
- Huffman WE, Rousu M, Shogren JF, Tegene A. The effects of prior beliefs and learning on consumers’ acceptance of genetically modified foods. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization. 2007; 63: 193-206.
- Wuepper D, Wree P, Ardali G. Does information change German consumers’ attitudes about genetically modified food? European Review of Agricultural Economics. 2018; 46: 53-78.
- McFadden BR, Lusk JL. What consumers don’t know about genetically modified food, and how that affects beliefs. The FASEB Journal. 2016; 30: 3091-3096.
- Frewer LJ, van der Lans IA, Fischer AR, Reinders MJ, Menozzi D, Zhang X, et al. Public perceptions of agri-food applications of genetic modification: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2013; 30: 142-152.
- Lu L, Gursoy D. Would consumers pay more for nongenetically modified menu items? An examination of factors influencing diners’ behavioral intentions. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management. 2017; 26: 215-237.
- Lusk JL, Briggeman BC. Food values. American journal of agricultural economics. 2009; 1: 184-196.
- Grobe D, Douthitt R, Zepeda L. A model of consumers’ risk perceptions toward recombinant bovine growth hormone (rbGH): The impact of risk characteristics. Risk Analysis. 1999; 19: 661-673.
- Kirk SFL, Greenwood D, Cade JE, Pearman AD. Public perception of a range of potential food risks in the United Kingdom. Appetite. 2002; 38: 189-197.
- Edgar LD, Johnson DM, Estes S. Poultry Production Messaging in Two National-Circulation Newspapers. Journal of Applied Communications. 2017; 101: 1, 6-18.
- McGarry Wolf M, Bertolini P, Shikama I, Berger A. A comparison of attitudes toward food and biotechnology in the U.S., Japan, and Italy. Journal of Food Distribution Research. 2012; 43: 103-110.
- Uçar A, Türkoğlu M. Kaliteli ve dengeli beslenme açısından kanatlı üretiminin etkinliği. Türk Tarım Gıda Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi. 2018; 6: 1: 69-72.