
Special Article – Diet, Nutrition and Obesity
Austin J Nutri Food Sci. 2017; 5(1): 1084.
The Role of Nutrition in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Shahbazi H and Ghofranipour F*
Department of Health Education and Health Promotion, Faculty of Medical Sciences, TarbiatModares University, Iran
*Corresponding author: Ghofranipour F, Department of Health Education and Health Promotion, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran
Received: December 05, 2016; Accepted: January 25, 2017; Published: January 26, 2017
Editorial
Type I diabetes (T1D) is the most common metabolic disorder in childhood and adolescence [1,2], which caused by the destruction of pancreatic beta cells and defective insulin production [3] and its prevalence and incidence is increasing [4]. In 2014, about 422 million people worldwide have been diagnosed with diabetes that 10 percent of them with had Type I diabetes [5]. The disease affects one person from every 400 to 600 children [6] and 3-4 percent increases each year in European children [7].
The most important attempt to control the blood glucose and prevent the complications of diabetes is Self-Management [2,8] that is a dynamic, interactive and daily process in which a person uses his ability with a combination of family, community and professional cares of health to change lifestyle, control his disease symptoms and treatment [9]. Nutrition and diet is the cornerstone of Type I diabetes management [10-12] and the purpose of nutritional management in patients with Type I diabetes includes:
- Encourage patients to choose and use proper and healthy food
- Use a wide range of nutrients in various food groups and healthy snack (if needed)
- Maintain a healthy weight and prevent overeating and establish a framework for regular monitoring of Blood Glucose (BG)
- Achieve maintaining Body Mass Index (BMI) and waist fit
- Achieve a balance between food intake and bodies needed metabolism, energy and insulin consumption to achieve the favorable glycemic control
- Prevention and treatment of acute and chronic complications of diabetes, such as: hypoglycemia, hyperglycemic episodes
- Reduction of cardiovascular complications
- Maintain and improve the life quality of patients
- Develop supportive relationships to facilitate behavior change and diet changes [13].
- Different countries and regions have different cultures and socioeconomic status which is effective on their dietary habits and diet. Therefore, nutritional recommendations should be proportionate to culture, ethnicity, family traditions, as well as cognitive and psychological needs of patients with Type I diabetes [13].
- Training diet should be done individually proportionate to the age of patients with Type I diabetes to help the interaction and active learning of patients [13].
- There should be a dietitian with experience of working on field of Type I diabetes in the treatment team which to be available and has the supervision and support on nutrition of adolescents with Type I diabetes [13]. The American Diabetes Association recommends that diabetic patients should annually refer to a dietitian or attend in a diabetes self-management training program that also includes nutritional therapy training. In Jaacks et al. research, less than half of patients with Type I diabetes “always” referred to a dietitian and only 18 percent of patients participated in training sessions over the past year [17].
- Research has shown that children and adolescents with Type I diabetes consume fats, especially saturated fats more than the recommended dose [13]. In study of Patton [1], percent of calories from fat in Type I diabetes patients is in the range of 31 to 47 percent which is more than the recommended dose for healthy people (less than 30%). In research of The et al., percent of calories from fat in Type I diabetes patients is significantly higher than the amount recommended for healthy individuals [15]. Eating some healthy fats such as olive oil, reducing the use of saturated fats, decrease, or no use of Tran’s fats are recommended [22].
- Alcohol is dangerous due to suppression of gluconeogenesis and may cause prolonged hypoglycemia (10 to 12 and more, depending on the dosage) in patients with Type I diabetes [13]. Therefore, its use should be restricted for children and adolescents with Type I diabetes.
- Sucrose should be contained to 10 percent of total daily energy expenditure and can be replaced by other carbohydrate sources which do not produce hyperglycemia [13].
- Protein consumption in the worldwide depends more on economic situation and the availability of them. Dietary protein should be maintained at the recommended daily allowance of 0.8 g/kg body weight per day. High protein diet, more than 25% of the energy, is not recommended for children and adolescents with Type I diabetes, because it may affect their growth and taking vitamins and minerals. Plant sources of protein such as legumes and animal sources of protein such as fish and low-fat dairy products are recommended [13,23].
