
Case Report
Austin J Radiol. 2019; 6(2): 1094.
Colonic Angioinvasive Mucormycosis - Case Report
Sruthi J, Shrivalli N, Aruna Raman P* and Ashitha S
Department of Radiology, Apollo Hospitals, India
*Corresponding author: Aruna Raman Patil, Consultant, Department of Radiology, Apollo Hospitals, Bannerghatta Road, Bangalore-560 076, Karnataka, India
Received: May 29, 2019;Accepted: July 01, 2019; Published: July 08, 2019
Abstract
Mucormycosis is a rare fatal fungal infection, prevalent in immunosuppressed patients. Rhinocerebral infection is the most common presentation followed by pulmonary, primary cutaneous, gastrointestinal and disseminated disease. Cases of gastrointestinal mucormycosis are rarely reported. This case report presents an atypical presentation of gastrointestinal angio invasive mucormycosis which led to bowel ischemia and perforation.
Keywords: Mucormycosis; Angioinvasive; Ultrasonography; Computed Tomography
Abbreviations
USG: Ultrasonography; CT: Computed Tomography
Case Presentation
A 76 year old female patient with uncontrolled diabetes and hypertension presented with altered sensorium, fever and breathlessness. There was a recent history of right gluteal abscess drainage. As a part of initial workup, Ultrasonography (USG) of abdomen and Doppler study of lower limbs was done whose results were unremarkable. She then underwent Computed Tomography (CT) study of pelvis which showed multiple abscess in the right gluteal region and necrotizing fasciitis. The abscess was drained through gluteal and thigh approach.
Inspite of abscess drainage, she continued to have persistent breathlessness and fever. For further evaluation, contrast enhanced CT of chest and abdomen was done using 100mL of iohexol (300mg iodine per milliliter, Omnipaque). CT abdomen revealed a short segment focal thickening of the transverse colon with hypo enhancement and adjacent mesocolic fat stranding suggesting bowel ischemia (Figure 1a). Two hypodense lesions with faint rim enhancement was noted in segment VIII and IV respectively suggestive of abscesses (Figure 1b). CT thorax showed acute pulmonary thromboembolism involving right lower lobar and subsegmental pulmonary arteries (Figure 1c).
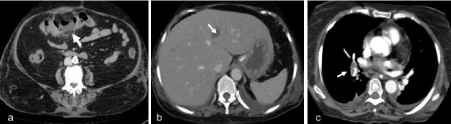
Figure 1: a. CECT axial section shows focal hypo enhancement of the mid transverse colon (arrow) with surrounding mesocolic inflammation. b. Faint rim
enhancing lesion in liver (arrow) suggesting abscess. c. CT pulmonary angiography chest shows right pulmonary thromboembolism (arrow).
Patient was managed conservatively and repeat CT was done after two days. The follow up contrast enhanced CT abdomen showed interval development of extraluminal air adjacent to hypoenhancing transverse colonic segment suggestive of bowel perforation (Figure 2a,b).
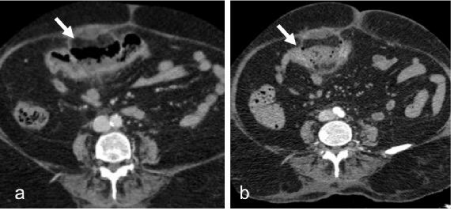
Figure 2: a. Repeat CECT abdomen after 2 days shows persistent hypo
enhancement of the transverse colon segment with b. extraluminal air
suggesting perforation.
Due to non resolving symptoms of infection and interval development of abdominal guarding, emergency laparotomy was performed. Intraoperatively, perforation was noted in the mid transverse colon measuring ~ 3 x 3 cm with fecal contamination of peritoneal cavity. Colon was mobilized at hepatic and splenic flexure and the perforated transverse colon segment was resected following which colocolic anastomosis and loop ileostomy were done.
pGross specimen showed perforation of the large intestine with ulcerations that was covered with greenish necrotic material along with mesocolic thickening (Figure 3). Microscopic examination showed ulcers covered with necrotic debris, inflammatory exudate along with granulation tissue (Figure 4a&b). There were plenty of the fungal hyphae amidst the necrosis and inflammatory exudate. The hyphae were broad, aseptate and showed obtuse angle branching (Figure 5a&b) consistent with Mucormycosis. Mesenteric vessels showed features of angio-invasion by the fungal hyphae (Figure 6a&b). There was no evidence of malignancy.
