
Case Report
Austin J Radiol. 2019; 6(1): 1088.
Multiple Thoracic Hydatidosis with Mediastinal, Cardiac, and Pulmonary Arterial Localization
Malika Amarir*, Meriam Edderai, Laila Benaissa, Mohammed Mahi, Hassan En-nouali, Amal Fenni J and Hassan Boumdin
Department of Radiology, Mohammed V University, Morocco
*Corresponding author: Malika Amarir, Department of Radiology, Military Hospital Mohammed V, Mohammed V University, Rabat, Morocco
Received: January 22, 2019; Accepted: February 26, 2019; Published: March 05, 2019
Abstract
Hydatidosis is a cosmopolitan infection prevalent especially in breeding areas. The lung is the organ most often affected (20-30%) after the liver (60-70%). Pulmonary cysts are unique in 60% of cases but can be multiple. Multiple thoracic hydatidosis is rare, the involvement is exceptional and often associated with other localizations, liver and lung. The increased risk of serious complications and the difficulties of therapeutic management of these forms invite their prognosis hence the interest of the prevention of hydatid disease. This observation highlights the interest of the radiological assessment, to evaluate the multiple thoracic hydatidosis, to establish the diagnosis and to discuss a curative surgical act as well as medical treatment.
Keywords: Multiple thoracic hydatidosis; Pulmonary hydatid embolism
Case Presentation
It’s about a 29-year-old man who consults for dyspnoea with diffuse chest pain, coughing and low-abundance hemoptysis in a febrile context and preservation of the genaral state. The interrogation reveals periodic chest pain; Clinical examination found a febrile patient at 38°C. Cardiovascular examination does not show signs of right heart failure or pulmonary hypertension, chest x-ray shows bilateral parenchymal opacities of varying size, associated with mediastinal opacities and a large-heart appearance, thoracic CT scan with and without ICP injection is realised, found a the trunk of the right pulmonary artery, a material with multi-cystic fluid density (Figure 1), associated with many cystic multi-vesicular masses sit in periventricular, mediastinal, pre-vascular and pré-tracheal and many pulmonary parenchymal localizations, the biggest of them occupies the left fowler (Figures 2,3).
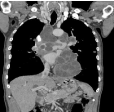
Figure 1: CT thoracic coronale cut in mediastinal window after injection of
PCI: multiple multi vesicular cystic formations of staged mediastinal seat and
of the right pulmonary artery.
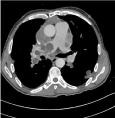
Figure 2: CT thoracic axial cut in mediastinal window with injection: many
rounded cystic formations with fine wall at the level of the right pulmonary
artery, pera-aortic and at the level of the left Fowler.
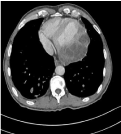
Figure 3: CT thoracic axial cut in mediastinal window with injection: cystic
formation multi-vesicular rounded with thin wall at the pericarde of the left
ventricle.
The hydatid serology is positive (haemagglutination and Elisa). The blood count shows hyper eosinophilia at 1900/mm3. Abdominal ultrasound found no other hydatid localization.
Discussion
Multiple Thoracic Hydatid Disease (MTH) is rare, involvement of the pulmonary artery is exceptional and has a poor prognosis. It may be primitive, or as a result of massive and / or repeated liver damage. Bronchogenic transmission is possible but exceptional [1]. Cardiac involvement accounts for 0.5 to 2% of all other sites [2,3] and is more often associated with MTH. In 20% of cases, it is fatal from the start by sudden rupture of the cyst [4,5], but in some cases the cyst can calcify or regress [2,4,6]. pulmonary arterial hydatidosis has a very poor prognosis due to the risk of pulmonary embolism, arterial erosion and acute or chronic post-embolic pulmonary heart disease, in addition to the risk of multiple pulmonary dissemination. The hydatid embolus is most often derived from a hepatic hydatid cyst through the lower vena cava system, after spontaneous or iatrogenic fistula. In effect, the majority of cases of hydatid embolism described in the literature had a history of hepatic hydatid cyst liver surgery [7,8]. Pulmonary arterial migration of hydatic cysts can also be done from cardiac cysts. This mechanism is infrequent.
It is noted in only 2.6% of cases [9], and is even rare in the absence of liver localization. But according to the study by Maiouak and al on a series of 3 cases, the cardiac origin of pulmonary arterial hydatidosis is most probable in all their patients after highlighting right heart hydatid cysts and moreover it is the most probable mechanism in our case because of the absence of any other location outside of cardiac involvement.
Aortic localization is often referred to as incidental preoperative discovery. According to Maiouak et al’s study all their patients were male as our patient. The rare cases of pulmonary arterial hydatidosis reported in the literature are generally from North Africa [7] as our case of Moroccan origin, MTH is distinguished by its high clinical latency.
The polymorphism of the arterial hydatid cyst is explained by the variable seat of the cyst and the diversity of the hemodynamic repercussions of embolization [7].
The clinic of hydatid pulmonary embolism is not very specific pulmonary artery localization of hydatid cysts can take three clinical situations: acute clinic with high risk of sudden death by massive pulmonary embolism or anaphylactic shock; Subacute clinic with pulmonary embolism and Pulmonary Hypertension (PHT) cause of death in the first year that follows: chronic postembolic PHT, there is no characteristic clinical in case of cardiac involvement [10]. Clinical signs are dyspnea, precordialgia, palpitations, syncope. Sometimes the cyst can be discovered during a radiological exam. The hydatid origin may be suspected if the patient has a history of hydatid disease, its rural origin, and positive hydatid serology.