- Increased fiber intake at least 10-12 grams per day increases the healthy functioning of the intestines and may be useful in feeling of fullness and alternative to high-energy foods. In many countries, the amount of fiber intake in the diet of children and adolescents is lower than the recommended level [13]. Results of Balk et al. study showed that low intake of vegetable protein and dietary fiber has been associated with poor blood glucose in control of Type I diabetes [7]. The fiber of processed foods is generally low; therefore, intake of fresh and unprocessed foods should be encouraged [13].
- Monitoring patient weight and preventing overweight and obesity in patients with Type I diabetes is a key strategy of care and should include family-based approach. Patients with Type I diabetes in all ages and in both genders are heavier compared to their peers without diabetes. Thus drawing growth curve, BMI and waist, if possible, are recommended for every three months [13]. As well as, studies have confirmed the relationship between suitable quality of diet to improve the weight management and advising and encouraging children and adolescents to intake a healthy diet including intake of fruits is effective for the prevention of overweight and obesity [12].
- Patton SR. Adherence to diet in youth with type 1 diabetes. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 2011; 111: 550-555.
- Lin K, Yang X, Yin G, Lin S. Diabetes Self-Care Activities and Health-Related Quality-of-Life of individuals with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Shantou, China. The Journal of international medical research. 2016; 44: 147-156.
- Lempainen J, Tauriainen S, Vaarala O, Mäkelä M, Honkanen H, Marttila J, et al. Interaction of enterovirus infection and cow’s milk based formula nutrition in type 1 diabetes associated autoimmunity. Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews. 2012; 28: 177-185.
- Patton SR, Odar C, Midyett LK, Clements MA. Pilot study results for a novel behavior plus nutrition intervention for caregivers of young children with type 1 diabetes. Journal of nutrition education and behavior. 2014; 46: 429-433.
- Rollo ME, Aguiar EJ, Williams RL, Wynne K, Kriss M, Callister R, et al. eHealth technologies to support nutrition and physical activity behaviors in diabetes self-management. Diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity: targets and therapy. 2016; 9: 381-390.
- Samadi N, Allahyari I, Zamanzadeh V, Dadkhah B, Mohammadi MA. Educational Points for Prevention of Type 1 Diabetes and its Complications: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical & Cellular Immunology. 2012; 2013.
- Balk SN, Schoenaker DA, Mishra GD, Toeller M, Chaturvedi N, Fuller JH, et al. Association of diet and lifestyle with glycated haemoglobin in type 1 diabetes participants in the EURODIAB prospective complications study. European journal of clinical nutrition. 2016; 70: 229-236.
- Gao J, Wang J, Zheng P, Haardörfer R, Kegler MC, Zhu Y, et al. Effects of self-care, self-efficacy, social support on glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. BMC family practice. 2013; 14: 1.
- Grey M, Schulman-Green D, Knafl K, Reynolds NR. A revised self-and family management framework. Nursing outlook. 2015; 63: 162-170.
- Rovner AJ, Nansel TR, Mehta SN, Higgins LA, Haynie DL, Laffel LM. Development and validation of the type 1 diabetes nutrition knowledge survey. Diabetes care. 2012; 35: 1643-1647.
- Patton SR, Dolan LM, Chen M, Powers SW. Dietary adherence and mealtime behaviors in young children with type 1 diabetes on intensive insulin therapy. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. 2013; 113: 258-262.
- Nansel TR, Haynie DL, Lipsky LM, Laffel LM, Mehta SN. Multiple indicators of poor diet quality in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes are associated with higher body mass index percentile but not glycemic control. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. 2012; 112: 1728-1735.
- Smart CE, Annan F, Bruno LP, Higgins LA, Acerini CL. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2014. Nutritional management in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatric diabetes. 2014; 15: 135-153.
- Patton SR, Dolan LM, Powers SW. Dietary adherence and associated glycemic control in families of young children with type 1 diabetes. J Am Diet Assoc. 2007; 107: 46-52.
- The NS, Crandell JL, Thomas J, Couch SC, Shah AS, Maahs DM, et al. Correlates of medical nutrition therapy and cardiovascular outcomes in youth with type 1 diabetes. Journal of nutrition education and behavior. 2013; 45: 661-668.
- Patton SR, Goggin K, Clements MA. The cost of a healthier diet for young children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Journal of nutrition education and behavior. 2015; 47: 361-366.
- Jaacks L, Liu W, Ji L, Mendez MA, Du S, Crandell J, et al. Diabetes nutrition therapy and dietary intake among individuals with type 1 diabetes in China. Diabetic Medicine. 2015; 32: 399-406.