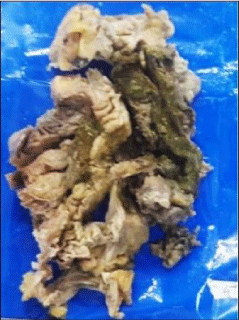
Figure 3: Gross specimen showing colonic ulcer covered with necrotic
material (arrow).
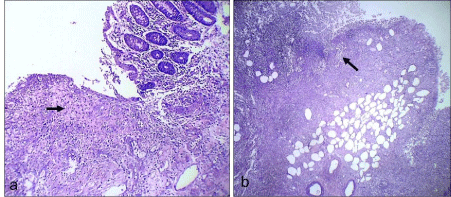
Figure 4: Microphotograph (H&E stain) shows mucosal ulceration with
granulation tissue and fibrinoid necrosis (arrow in a). Arrow in b shows full
thickness necrosis with inflammation.
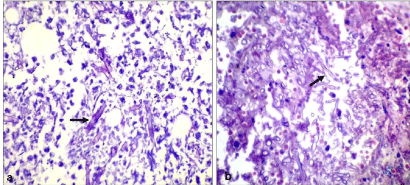
Figure 5: Microphotograph (H&E stain) shows fungal colonies with
broad aseptate hyphae with right angle branching (arrows) within the necrotic
tissue.
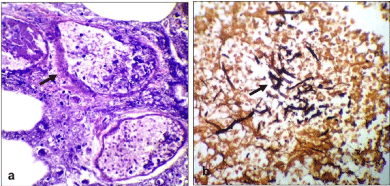
Figure 6: a. Microphotograph (H&E stain) shows angioinvasion (arrow) by
fungal hyphae. b. GMS stain highlights the fungal elements (arrow).
Discussion
pMucormycosis is a fatal opportunistic fungal infection. It commonly presents as rhino cerebral infection. Gastrointestinal mucormycosis is most rare among all clinical manifestations of mucormycosis and accounts for only 4-7% of all [1]. Stomach is the most common affected site followed by colon and ileum.The most common species causing mucormycosis are Rhizopus which constitute approximately 40% followed by Rhizomucor, Absidia and Mucor species. The typical infective forms are sporangiospores, whereas angio-invasive hyphal forms contribute to tissue invasion and dissemination [2,3].
The risk factors include immunosuppressed state such as HIV infection, transplant recipients, diabetes mellitus, corticosteroid intake, malnutrition, malignancy, etc. This rare infection has been reported in neonates presenting with clinical features of necrotizing enterocolitis likely due to immature immunity [1].
Gastric mycoses are known to develop following nasogastric intubation or other conditions causing gastric or colonic ulcers which facilitate fungal entry [3]. Rarely mucormycosis of GIT can also occur following ingestion of fungal spores. Patients with gastric mucormycosis may present with massive gastric bleeds, whereas intestinal mucormycosis usually presents with non-specific symptoms (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or distension). Often patients may have intra-abdominal abscess. The pathologic hallmark of mucormycosis is angioinvasion by fungal hyphae resulting in infarction of the host tissue [4,5]. This in turn leads to GI hemorrhage, perforation and peritonitis and hence high mortality.
pImaging findings of invasive fungal infections in gastrointestinal system are very non-specific. Bowel wall thickening, adjacent inflammation and spread to peritoneum are seen. Bowel ischemia occurs due to fungal invasion of blood vessels. These fungal infections can become generalized to involve visceral organ or tissue. Seeding of the portal venous system may result in fungal involvement of liver [5]. Usually fungal infection of liver manifests as multiple micro abscesses (less than 1cm) and are seen as hypoattenuating foci on CT. pHigh index of suspicion and early diagnosis by histopathological examination is essential in gastrointestinal mucormycosis since diagnosis is almost always delayed to postmortem due to nonspecific presentation [6,7]. Our patient was treated symptomatically for persistent septicemia during the initial course in hospital. CT features of focal colon ischemia, pulmonary thromboembolism and liver abscess pointed towards septic emboli related changes. However final histopathological diagnosis of angioinvasive mucormycosis completely changed the treatment plan. The liver lesions visualized in contrast CT abdomen are likely fungal abscesses which could be due to portal venous seeding. Retrospective review of sequential CT examinations revealed the evolution of the colonic mycotic infection as in initial thickening followed by hypo enhancement and eventually perforation (Figure 7a&b,c).
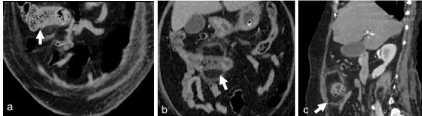
Figure 7: Sequential CT images show the evolution of the pathology from focal colonic thickening (a), hypo /non enhancement with mesocolic inflammation (b)
followed by perforation (c).
