
Clinical Image
Austin J Nutri Food Sci. 2019; 7(2): 1115.
It Needs to be Taken Seriously of the new Rising Disease: Bacterial Brown Stripe of Rice
Huang S*
China National Rice Research Institute (CNRRI), China
*Corresponding author: Shiwen Huang, China National Rice Research Institute (CNRRI), Hangzhou, China
Received: April 19, 2019; Accepted: April 27, 2019; Published: May 04, 2019
Clinical Image
Bacterial brown stripe of rice (BBSR), caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. panici (Elliott) stepp and/or Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae, also called heart rot disease of rice, was firstly reported in 1989 in China. BBSR was minority and occasionally occurred at small scale in rice production area of Yangtze River basin, southern Chinaandnorthern cold regionin the past three decades. It occurred and aggravated in recent years, the rate of the diseased plants was 20- 25% in common paddy fields infected by BBSR, whereas the disease happened seriously, the mortality rate of seedling could reached above 60%. However, the BBSR was seriously outbreak in 2018 in partial areas in China, including Sichuan, Hunan, Hubei, Anhui and Chongqing provinces (municipality) in upper reaches of Yangtze River, Liaoning and Jilin provinces in northeast. There are more than 100 thousand hectare of rice field were seriously infected (caused large scale of rice plants destroyed) by BBSR, the major infected varieties are Y Liangyou 957 (hybrid rice) and Yanjing 47 (japonica) (Figures 1-4).

Figure 1: Heart leaf dead.

Figure 2: Bacterial concentration.

Figure 3: Symptoms of BBSR in the field.
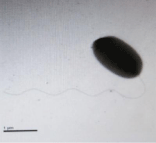
Figure 4: Cell of the pathogenic bacterium.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the projects: The key R&D project of Zhejiang(2019C02018), The National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0200304, 2016YFD0200801), Innovation project of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) (CAAS-ASTIP -2013-CNRRI, CAAS-XTCX2016012).