The diagnosis of HTM is based primarily on imaging, including thoracic CT with cardiac synchronization which ensures complete lesion mapping especially the pericardial mediastinal site., pulmonary or intra-arterial, the hydatic cyst of the pulmonary artery manifests itself as a fluid intra-arterial mass with peripheral enhancement after injection of the contrast product [8,9].
Magnetic resonance imaging is better in cases of diagnostic doubt, CT-ETO dissociation and in pseudo-tumoral forms [8,9], the cyst appears as a well-circumscribed intra-arterial lesion of hypointense signal in T1 sequence and hyper-intense in T2 sequence with sometimes a hypo-intense peripheral ring in T2 sequence representing the pericyst [8,9]. The Transthoracic ultrasound (ETT), or better Trans-Esophageal (TEO) is the exams of choice. It visualizes small cysts or intra-auricular localization with excellent sensitivity and specificity [8,9]. it can also be used to evaluate the impact on cardiac function, as well as the evaluation and follow up of PHT.
In our case, the thoracic CT scan has quickly made the diagnosis, especially considering the patient’s history and then positif hydatid serology, which support the diagnosis.
The treatment of multiple chest hydatidosis is based on first-line in surgery. The surgical indication is formal and urgent [7] especially in case of arterial localization. The gesture consists first of all in the removal of intra-arterial, pericardial cysts, then conservative or nonconservative of the lung [8].
Perioperative mortality is a function of the severity of PHT and parenchymal hydatid spread [4].
Pre-surgical medical treatment with albendazole reduces the risk of postoperative dissemination [7].
It can also be given after surgery to reduce the risk of spread during surgery.
In case of surgical contraindication, inoperable patient or disseminated hydatidosis, medical treatment is indicated alone, but its effectiveness is inconstant and not easy to distinguish from the natural evolution of the pathology [10-12].
The combination of anticoagulant therapy is widely discussed [8]. The best treatment for hydatidosis is prevention, based on individual and collective prophylactic measures.
Conclusion
Multiple thoracic hydatidosis with pulmonary and cardiac localization is rare. Pulmonary and aortic artery disease are exceptional and dangerous threatens life. MTH is distinguished by a high clinical latency. Chest imaging can establish lesion mapping, estimate the origin of dissemination (hepatic or cardiac) and assess pulmonary artery involvement and its hemodynamic impact. They pose the problem of treatementt, hence the importance of preventing disseminated forms by the early diagnosis and treatment of cardiac and/or hepatic localizations.
References
- Chafik A, El Messlout A, Khallafi S, Achir A, Smahi M, Alaziz A, et al. La dissemination bronchogène du kyste pulmonaire. Rev Mal Respir. 2001; 18: 333.
- Afif H, Aïchane A, Thrombati N, Bahlaoui A, Bouayad Z, Boumzebra M, et al. Hydatidose pulmonaire multiple en lÎcher de ballon avec localisation cardiaque. Rev Mal Respir. 2000; 17: 697-698.
- M’Raihi ML, Djemel A, M’Zah N, Mechmeche R, Zegaya M, BenIsmail M. Hydatidose pulmonaire multiple associée à un kyste hydatique intra cardiaque. Rev Pneumol Clin. 1989; 45: 78-80.
- Struillou S, Rabaud C, Bischoff N, Preiss MA, May T, Canton Ph. Complications du kyste hydatique cardiaque. Presse Med. 1997; 26: 1192- 1194.
- Laglera S, Garcia-Enguita MA, Martinez-Gutierrez F, Ortega JP, Gutierrez- Rodriguez A, Urieta A. A case of cardiac hydatidosis. Br J Anaesth. 1997; 79: 671.
- Kabbaj N, Chat L, Dafiri R, Imani F. Cause rare d’accident vasculaire cérébral ischémique chez le sujet jeune: le kyste hydatique cardiaque. J Radiol. 1998; 79: 53-56.
- Mayoussi C, El Mesnaoui A, Lekhal B, Sefiani Y, Benosman A, Bensaid Y. Les complications artérielles de la maladie hydatique. J Mal Vasc. 2002; 27: 100-104.
- Mussot S, Bensari N, Cordier JF, Fabre D, Fadel E, Dartevelle P. Chronic pulmonary arterial hydatidosis. Presse Med. 2009; 38: e21-e24.
- Ghrairi H, Khouadja MA, Abouda M, Ammar J, Hantous S, KilaniT, et al. Kyste hydatique du coeur et des vaisseaux: 4 cas. PresseMed. 2005; 29: 101-104.
- Menassa-Moussa L, Braidy C, Riachy M, Tabet G, SmayraT, Haddad- Zebouni S, et al. Une hydatidose diagnostiquée à l’occasion d’une embolie pulmonaire. J Mal Vasc. 2009; 34: 354-357.
- Karantanas AH, Bistios G, Karaiskou E. Echinococcus of the pul-monary artery: CT, MRI and MRA findings. Comput Med ImagingGraph. 2000; 24: 265-267.
- De Rosa F, Tegmen A. Treatment of Echinococcus granulo-sus hydatid disease with albendazole. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1990; 84: 467-472.