The gold standard for diagnosis of mucormycosis is demonstration of tissue invasion by fungal hyphae in histopathological specimen. Presently serologic tests have no significant role in diagnosis [2,8]. Positive fungal cultures are seen in only 50% cases [6]. Polymerase chain reaction can be useful for the diagnosis of mucormycosis and for species identification. However, it is not completely reliable for confirmation of diagnosis.
A combination of medical and surgical therapy is the treatment of choice. Surgery aims at debulking fungal infection and resecting infected tissue for effective cure. Primary antifungal therapy is a polyene antifungal agent. Lipid formulations of amphotericin B are preferred over amphotericin B deoxycholate as former can be administered at higher doses with less toxic effects [7]. Overall, the prognosis is poor due to rapid progression of infection.
pDiagnosing intra-abdominal conditions in critically ill patients is challenging. In cases of uncontrolled septicemia and bowel ischemia especially with underlying uncontrolled diabetes, unusual causes like mucormycosis should be considered in differential diagnosis.Other differential diagnosis that needs to be considered in similar case scenario is occult carcinoma colon with secondary infection / infarction and septicemia. Nodular polypoidal colonic lesion with irregular adjacent bowel wall thickening and pericolic lymph nodes gives high suspicion of colonic malignancy which helps to differentiate from colonic mucormycosis [1]. Perforation of colonic malignancy though rare (2.5-10% of patients with colon cancer), has been reported in patients with acute obstruction [9].
In conclusion, mucormycosis needs to be considered as differential in case of nonspecific abdominal complaints. Rapid diagnosis and early treatment are essential for better outcome. Demonstration of fungal hyphae in histopathological examination is the final confirmation in mucormycosis. Surgical debridement associated with antifungal medical treatment is essential for successful management. However, the prognosis of gastrointestinal mucormycosis is very poor due to rapid progression and dissemination [10-12].
Acknowledgement
Dr. Satyajit Godhi for providing surgical and clinical details and Dr. Swarna Shivakumar for contributing histopathology images.
References
- Debata PK, Panda SK, Dash A, Mohanty R, Mallick BN, Tadu D, et al. An unusual presentation of colonic mucormycosis mimicking carcinoma colon-a surgeon’s perspective. International journal of surgery case reports. 2015; 10: 248-251.
- Choi HL, Shin YM, Lee KM, Choe KH, Jeon HJ, Sung RH, et al. Bowel infarction due to intestinal mucormycosis in an immunocompetent patient. Journal of the Korean Surgical Society. 2012; 83: 325-329.
- Kontoyiannis DP, Lewis RE. Invasive zygomycosis: update on pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and management. Infectious Disease Clinics. 2006; 20: 581-607.
- Martinello M, Nelson A, Bignold L, Shaw D. “We are what we eat!” Invasive intestinal mucormycosis: A case report and review of the literature. Medical mycology case reports. 2012; 1: 52-55.
- Petrikkos G, Skiada A, Lortholary O, Roilides E, Walsh TJ, Kontoyiannis DP. Epidemiology and clinical manifestations of mucormycosis. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2012; 54: 23-34.
- Alghamdi A, Lutynski A, Minden M, Rotstein C. Successful treatment of gastrointestinal mucormycosis in an adult with acute leukaemia: case report and literature review. Current Oncology. 2017; 24: 61-64.
- Vikum D, Nordøy I, Torp Andersen C, Fevang B, Line PD, Kolrud FK, et al. A Young, Immunocompetent Woman with Small Bowel and Hepatic Mucormycosis Successfully Treated with Aggressive Surgical Debridements and Antifungal Therapy. Case reports in infectious diseases. 2017.
- Lehrer RI, Howard DH, Sypherd PS, Edwards JE, Segal GP, Winston DJ. Mucormycosis. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1980; 93: 93-108.
- Tondela JR, Viseu V, Tondela-Viseu ÂF, Tondela VA, Viseu VD, Tondela- Viseu V. Atypical presentation of colon cancer: perforation with hepatic fistulisation. Acta radiológica portuguesa. 2015; 27: 67-69.
- Kudva R, Kudva A. Mucormycosis of Intestine in an Immunocompetent Individual. Int J Sci Res. 2014; 4: 1-3.
- Orlowski HL, McWilliams S, Mellnick VM, Bhalla S, Lubner MG, Pickhardt PJ, et al. Imaging spectrum of invasive fungal and fungal-like infections. RadioGraphics. 2017; 37: 1119-1134.
- Spellberg B. Gastrointestinal mucormycosis: an evolving disease. Gastroenterology & hepatology. 2012; 8: 140-142.