- Wylie-Rosett J, Aebersold K, Conlon B, Ostrovsky NW. Medical nutrition therapy for youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus: more than carbohydrate counting. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. 2012; 112: 1724- 1727.
- Krebs JD, Parry Strong A, Cresswell P, Reynolds AN, Hanna A, Haeusler S. A randomised trial of the feasibility of a low carbohydrate diet vs standard carbohydrate counting in adults with type 1 diabetes taking body weight into account. Asia Pacific journal of clinical nutrition. 2016; 25: 78-84.
- Franz MJ, Powers MA, Leontos C, Holzmeister LA, Kulkarni K, Monk A, et al. The evidence for medical nutrition therapy for type 1 and type 2 diabetes in adults. J Am Diet Assoc. 2010; 110: 1852-1889.
- American Diabetes Association. All about Carbohydrate Counting. Toolkit No. 14. 2009.
- American Dietetic Association. Type 1 Diabetes Nutrition Therapy 1-4.
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. 2016.
Nutritional management requires a high level of cooperation between parents and patients to overcome obstacles [1] and diabetic diet and adhere to it is complicated and difficult for many patients and their families [14], so that many of Type I diabetes patients do not adhere to a healthy diet [11,15,16]. Based on studies, adherence to the diet in children and adolescents with Type I diabetes is 21 to 56 percent [14]. In Jaacks et al. study [17], only 32% of them sometimes pursued the nutritional program provided by the health care providers. In study of Nansel et al. [12], more than 48 percent of energy consumption of children and adolescents was supplied by processed foods including cereal, desserts, chips and soda, while only 17% of energy was provided by plant foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts and seeds. Wylie-Rosett et al. [18] state that less than 1 percent of diabetic patients have a “good” diet according to (Health Eating Index). In a study conducted in the US, data showed that adolescents used inadequate amounts of fruit, vegetables, and whole grains as well as, excessive consumption (twice the recommended amount) of saturated fats [12].
When the only treatment for Type I diabetes was low carbohydrate diets, it was very hard and flexibility in diet became more by discovery of insulin and its resulting developments [11,19]. Amount of carbohydrate in meals or snacks have a greater impact on blood glucose compared to other sources [12,15]. The core of nutrient management in Type I diabetes is monitoring carbohydrate intake and its balance and insulin levels [1,20] and the mismatch between the two can cause short term and long-term complications of hypoand hyperglycemia [1].
Counting carbohydrates is often as a simple strategy for measuring and calibrating bolus insulin dose for meals and snacks in the management of Type I diabetes. However, having regularity in time of eating food and overall quality of nutrition for ideal blood glucose should not be neglected [18]. Recent studies show that a low carbohydrate diet should contain less than 130 grams of carbohydrate per day [19]. Results of the Nansel and colleagues study showed that adolescents with Type I diabetes do not consume the recommended carbohydrates that are necessary for their health, so that they consumed the fruits, vegetables and whole grains less than half of the recommended amount [18]. Caregivers should encourage patients to consume healthy food sources with carbohydrates such as whole grain breads and cereals, legumes (peas, lentils and beans), fruits and vegetables and low-fat dairy products [13]. The chart 1 shows foods that have carbohydrate and affect your blood glucose much more than other foods. Also the chart 2 shows serving sizes for some carbohydrate foods [21].
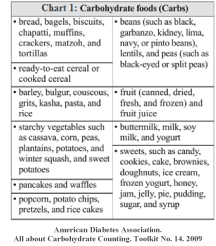
Figure 1:
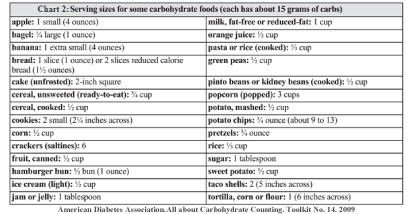
Figure 2:
In nutrition and diet of children and adolescents with Type I diabetes, it should be noted that:
In general, we can say that there is no certain nutritional guideline for children and adolescents with Type I diabetes and it is similar to the ones in normal peers. Most dietary recommendations are for change and reform of diet and trying to achieve, maintain optimal weight and ultimately improve the quality of life of patients and their families. It should be noted that regular physical activity and regular drug use, blood glucose monitoring (6-8 times per day) in children and adolescents with Type I diabetes are important, in addition to following a healthy diet.
References